Price: $24.95
- 3 magazines and 7 manuals
- PDF contains 2,121 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
December 1978
- Special Flying Salon
- 100 of Aviation’s Greatest Flight Portraits
December 1985
- The Fabulous Phantom – Special Edition
- Exclusive Color Photos, Cutaway Design, Construction, and Systems
June 1987
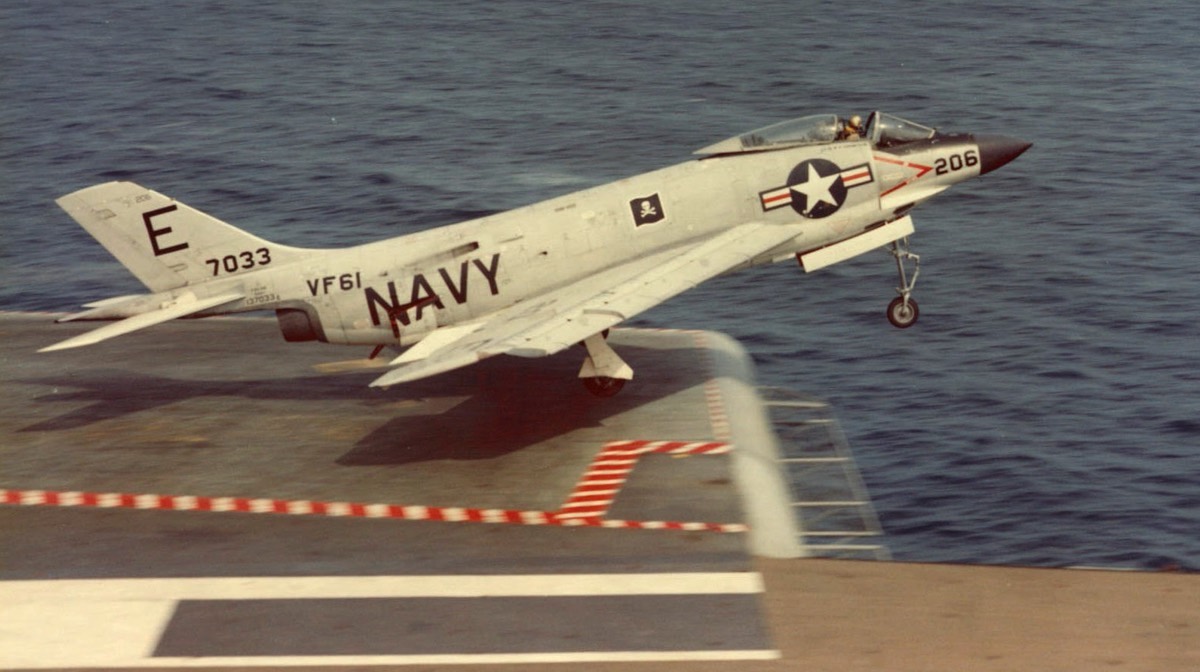
- Carrier Borne, Part II
- EF-111 Radar Jammers
Manuals & Photos
- XF3H-1 Pilot’s Handbook, 1951
- F3H-2 -2M -2N Demon Flight Handbook, 1960
- F3H-2 -2M Flight Handbook, 1961
- F3H-2 -2M -2N Parts Breakdown, 1960
- McDonnell F3H Demon Brochure
- McDonnell Demon Combat Capability Report, 1953
- McDonnell Photo Demon Handbook
- Over 380 McDonnell F3H Demon photos
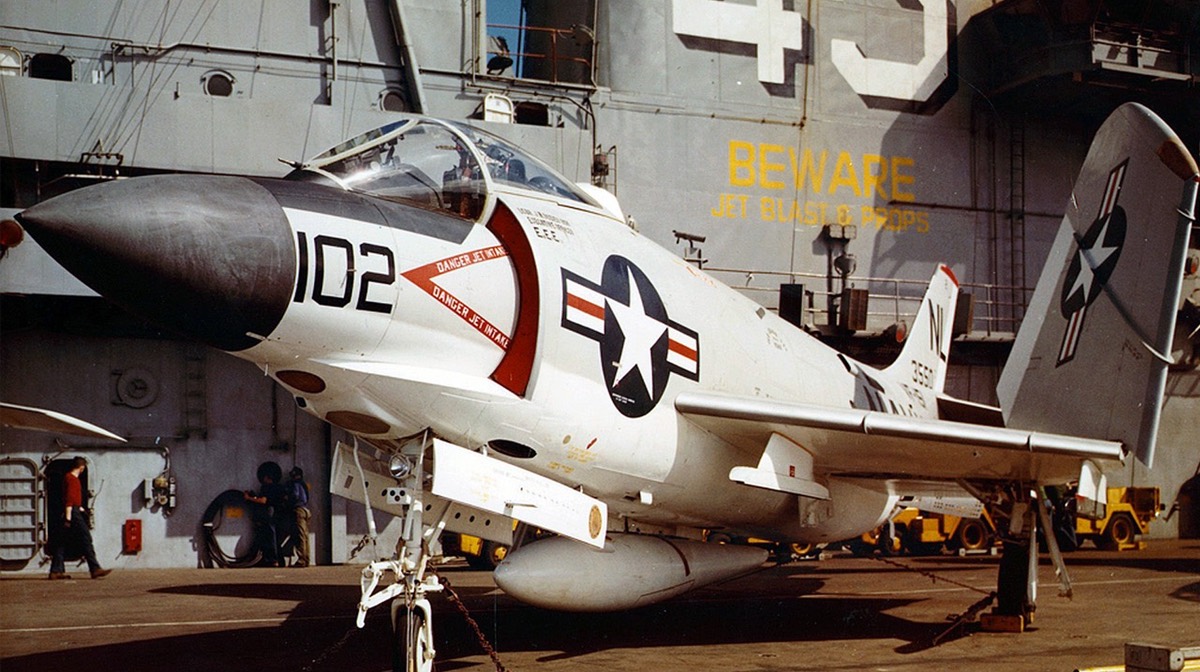
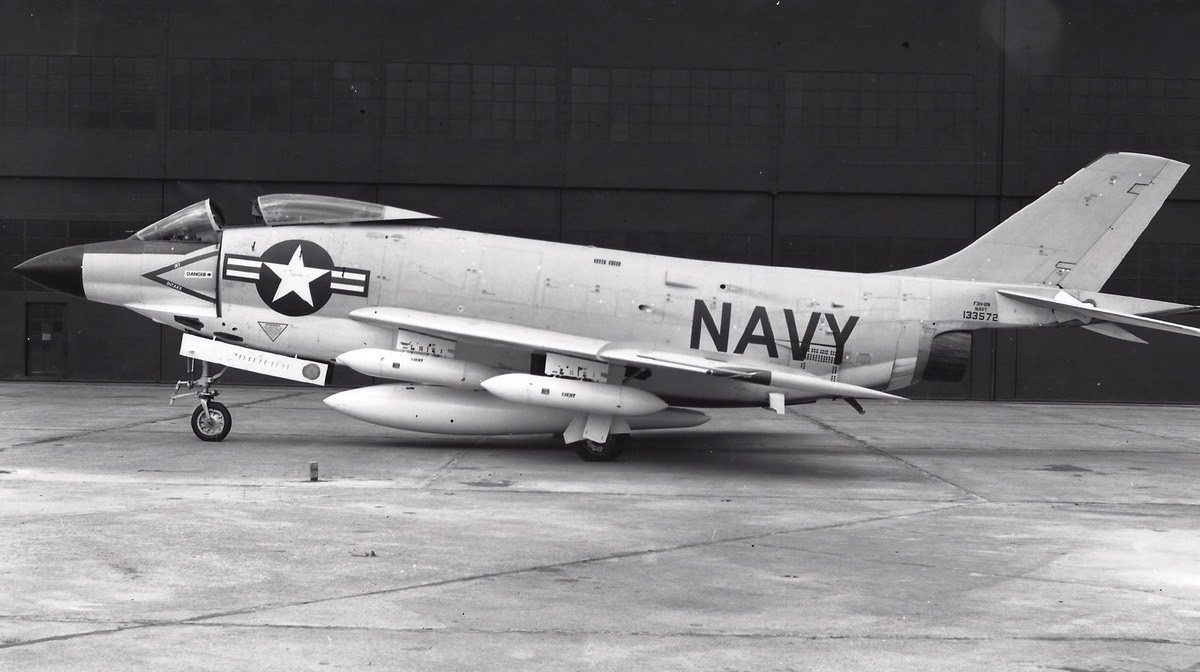
McDonnell F3H Demon
F3H-2 Specifications
Variants
On Display
Cutaway
Videos
General Characteristics
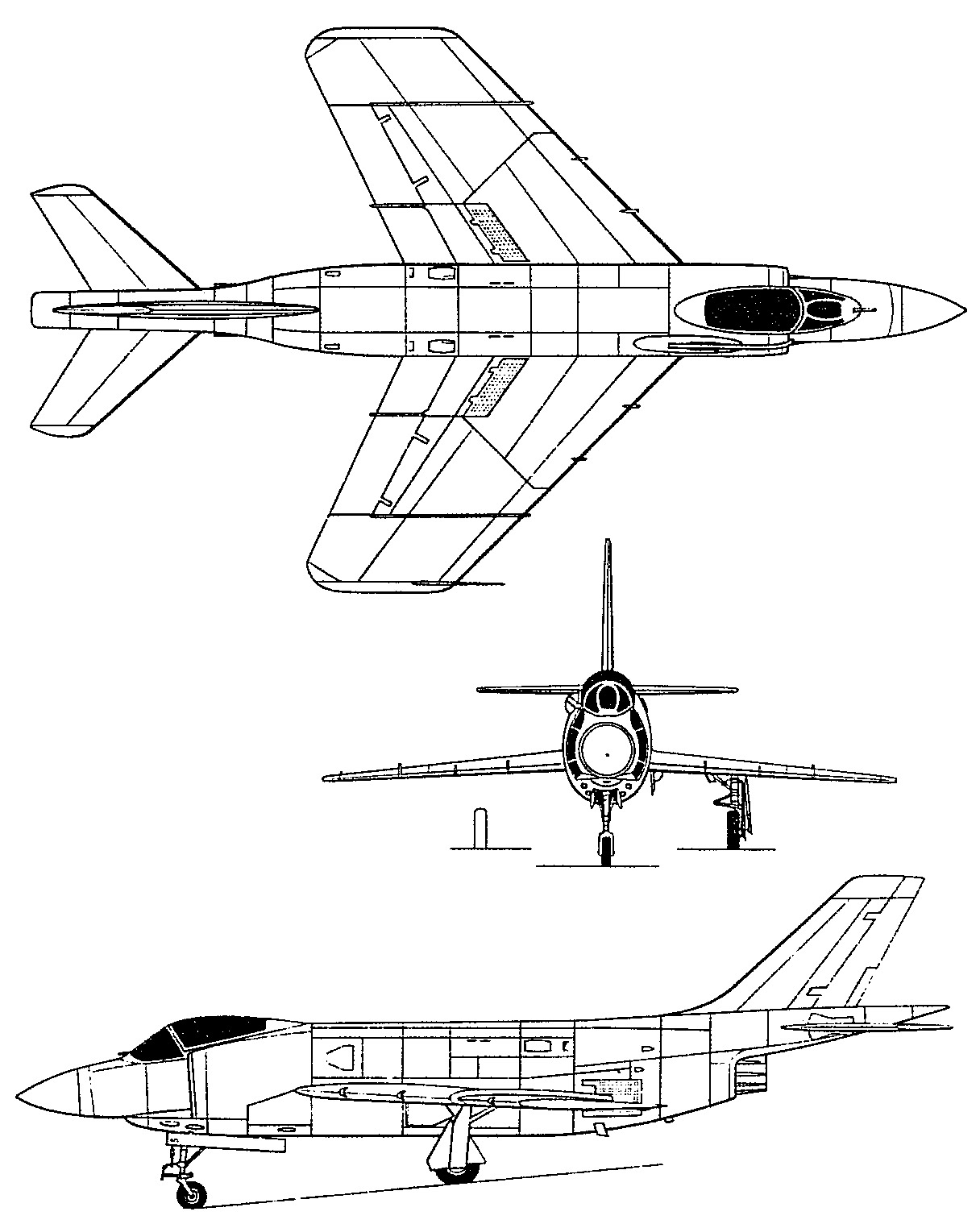
- Crew: 1
- Length: 59 ft (18 m)
- Wingspan: 35 ft 4 in (10.77 m)
- Height: 14 ft 7 in (4.45 m)
- Wing area: 519 sq ft (48.2 m2)
- Empty weight: 21,133 lb (9,586 kg)
- Gross weight: 33,900 lb (15,377 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Allison J71-A-2E afterburning turbojet engine, 9,700 lbf (43 kN) thrust dry, 14,750 lbf (65.6 kN) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 716 mph (1,152 km/h, 622 kn) at sea level. 647 mph (562 kn; 1,041 km/h) at 30,000 ft (9,144 m)
- Range: 1,370 mi (2,200 km, 1,190 nmi)
- Endurance: 3 hours at 575 mi (500 nmi; 925 km) radius
- Service ceiling: 35,050 ft (10,680 m)
- Rate of climb: 12,795 ft/min (65.00 m/s)
Armament
- Guns: 4x 20 mm (0.787 in) Colt Mk 12 cannon with 150 rpg
- Missiles: 4x AIM-7 Sparrow or 4x AIM-9 Sidewinder
- Bombs: 6,000 lb (2,700 kg) of bombs
Avionics
- AN/APG-51A, B, and C radar
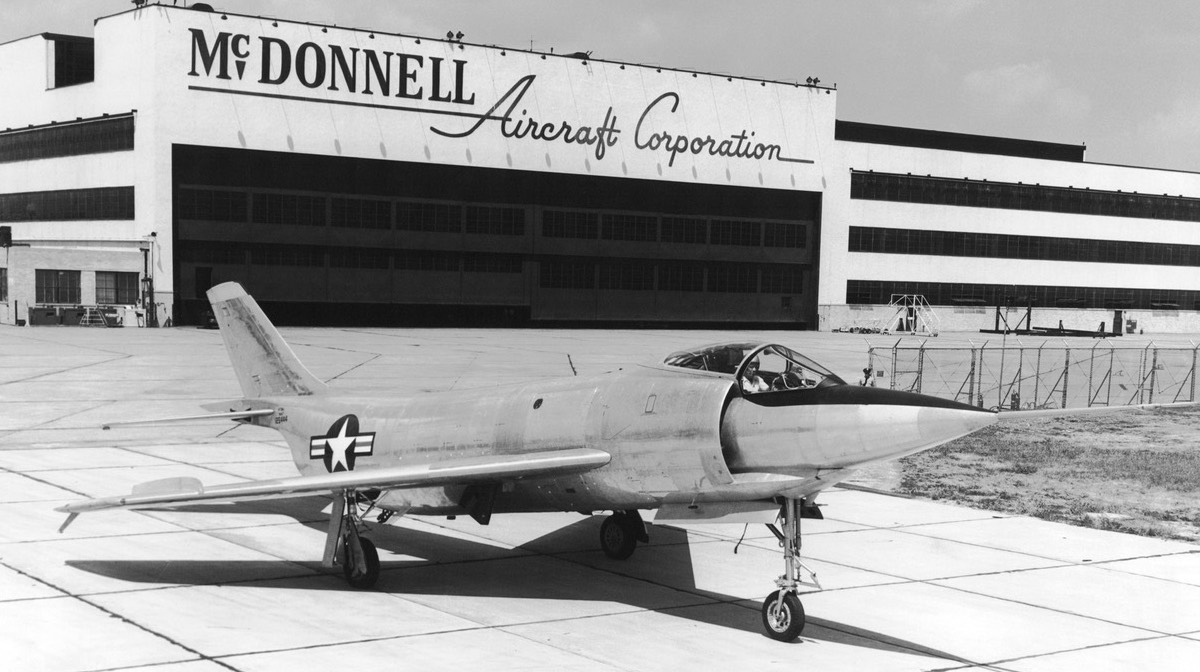
- XF3H-1
Prototype single-seat clear-weather interceptor fighter. Powered by 6,500 lbf (29 kN) (9,200 lbf (41 kN) with afterburner) Westinghouse XJ40-WE-6 engine. Two built. - F3H-1N
Initial production version. Single-seat all-weather fighter version, powered by 7,200 lbf (32 kN) (10,900 lbf (48 kN) with afterburner) J40-WE-22 engine. 58 built. - F3H-1P
Proposed reconnaissance version of F3H-1. Never built. - F3H-2N
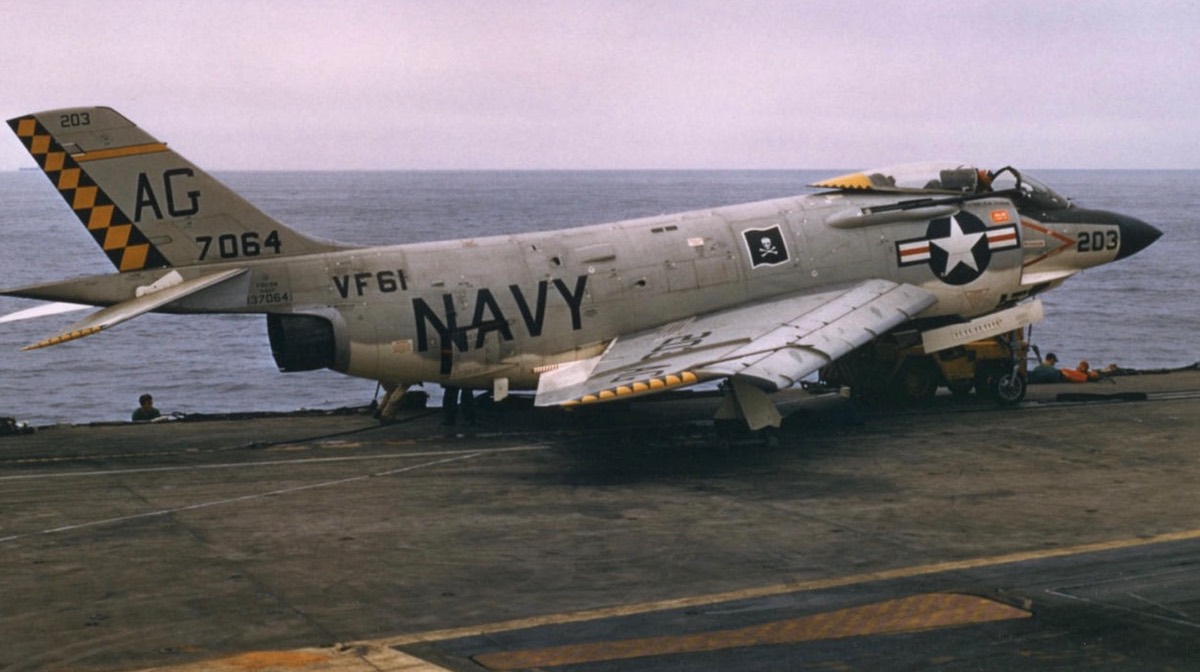
All-weather fighter powered by 9,500 lbf (42 kN) (14,250 lbf (63.4 kN) Allison J71-A-2 engine and equipped to carry AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles. 239 built. Redesignated F-3C in 1962. - F3H-2M
Derivative of F3H-2N armed with four AIM-7 Sparrow air-to-air missiles. 80 built. Redesignated MF-3B in 1962. - F3H-2
Single-seat strike fighter version, retaining Sidewinder and Sparrow capability of the ?2M/N and adding payload of 6,000 lb (2,730 kg) bombs or rockets. 239 built. Redesignated F-3B in 1962. - F3H-2P
Proposed photo-reconnaissance version of ?2. Unbuilt. - F3H-3
Proposed version with the General Electric J73 engine. Unbuilt.
- F3H-2M
- BuNo 137078 – National Museum Naval Aviation at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
- F3H-2N
- BuNo 133566 – USS Intrepid Museum in New York City, New York.
- BuNo 145221 – Pima Air & Space Museum, adjacent to Davis-Monthan AFB in Tucson, Arizona.