Price: $14.95
- 3 magazines, 3 manuals, & photos
- PDF contains 1750 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
July 1989
- A-10 Close Support
- Dyna-Soar – Also Ran in the Race for Space
- Navy Wings of Gold
July 1990
- Combat nose art for the 90s
- E-2C Hawkeye, All seeing eye in the sky
- Arado & the making of the Secret Luftwaffe
January 2006
- Convair 990 – Fastest Jetliner ’till the Concorde
- Two-seat A-10 – Would it have made a difference?
- “The High and the Mighty” – Hollywood movie magic with a DC-4
- F-86E to F-4D – Korean War Ace to Vietnam Gunfighter
Manuals & Photos
- A-10A Flight Manual 1988
- A-10A Flight Manual Supplement 1987
- A-10C Flight Manual 2012
- Over 300 A-10 Thunderbolt II photos
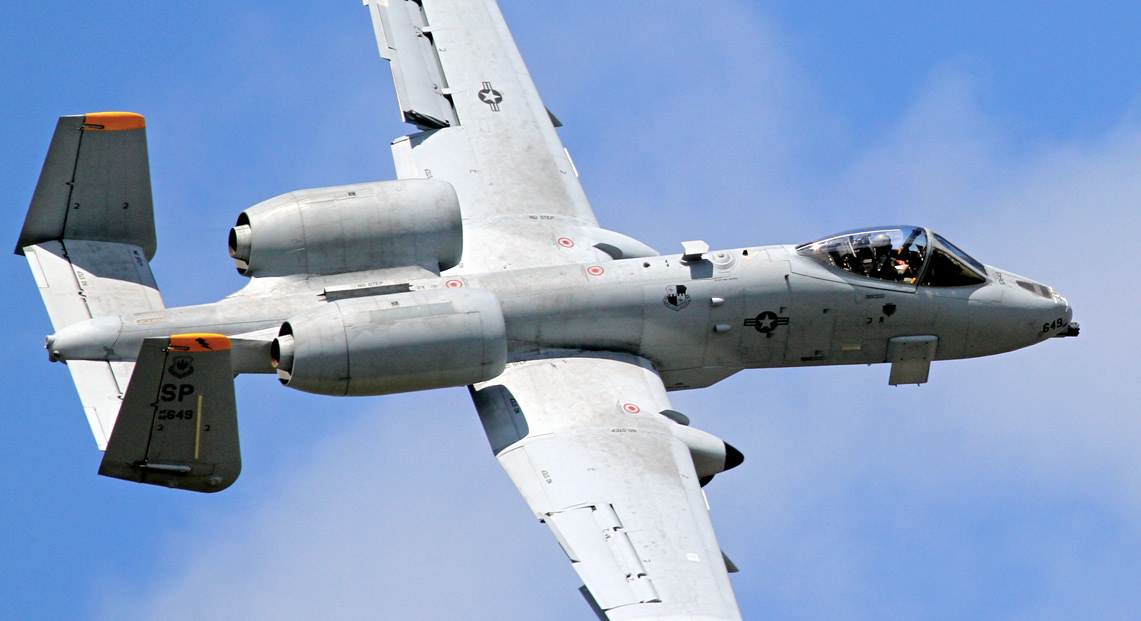
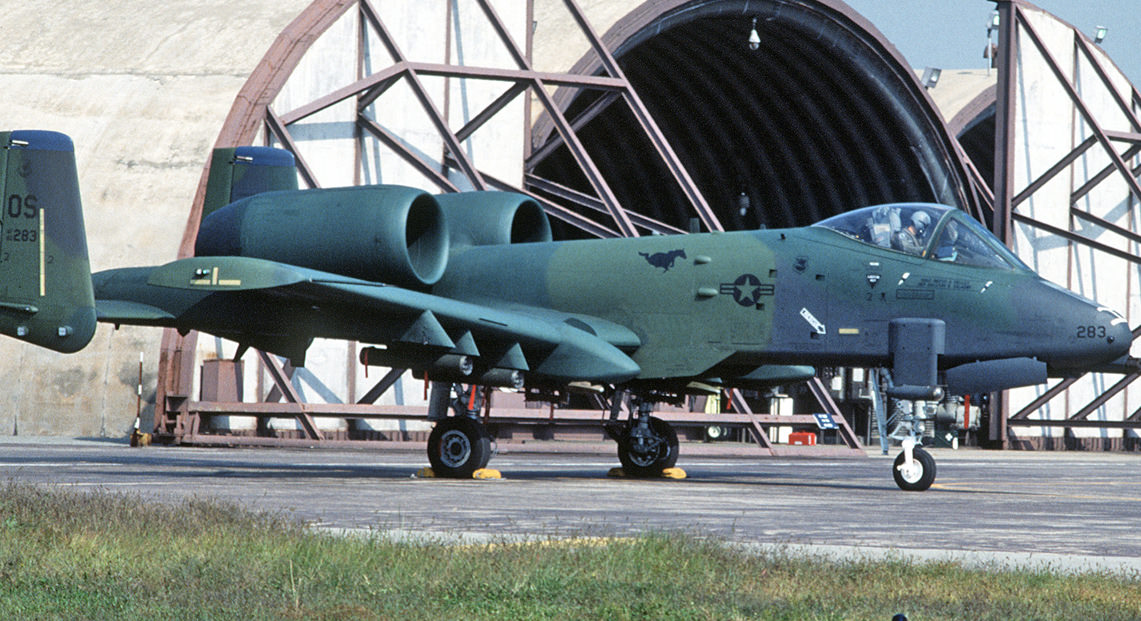
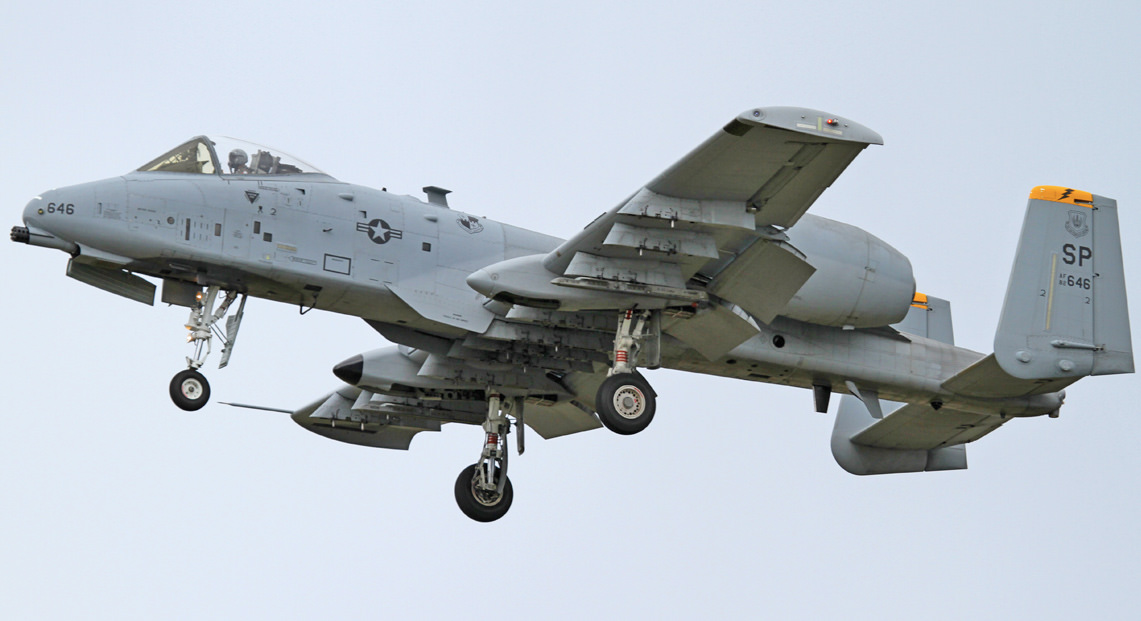
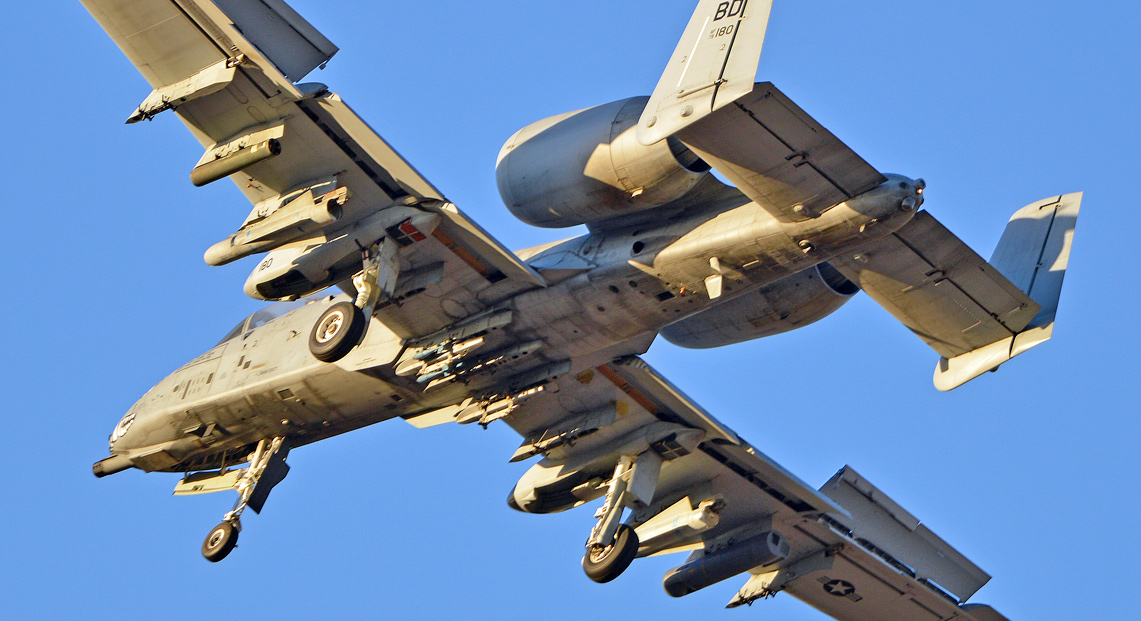
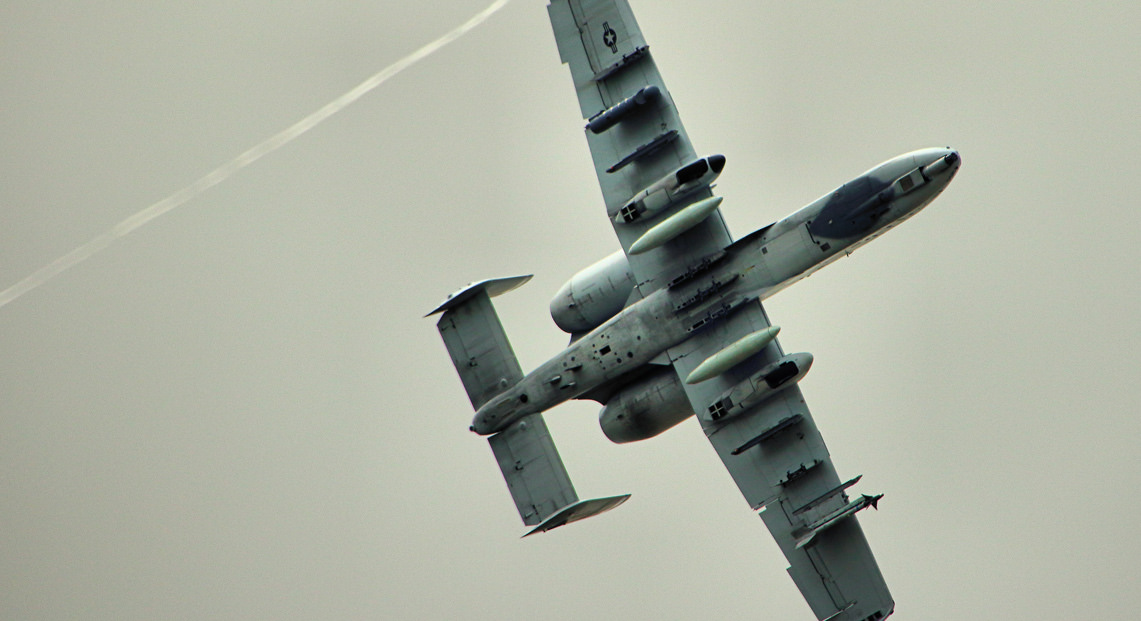
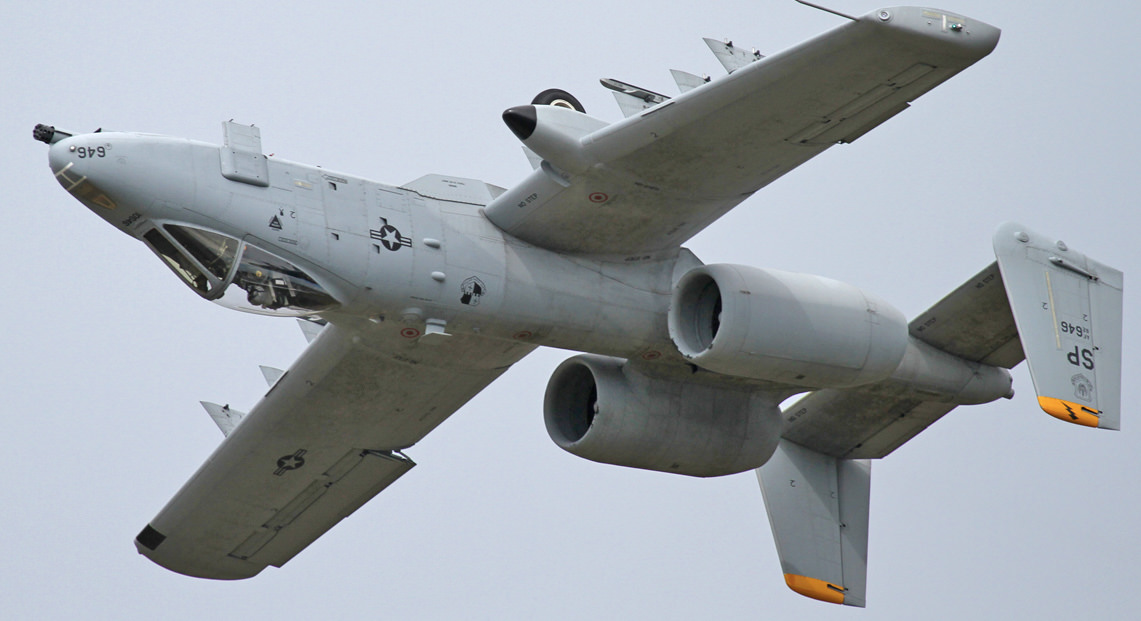
Fairchild-Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II
A-10A Specs
Variants
On Display
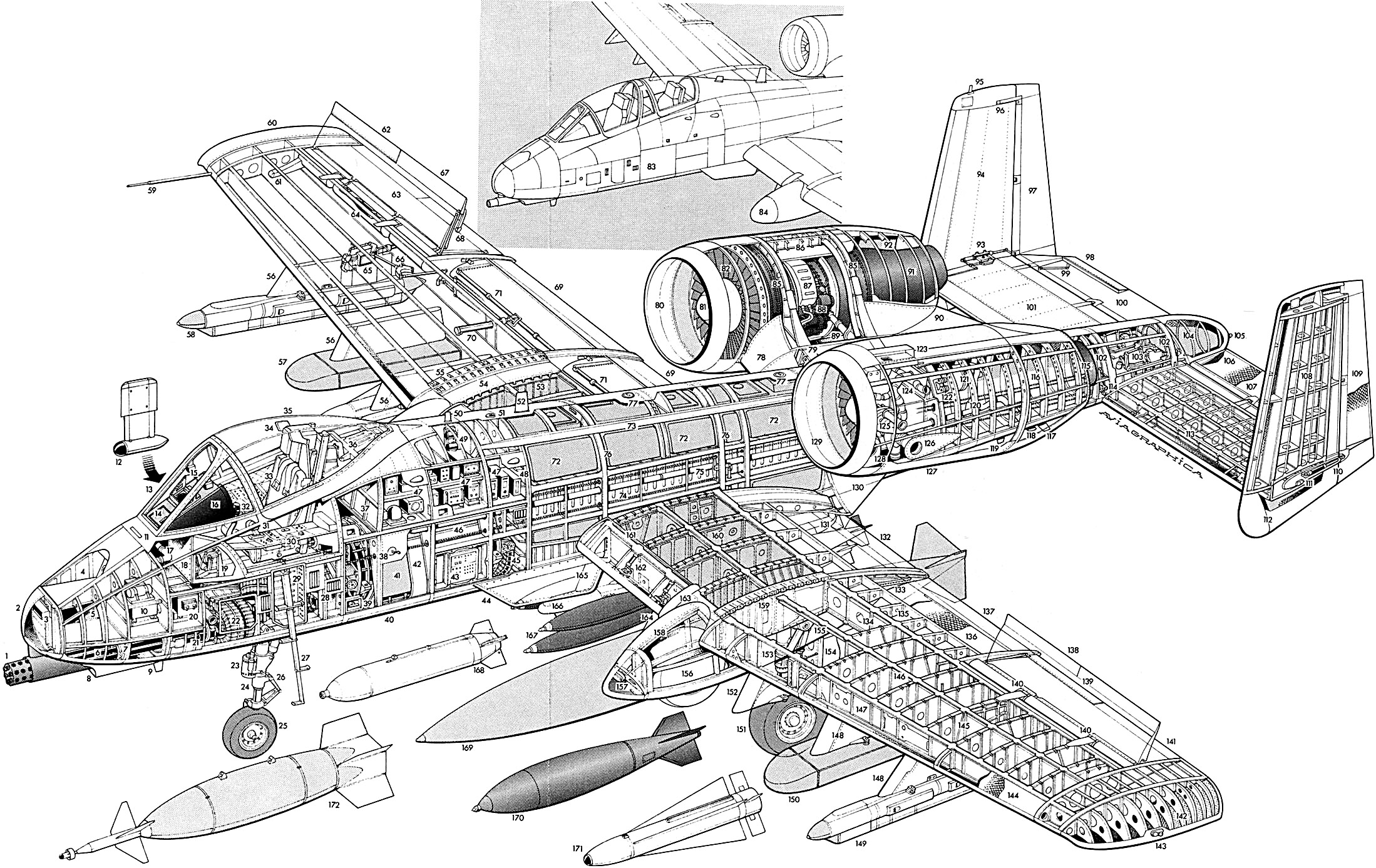
Cutaway
Videos
General Characteristics
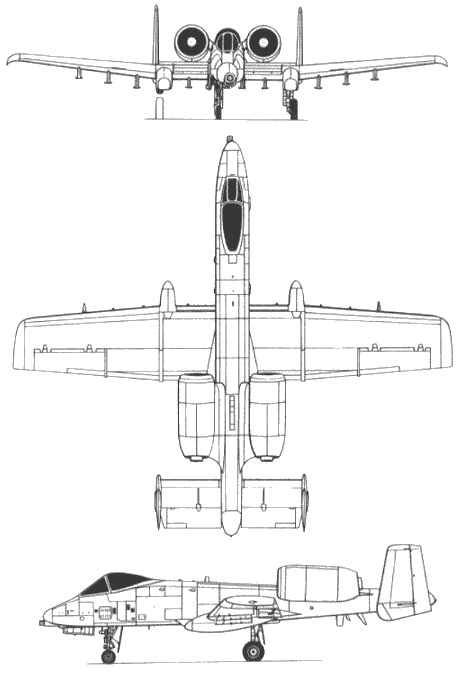
- Crew: 1
- Length: 53 ft 4 in (16.26 m)
- Wingspan: 57 ft 6 in (17.53 m)
- Height: 14 ft 8 in (4.47 m)
- Wing area: 506 ft² (47.0 m²)
- Airfoil: NACA 6716 root, NACA 6713 tip
- Empty weight: 24,959 lb (11,321 kg)
- Loaded weight: 30,384 lb (13,782 kg)
CAS mission: 47,094 lb (21,361 kg)
Anti-armor mission: 42,071 lb (19,083 kg) - Max. takeoff weight: 50,000 lb (23,000 kg)
- Internal fuel capacity: 11,000 lb (4,990 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × General Electric TF34-GE-100Aturbofans, 9,065 lbf (40.32 kN) each
Performance
- Never exceed speed: 450 knots (518 mph, 833 km/h) at 5,000 ft (1,500 m) with 18 Mk 82 bombs
- Maximum speed: 381 knots (439 mph, 706 km/h) at sea level, clean
- Cruise speed: 300 knots (340 mph, 560 km/h)
- Stall speed: 120 knots (138 mph, 220 km/h)
- Combat radius:
- CAS mission: 250 nmi (288 mi, 460 km) at 1.88 hour loiter at 5,000 ft (1,500 m), 10 min combat
- Anti-armor mission: 252 nmi (290 mi, 467 km), 40 nmi (45 mi, 75 km)) sea-level penetration and exit, 30 min combat
- Ferry range: 2,240 nmi (2,580 mi, 4,150 km) with 50 knot (55 mph, 90 km/h) headwinds, 20 minutes reserve
- Service ceiling: 45,000 ft (13,700 m)
- Rate of climb: 6,000 ft/min (30 m/s)
- Wing loading: 99 lb/ft² (482 kg/m²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.36
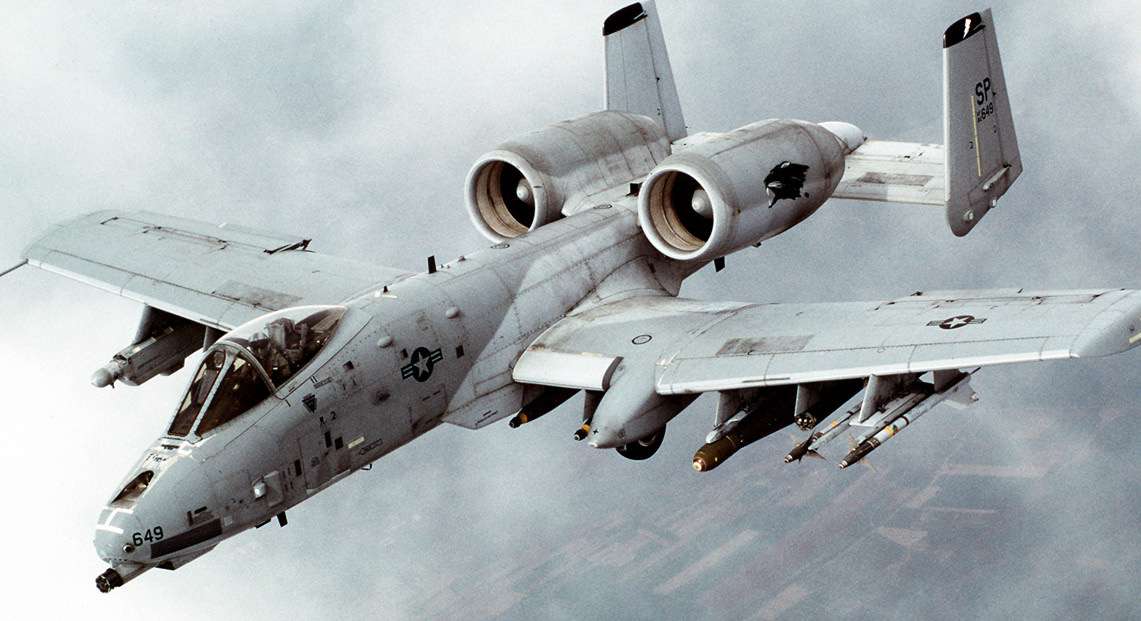
Armament
- Guns: 1× 30 mm (1.18 in) GAU-8/A Avengerrotary cannon with 1,174 rounds (capacity 1,350 rd)
- Hardpoints: 11 (8× under-wing and 3× under-fuselage pylon stations) with a capacity of 16,000 lb (7,260 kg) and provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets:
- 4× LAU-61/LAU-68 rocket pods (each with 19×/7× Hydra 70mm/APKWS rockets, respectively)
- 4× LAU-5003 rocket pods (each with 19× CRV7 70 mm rockets)
- 6× LAU-10 rocket pods (each with 4× 127 mm (5.0 in) Zuni rockets)
- Missiles:
- 2× AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles for self-defense
- 6× AGM-65 Maverick air-to-surface missiles
- Bombs:
- Mark 80 series of unguided iron bombs or
- Mk 77 incendiary bombs or
- BLU-1, BLU-27/B Rockeye II, Mk20, BL755 and CBU-52/58/71/87/89/97 cluster bombs or
- Paveway series of Laser-guided bombs or
- Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) (A-10C) or
- Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser (A-10C)
- Other:
- SUU-42A/A Flares/Infrared decoys and chaff dispenser pod or
- AN/ALQ-131 or AN/ALQ-184 ECM pods or
- Lockheed Martin Sniper XR or LITENING targeting pods (A-10C) or
- 2× 600 US gal (2,300 L) Sargent Fletcher drop tanks for increased range/loitering time.
- Rockets:
Avionics
- AN/AAS-35(V) Pave Penny laser tracker pod (mounted beneath right side of cockpit) for use with Paveway LGBs (currently the Pave Penny is no longer in use)
- Head-up display (HUD) for improved technical flying and air-to-ground support.
- YA-10A
- Pre-production variant. 12 were built.
- A-10A
- Single-seat close air support, ground-attack production version.
- OA-10A
- A-10As used for airborne forward air control.
- YA-10B Night/Adverse Weather (N/AW)
- Two-seat experimental prototype, for work at night and in bad weather. The one YA-10B prototype was converted from an A-10A.
- A-10C
- A-10As updated under the incremental Precision Engagement (PE) program.
- A-10PCAS
- Proposed unmanned version developed by Raytheon and Aurora Flight Sciences as part of DARPA’s Persistent Close Air Support program. The PCAS program eventually dropped the idea of using an optionally manned A-10.
- Civilian A-10
- Proposed by the South Dakota School of Mines and Technology to replace its North American T-28 Trojan thunderstorm penetration aircraft. The A-10 would have its military engines, avionics, and oxygen system replaced by civilian versions. The engines and airframe would receive protection from hail, and the GAU-8 Avenger would be replaced with ballast or scientific instruments.
Germany
- A-10A
- 77-0264 – Spangdahlem AB, Bitburg
South Korea
- A-10A
- 76-0515 – Osan AB
United Kingdom
- A-10A
- 77-0259 – American Air Museum at Imperial War Museum Duxford
- 80-0219 – Bentwaters Cold War Museum
United States
- YA-10A
- 71-1370 – Joint Base Langley-Eustis (Langley AFB), Hampton, Virginia
- YA-10B
- 73-1664 – Air Force Flight Test Center Museum, Edwards AFB, California
- A-10A
- 73-1666 – Hill Aerospace Museum, Hill AFB, Utah
- 73-1667 – Flying Tiger Heritage Park at the former England AFB, Louisiana
- 75-0263 – Empire State Aerosciences Museum, Glenville, New York
- 75-0270 – McChord Air Museum, McChord AFB, Washington
- 75-0293 – Wings of Eagles Discovery Center, Elmira, New York
- 75-0288 – Air Force Armament Museum, Eglin AFB, Florida
- 75-0289 – Heritage Park, Eielson AFB, Alaska
- 75-0298 – Pima Air & Space Museum (adjacent to Davis-Monthan AFB), Tucson, Arizona
- 75-0305 – Museum of Aviation, Robins AFB, Warner Robins, Georgia
- 75-0308 – Moody Heritage Park, Moody AFB, Valdosta, Georgia
- 75-0309 – Shaw AFB, Sumter, South Carolina. Marked as AF Ser. No. 81-0964 assigned to the 55 FS from 1994–96. The represented aircraft was credited with downing an Iraqi Mi-8 Hip helicopter on 15 Feb 1991 while assigned to the 511 TFS.
- 76-0516 – Wings of Freedom Aviation Museum at the former NAS Willow Grove, Horsham, Pennsylvania
- 76-0530 – Whiteman AFB, Missouri
- 76-0535 – Cradle of Aviation, Garden City, New York
- 76-0540 – Aerospace Museum of California, McClellan Airport (former McClellan AFB), Sacramento, California
- 77-0199 – Stafford Air & Space Museum, Weatherford, Oklahoma
- 77-0205 – USAF Academy collection, Colorado Springs, Colorado
- 77-0228 – Grissom Air Museum, Grissom ARB (former Grissom AFB), Peru, Indiana
- 77-0244 – Wisconsin Air National Guard Museum, Volk Field ANGB, Wisconsin
- 77-0252 – Cradle of Aviation, Garden City, New York (nose section only)
- 77-0667 – England AFB Heritage Park, Alexandria, Louisiana
- 78-0681 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Dayton, Ohio
- 78-0687 – Don F. Pratt Memorial Museum, Fort Campbell, Kentucky
- 79-0097 – Warbird Park, former Myrtle Beach Air Force Base, South Carolina
- 79-0100 – Barnes Air National Guard Base, Westfield, Massachusetts
- 79-0103 – Bradley Air National Guard Base, Windsor Locks, Connecticut
- 79-0116 – Warrior Park, Davis-Monthan AFB, Tucson, Arizona
- 79-0173 – New England Air Museum, Windsor Locks, Connecticut
- 80-0247 – American Airpower Museum, Republic Airport, Farmingdale, New York
- 80-0708 – Selfridge Military Air Museum, Selfridge Air National Guard Base, Harrison Township, Michigan