Price: $24.95
- 2 magazines and 9 manuals
- PDF contains 1,330 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
July 1989
- A-10 Close Support
- Dyna-Soar – Also Ran in the Race for Space
- Navy Wings of Gold
September 1992
- Rocketship, the Grumman XF5F
- Down on Flames, North America’s Firefighting Fleet
- Reclaiming a Mentor, Rebuilding a T-34 Trainer
Manuals & Photos
- T-34A Flight Handbook, 1958
- T-34B NATOPS Flight Manual, 1981
- T-34C NATOPS Flight Manual, 2000
- T-34B Flight Training Instructions Vol. 1 Primary Phase, 1961
- T-34A Condenses Flight Crew Check List, 1960
- T-34B NATOPS Checklist, 1981
- T-34 Basic Trainer Specification, 1952
- T-34 FAA Weight & Balance, 2007
- T-34A Illustrated Parts Breakdown, 1960
- Over 100 Beechcraft T-34 Mentor photos
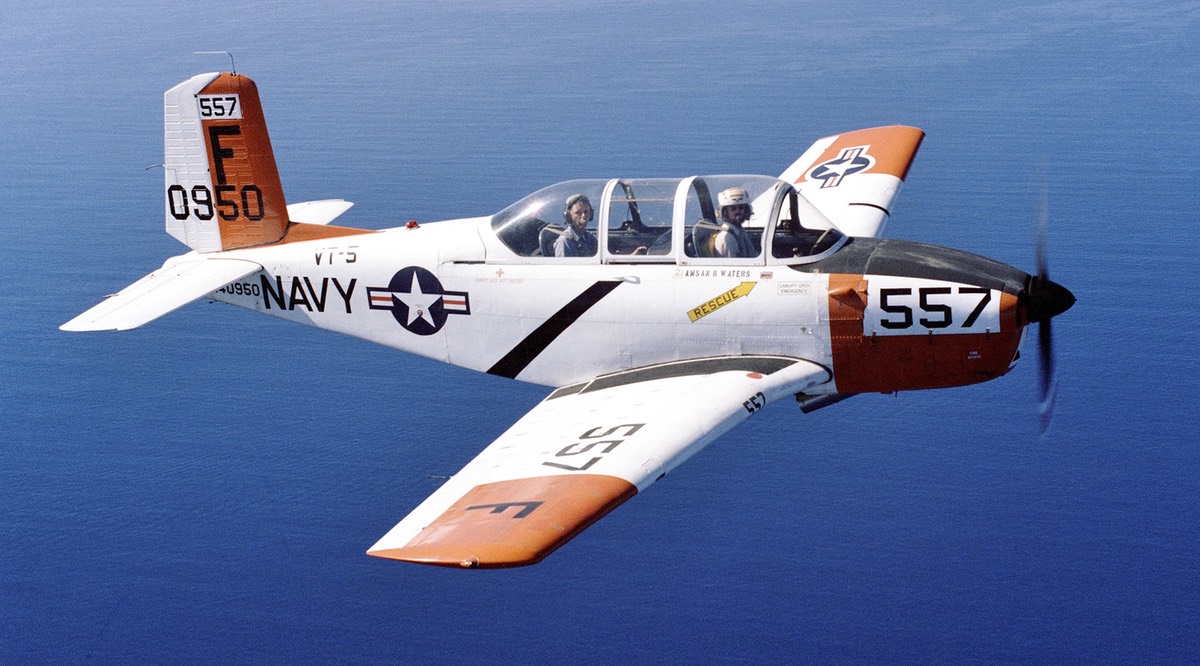
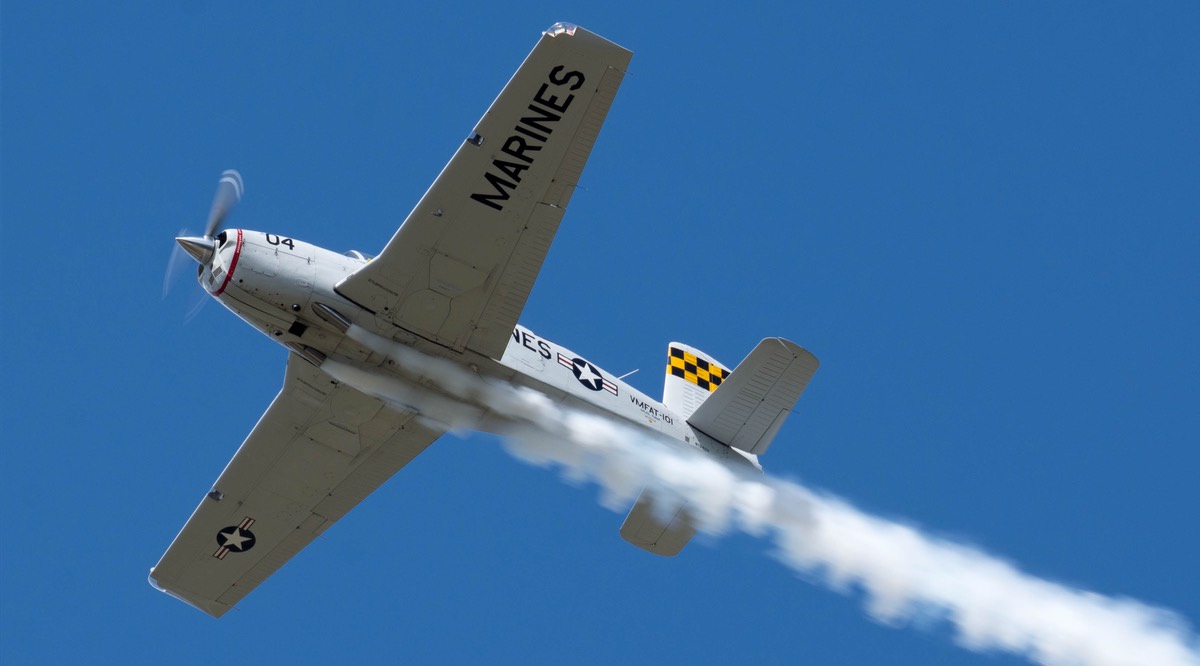
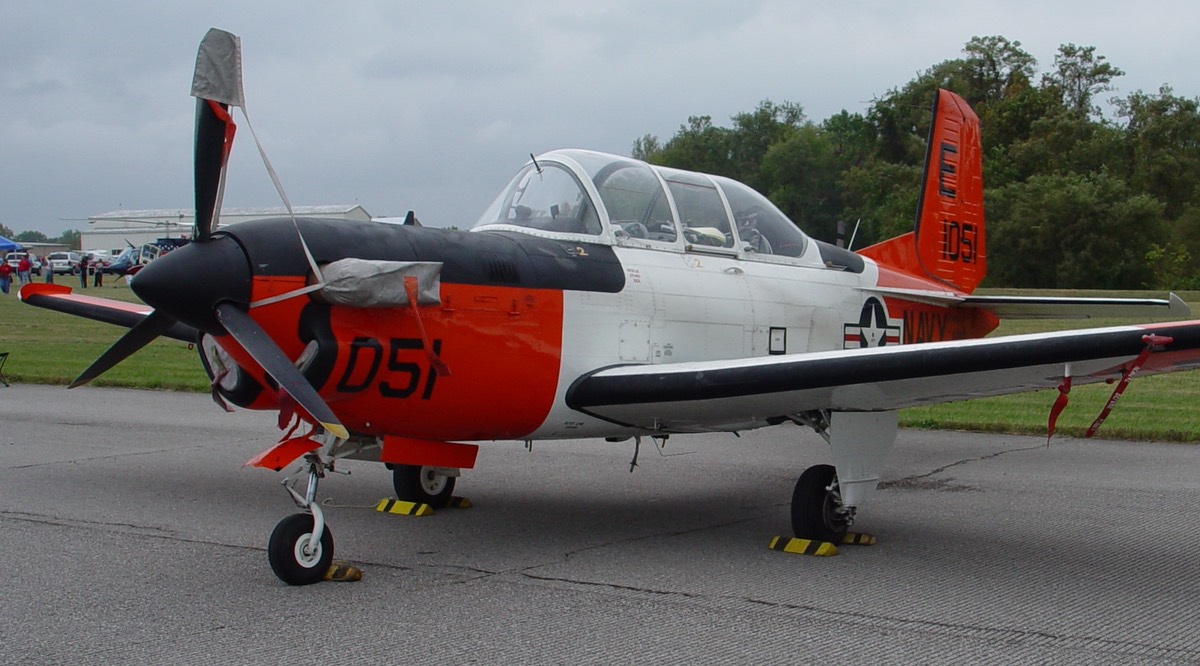
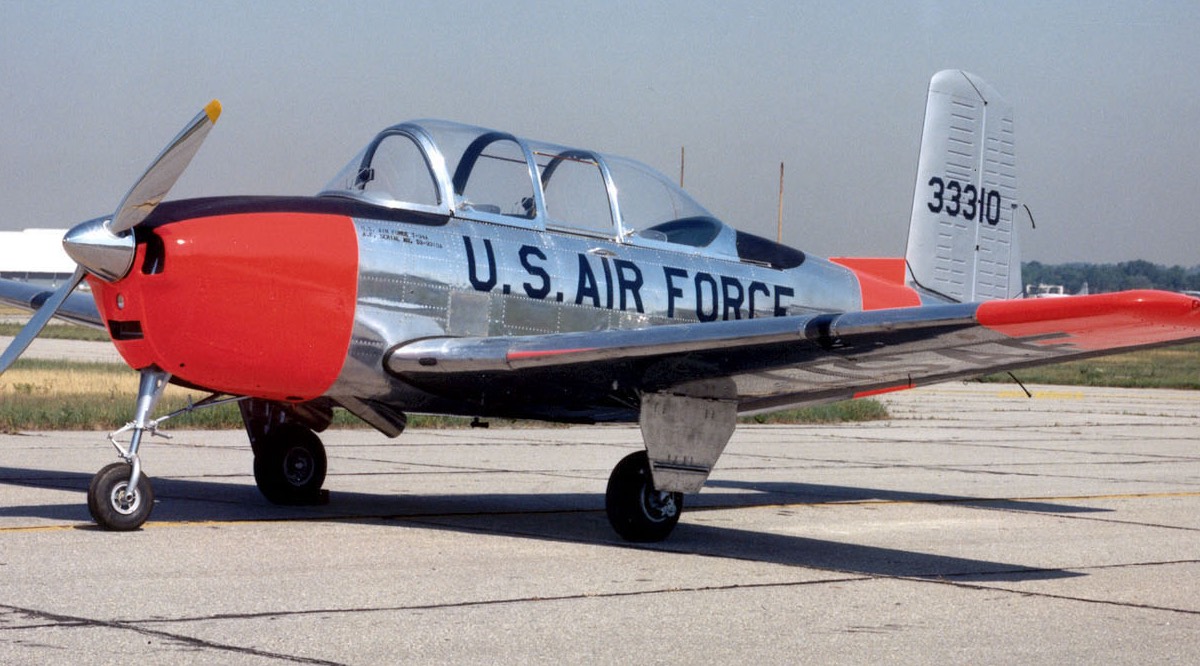
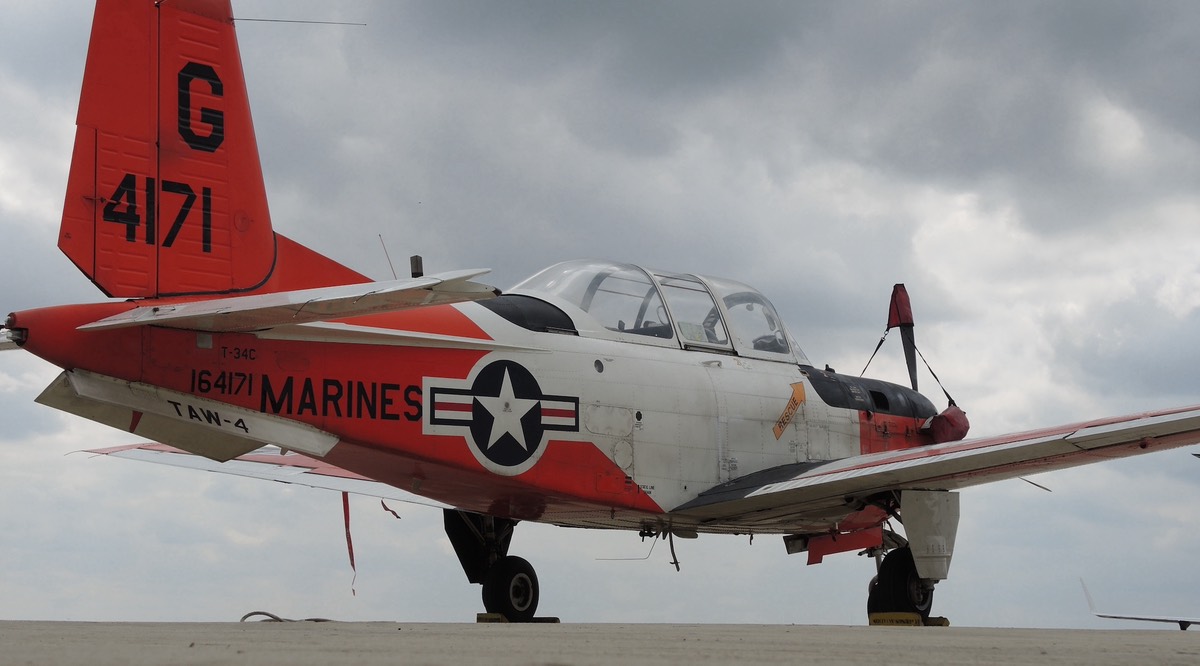
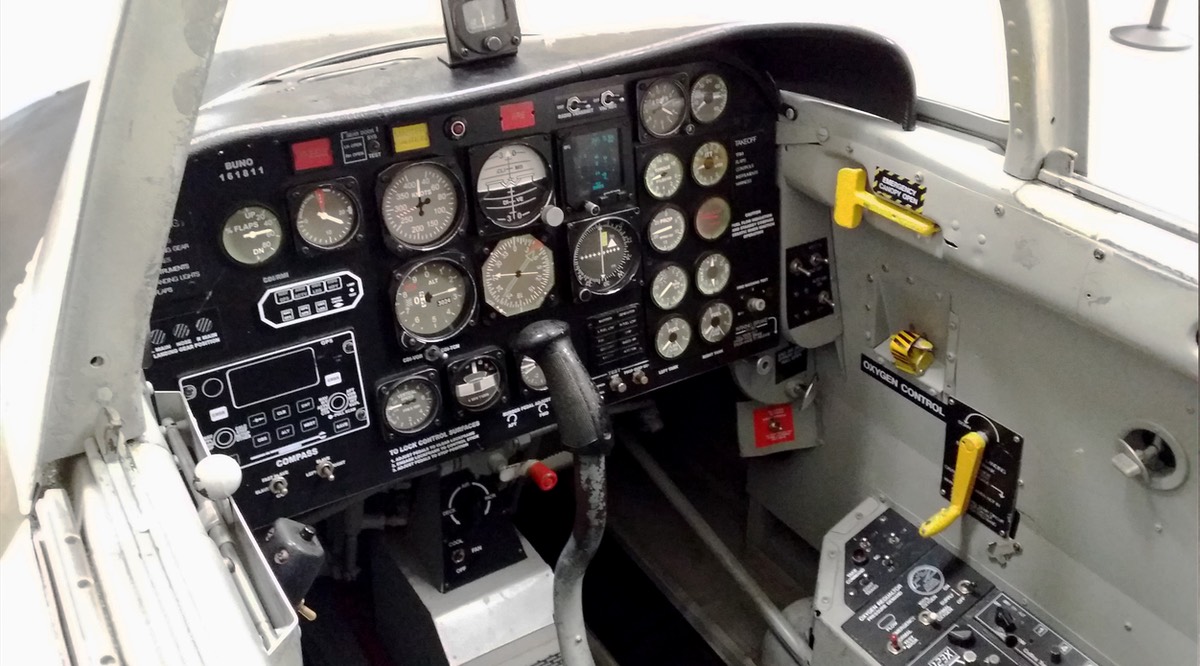
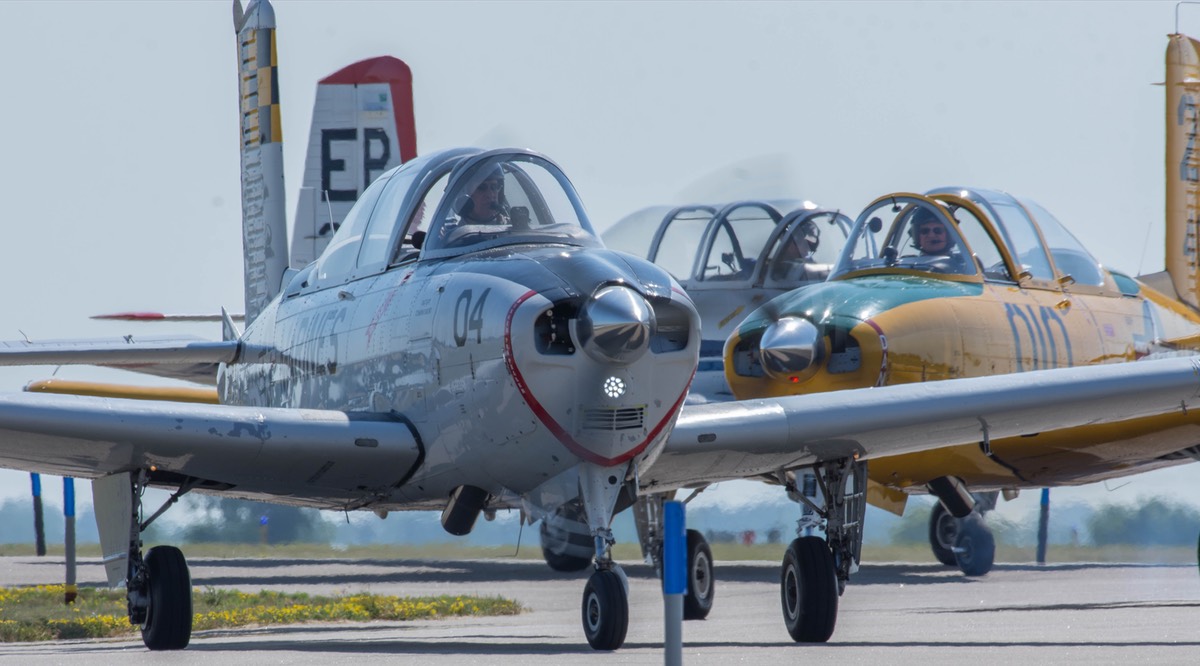
Beechcraft T-34 Mentor
T-34C Specifications
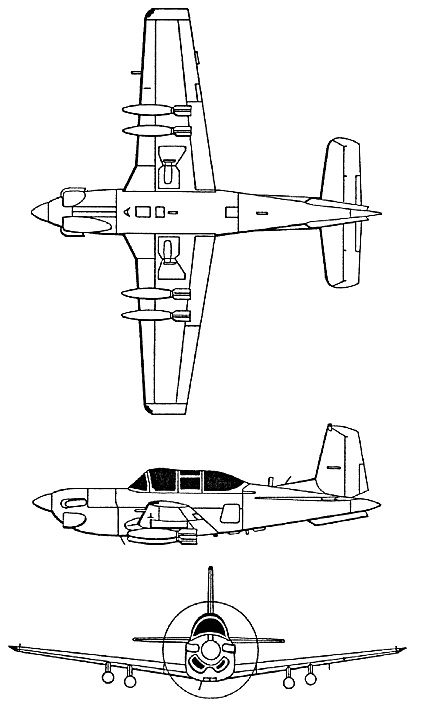
Variants
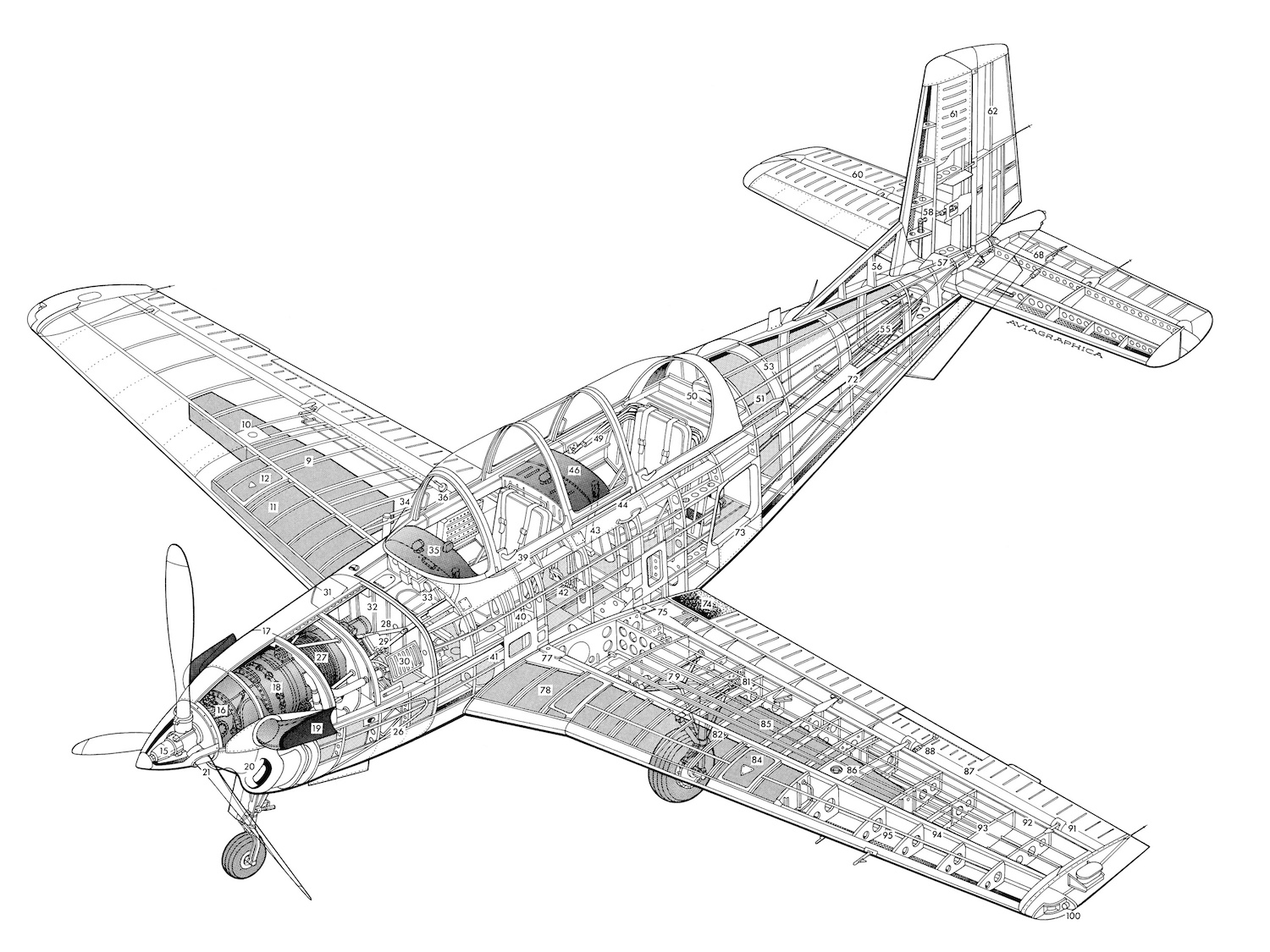
Cutaway
Videos
General Characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 28 ft 8+1?2 in (8.750 m)
- Wingspan: 33 ft 3+7?8 in (10.157 m)
- Height: 9 ft 7 in (2.92 m)
- Wing area: 179.6 sq ft (16.69 m2)
- Empty weight: 2,960 lb (1,343 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 4,300 lb (1,950 kg) (T-34C-1 weapons trainer 5,500 lb (2,500 kg))
- Fuel capacity: 130 US gal (110 imp gal; 490 L)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-25 turboprop, 550 shp (410 kW)
- Propellers: 3-bladed Hartzell constant-speed
Performance
- Cruise speed: 214 kn (246 mph, 396 km/h) at 17,000 ft (5,200 m) (max cruise)
- Stall speed: 53 kn (61 mph, 98 km/h) (flaps down, power off)
- Never exceed speed: 280 kn (320 mph, 520 km/h)
- Range: 708 nmi (815 mi, 1,311 km) at 180 kn (210 mph; 330 km/h) and 20,000 ft (6,100 m)
- Service ceiling: 30,000 ft (9,100 m)
- g limits: +6, -3
- Rate of climb: 1,480 ft/min (7.5 m/s)
Armament
- Hardpoints: 4 with a capacity of 600 lb (272 kg) inner, 300 lb (136 kg) outer, 1,200 lb (544 kg) total
- YT-34 – Prototype, three built.
- T-34A – US Air Force trainer. Replaced by the Cessna T-37 around 1960 (450 built).
- T-34B – US Navy trainer. Used as a trainer until 1976, when VT-1 and VT-5 were decommissioned. It was replaced by the T-34C (423 built by Beechcraft). T-34Bs were flown by pilots assigned to the Navy Recruiting Command until the mid-1990s.
- YT-34C – Two T-34Bs were fitted with turboprop engines, and were used as T-34C prototypes.
- T-34C Turbo-Mentor – Two-seat primary trainer, fitted with a turboprop engine.
- T-34C-1 – Equipped with hardpoints for training or light attack, able to carry 1,200 lb (540 kg) of weapons on four underwing pylons. The armament could include flares, incendiary bombs, rocket or gun pods and antitank missiles. Widely exported.
- Turbo-Mentor 34C – Civilian version
- Allison Turbine Mentor – Conversion of surplus T-34 Mentors to be powered by Allison Model 250 turboprop engines.
- Model 73 Jet Mentor – Powered by a 920 lbf (4.09 kN) Continental J69-T-9 turbojet engine. The sole aircraft first flew on 18 December 1955.