Price: $45.95
- 4 magazines, 19 manuals, & photos
- PDF contains 8,406 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
July 1977
- Crusader Without A Cause
- Skybolt Pt IX, P-38 Dive Bombers
- Breguet Battlewagons, WWI’s Champion Medium Bomber
July 1986
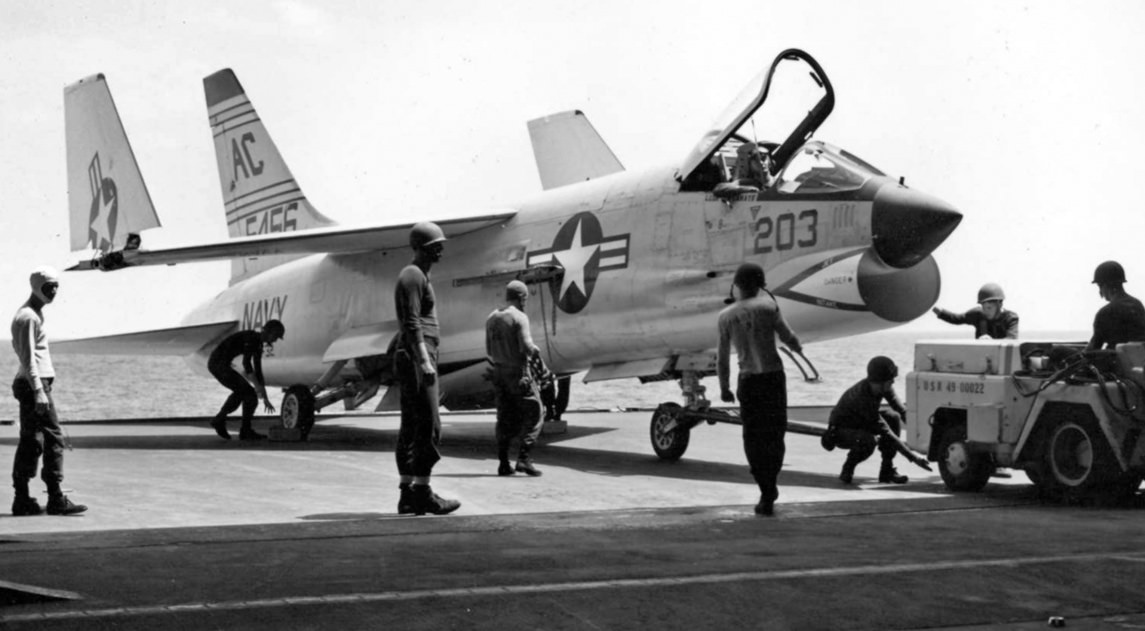
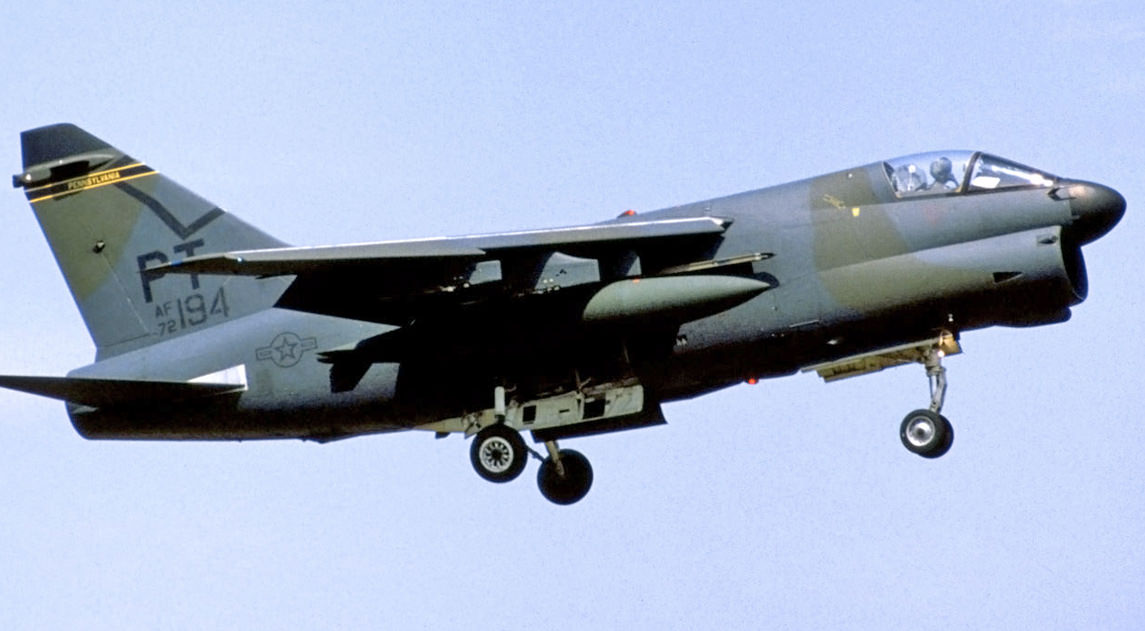
- Vought A-7 Corsair II
- WWII Canadian Aircraft
- CF.24 Biplane’s Last Hurrah
August 1994
- Three Generations of Combat Corsairs – O2U, F4U, A-7
- Seabirds of the Navy, Grumman’s Mighty Ducks – Geese & Widgeons
August 1987
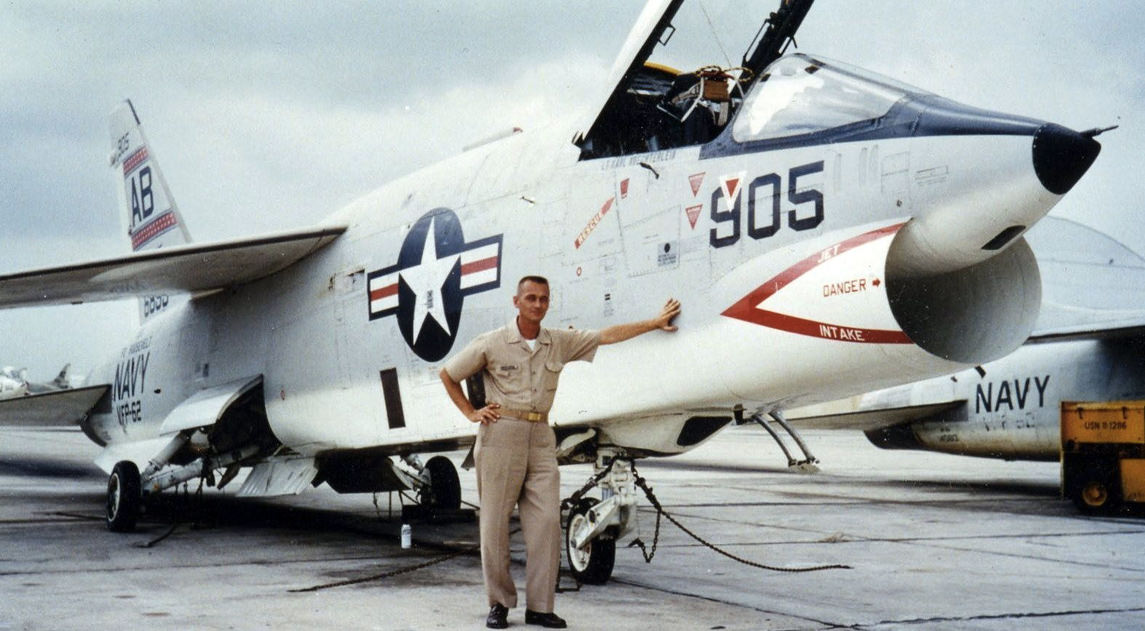
- Vought’s F-8 Crusader Special Edition
Manuals & Photos
- A-7D Flight Manual 1972
- A-7K Weapon Delivery Manual 1981
- F-8C Supplemental Flight Manual 1966
- F-8DE Flight Manual 1968
- F-8DE Flight Manual Supplemental 1968
- F-8HJ NATOPS Flight Manual 1974
- F-8U3 Vought Preliminary Flight Guide 1958
- RF-8G Flight Manual 1978
- Over 400 A-7 Corsair II / F-8 Crusader photos
Bonus Manuals!
- A-7D Technical Manuals, 4700+ pages
- F-8D/E Pocket Checklist
Vought A-7 Corsair II / F-8 Crusader
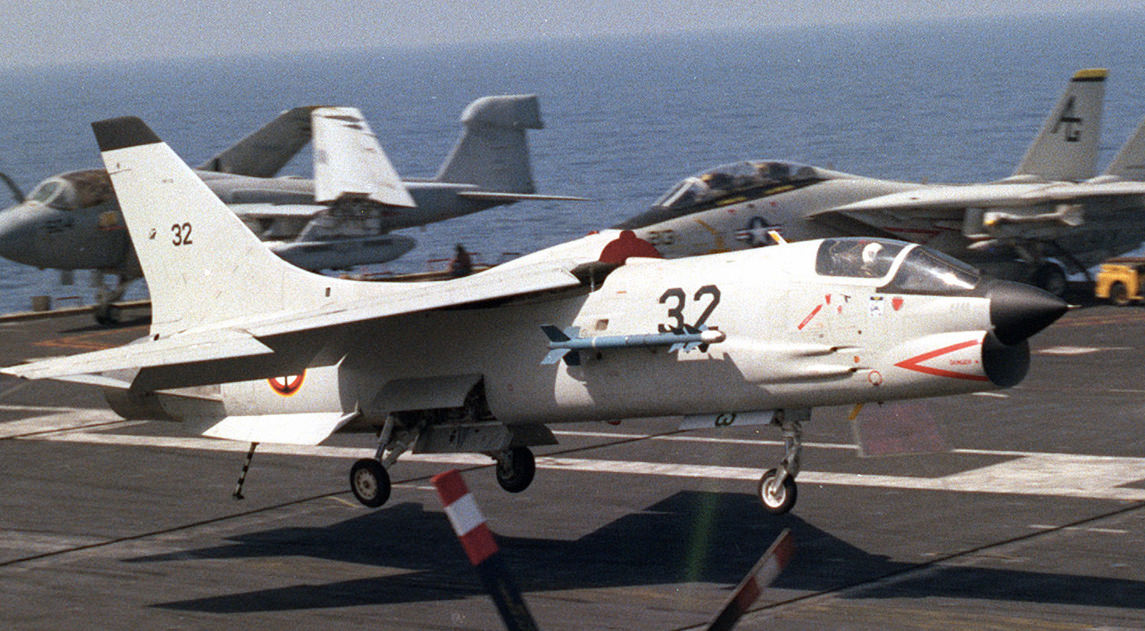
A-7E Specs
A-7 Variants
A-7 On Display
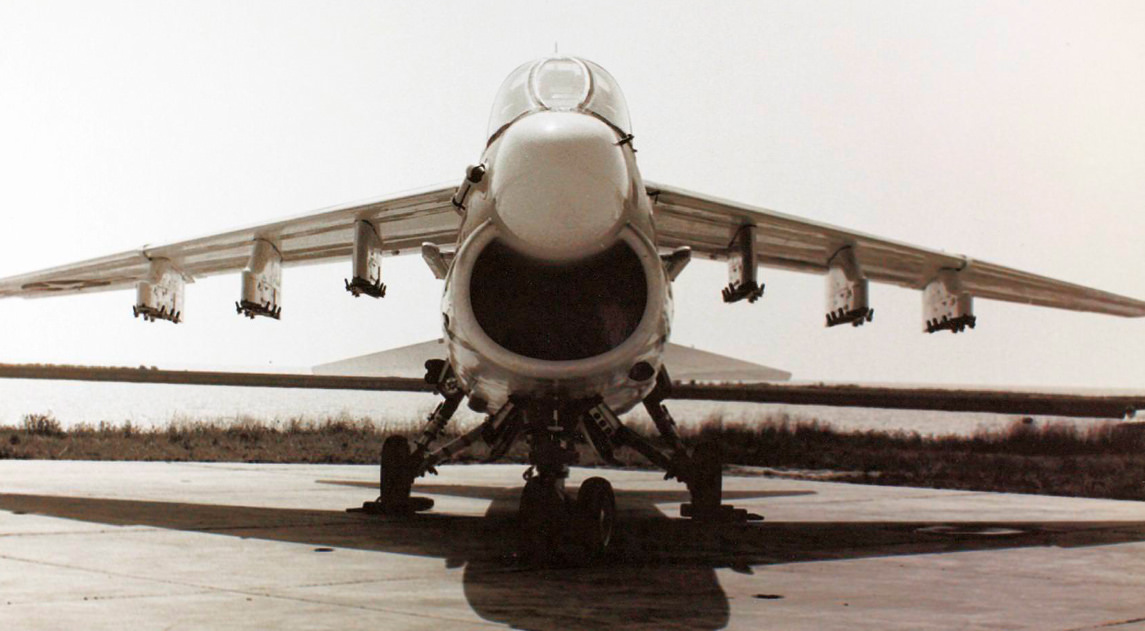
F-8E Specs
F-8 Variants
F-8 On Display
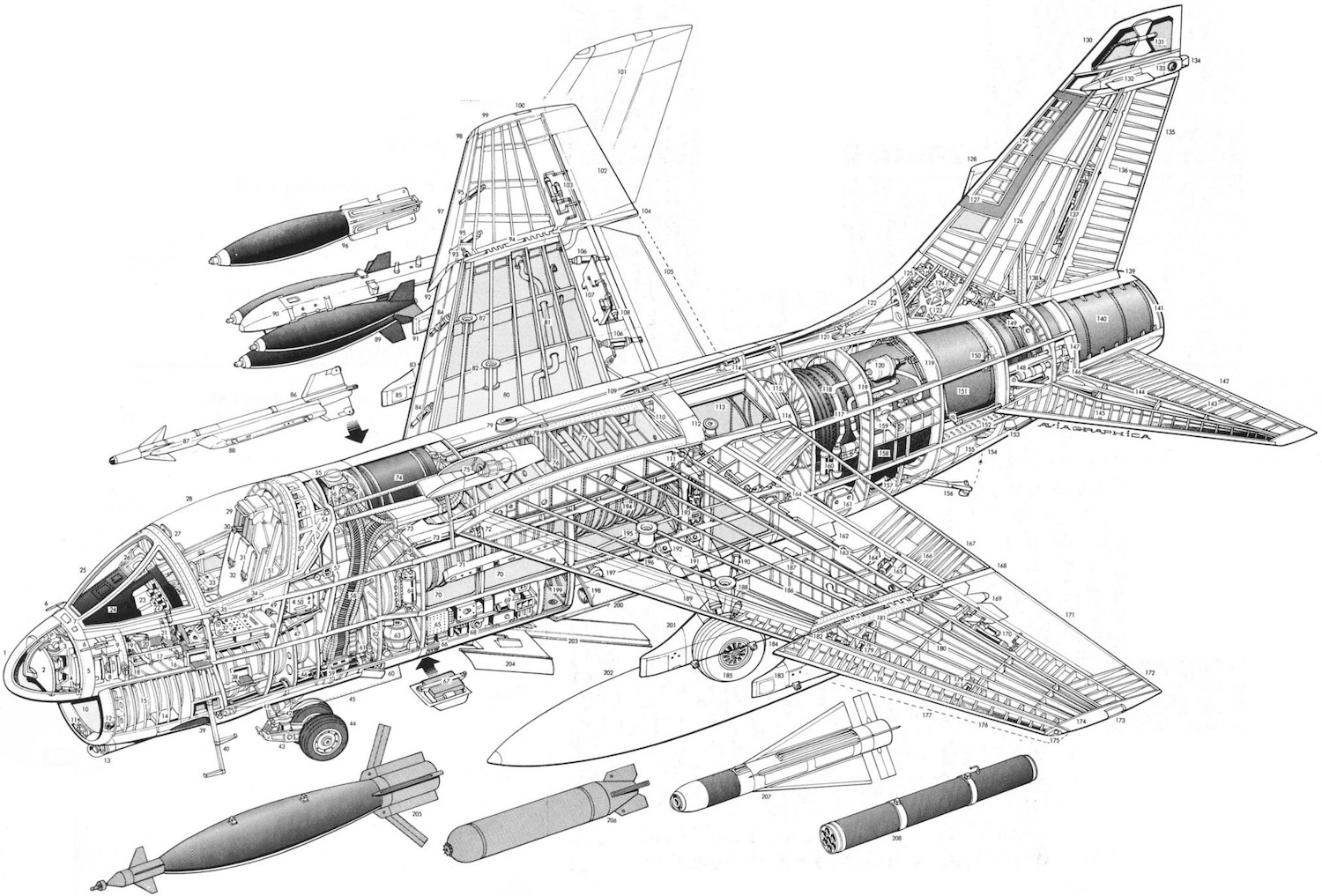
Cutaways
General Characteristics

- Crew: 1
- Length: 46 ft 2 in (14.06 m)
- Wingspan: 38 ft 9 in (11.8 m)
- Width: 23 ft 9 in (7.24 m) wings folded
- Height: 16 ft 1 in (4.9 m)
- Wing area: 374.9 sq ft (34.83 m2)
- Airfoil: NACA 65A007 root and tip
- Empty weight: 19,127 lb (8,676 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 41,998 lb (19,050 kg) overload condition.
- Fuel capacity: 1,338 US gal (5,060 l; 1,114 imp gal) (10,200 lb (4,600 kg)) internal
- Powerplant: 1 × Allison TF41-A-2 non-afterburning turbofan engine, 15,000 lbf (66.7 kN) thrust
Performance
- Maximum speed:
600 kn (690 mph; 1,111 km/h) at Sea level
562 kn (1,041 km/h; 647 mph) at 5,000 ft (1,524.0 m) with 12x Mk82 bombs
595 kn (1,102 km/h; 685 mph) at 5,000 ft (1,524.0 m) after dropping bombs
- Range: 1,070 nmi; 1,231 mi (1,981 km) maximum internal fuel
- Ferry range: 1,342 nmi; 1,544 mi (2,485 km) with maximum internal and external fuel
- Service ceiling: 42,000 ft (13,000 m)
- Wing loading: 77.4 lb/sq ft (378 kg/m2)
- Thrust/weight: 0.50
- Sustained maneuvering performance: 5,300 ft (1,615.4 m) turning radius at 4.3g and 500 kn (930 km/h; 580 mph) at an All Up Weight (AUW) of 28,765 lb (13,048 kg)
- Take-off run: 1,705 ft (519.7 m) at 42,000 lb (19,000 kg)
Armament
- Guns: 1× M61A1 Vulcan 20 mm (0.787 in) rotary cannon with 1,030 rounds
- Hardpoints: 6× under-wing and 2× fuselage pylon stations (for mounting AIM-9 Sidewinder AAMs only) with a capacity of 15,000 lb (6,803.9 kg) total capacity,with provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets: 4× LAU-10 rocket pods (each with 4× 127 mm (5.000 in) Mk 32 Zuni rockets)
- Missiles:
- 2× AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missile
- 2× AGM-45 Shrike anti-radiation missile
- 2× AGM-62 Walleye TV-guided glide bomb
- 2× AGM-65 Maverick air-to-ground missile
- 2× AGM-88 HARM anti-radiation missile
- 2× GBU-8 HOBOS electro-optically guided glide bomb
- Bombs:
- Up to 30× 500 lb (226.8 kg) Mark 82 bombs or Mark 80 series of unguided bombs(including 6.6 lb (3 kg) and 31 lb (14 kg) practice bombs)
- Paveway series of laser-guided bombs
- Up to 4× B28 nuclear bomb/B43 nuclear bomb/B57 nuclear bomb/B61 nuclear bomb/B83 nuclear bombs
- Other: up to 4 × 300 US gal (1,100 l), 330 US gal (1,200 l), or 370 US gal (1,400 l) drop tanks
Avionics
- AN/ASN-90(V) Inertial reference system
- AN/ASN-91(V) navigation/weapon delivery computer
- AN/APN-190(V) Doppler groundspeed and drift detector
- Texas Instruments AN/APQ-126(V) Terrain-following radar (TFR)
- AN/AVQ-7(V) Head Up display (HUD)
- CP-953A/AJQ solid state Air Data computer (ADC)
- AN/ASN-99 Projected Map Display (PMD)
- A-7A – First production version. Early USN Corsair IIs had two 20 mm Colt Mk 12 cannons with 250 rounds per gun. Maximum ordnance, carried primarily on the wing pylons, was theoretically 15,000 lb (6,804 kg), but was limited by maximum takeoff weight, so the full weapon load could only be carried with greatly reduced internal fuel; Equipped with AN/APN-153 navigational radar, AN/APQ-115 terrain following radar, and a separate AN/APQ-99 attack radar; 199 built.
- A-7B – Uprated TF30-P-8 engine with 12,190 lbf (54.2 kN) of thrust. In 1971, surviving A-7Bs were further upgraded to TF30-P-408 with 13,390 lbf (59.6 kN) of thrust; AN/APQ-115 terrain following radar in earlier A-7A is replaced by AN/APQ-116 terrain following radar; 196 built.
- A-7C – First 67 production A-7E with TF30-P-408 engines.
- TA-7C – Two-seat trainer version for USN, 24 converted from A-7B, 36 from A-7C. In 1984, 49 airframes, including the 8 EA-7Ls, were re-engined with the TF41-A-402 and upgraded to A-7E standard.
- A-7D – Version built for the USAF, with one Allison TF41-A-1 turbofan, and a single M61 Vulcan 20 mm rotary cannon; AN/APN-153 navigational radar in earlier models is replaced by AN/APN-185 navigational radar, AN/APQ-116 terrain following radar in earlier A-7B/C is replaced by AN/APQ-126 terrain following radar; 459 built.
- A-7E – Naval carrier-capable equivalent of the A-7D; AN/APN-185 navigational radar in earlier A-7D is replaced by AN/APN-190 navigational radar, AN/APQ-126 terrain following radar in earlier A-7D is replaced by AN/APQ-128 terrain following radar; 529 built.
- YA-7F Strikefighter (A-7D Plus) – Stretched, supersonic version of A-7 powered by an F100, optimized for interdiction role, but cancelled after two prototypes were built.
- A-7G – Proposed version for Switzerland, none built.[32]
- YA-7E/YA-7H – Two-seat prototypes built by Ling-Temco-Vought as a private venture.
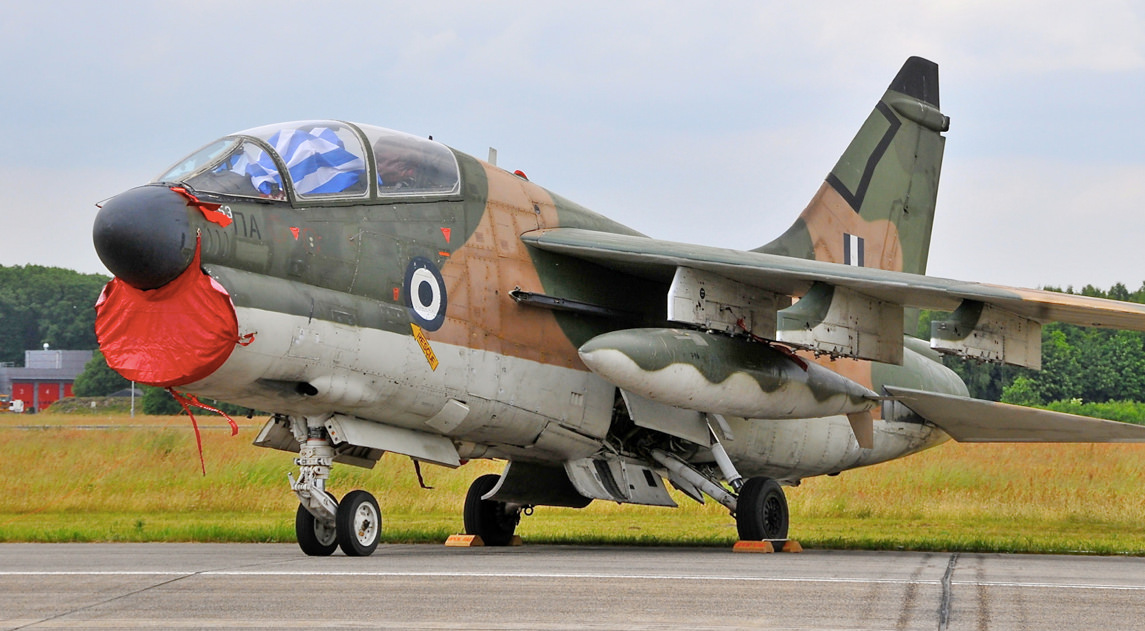
- A-7H – Modified A-7E for Greece without air-refueling capability, 60 built.
- TA-7H – Two-seat trainer version for Greece.
- EA-7L – 8 TA-7C modified into electronic aggressor aircraft used by VAQ-34, upgraded to A-7E standard while retaining twin seats in 1984.
- A-7K – Two-seat trainer version for Air National Guard, 30 built.
- A-7P – Ex-USN A-7As rebuilt for Portuguese Air Force, 44 refurbished with TF30-P-408 engines and an avionics fit similar to the A-7E.
- TA-7P – Two-seat trainer version for Portuguese Air Force; six converted from ex-USN A-7As.
United States
-
A-7A
- 152647 – High Springs Community School, High Springs, Florida.
- 152650 – Don Garlits Museum of Drag Racing, Ocala, Florida.
- 152658 – Patuxent River Naval Air Museum, Patuxent River, Maryland.
- 152660 (displayed as 69-6234) – Flying Tiger Heritage Park, England AFB (formerly), Alexandria, Louisiana.
- 152668 – Museum of Science and Industry, Chicago, Illinois.
- 152681 – Prairie Aviation Museum, Bloomington, Illinois.
- 153135 – Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum, Titusville, Florida.
- 153142 – Alliance High School, Alliance, Ohio.
- 153150 – Pocahontas Municipal Airport, Pocahontas, Arkansas.
- 153163 – Fabricor Inc., Cleves, Ohio.
- 153220 – American Legion Post 1170, Round Lake, Illinois.
- 153241 – Pacific Coast Air Museum, Santa Rosa, California.
- 153242 – U.S. Space and Rocket Center, Huntsville, Alabama.
- 153266 – Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW) Post 8343 & 11038, Rochester, Wisconsin.
- 154345 – Hickory Aviation Museum, Hickory, North Carolina.
-
A-7B
- 154362 – NAS Alameda (formerly), Alameda, California.
- 154370 – USS Midway Museum, San Diego, California.
- 154420 – NAS Fallon, Nevada.
- 154431 – Texas Air Museum – Caprock Chapter, Slaton Municipal Airport, Lubbock, Texas.
- 154443 – NAS Lakehurst, Lakehurst, New Jersey.
- 154449 – Joe Davies Heritage Airpark at Palmdale Plant 42, Palmdale, California.
- 154474 – NASA Stennis Space Center, Bay Saint Louis, Mississippi.
- 154475 – Yanks Air Museum, Chino, California.
- 154476 – El Centro NAF, El Centro, California.
- 154479 – Fort Worth Aviation Museum, Fort Worth, Texas.
- 154485 – American Military Heritage Foundation Museum, Saint John the Baptist Peri Airport, Reserve, Louisiana.
- 154502 – Frontiers of Flight Museum, Dallas, Texas.
- 154505 – Celebrity Row, Davis-Monthan AFB (North Side), Tucson, Arizona.
- 154523 – Arkansas Air & Military Museum, Fayetteville, Arkansas.
- 154538 – Yanks Air Museum, Chino, California.
- 154548 – USS Lexington Museum, Corpus Christi, Texas.
- 154550 – Air Victory Museum, Medford, New Jersey.
- 154554 – San Diego Air and Space Museum, Gillespie Field Annex, San Diego, California.
-
A-7C
- 156734 – NAS Fallon, Fallon, Nevada.
- 156739 – Estrella Warbirds Museum, Paso Robles, California.
- 156763 (displayed as 160122) – NAS Lemoore, California.
- 156797 – United States Naval Museum of Armament and Technology, Ridgecrest, California.
-
TA-7C
- 154407 – National Museum of Nuclear Science and History, Albuquerque, New Mexico.
- 156751 – Russell Military Museum, Russell, Illinois.
- 156782 – New Century Air Center, Olathe, Kansas.
-
YA-7D
- 67-14583 – Air Force Flight Test Center Museum, Edwards AFB, California.
-
A-7D
- 68-8220 – Tomah Veterans Hospital, Wisconsin.
- 68-8222 – Dakota Territory Air Museum, Minot International Airport, Minot, North Dakota.
- 68-8223 – Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW) Post 728, Danville, Illinois.
- 68-8226 – American Veterans (AMVETS) Post 7, North Vernon, Indiana.
- 68-8229 – Warrior Park, Davis-Monthan AFB (North Side), Tucson, Arizona.
- 68-8230 – Cullom, Illinois.
- 69-6188 – March Field Air Museum, Riverside, California.
- 69-6190 – Octave Chanute Aerospace Museum, Rantoul, Illinois.
- 69-6191 – Freedom Park Naval Museum, Omaha, Nebraska.
- 69-6192 – Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW) Post 388, Wausau, Wisconsin.
- 69-6193 – Colorado State Veterans Center, Homelake, Colorado.
- 69-6197 – Glenn L. Martin Aviation Museum, Middle River, Maryland.
- 69-6200 – Wings of Eagles Discovery Center, Horseheads, New York.
- 69-6202 – Luis Munoz Marin International Airport, San Juan, Puerto Rico.
- 69-6208 – Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW) Post 4324, Harry Stern Airport, Wahpeton, North Dakota.
- 69-6239 – Faulkton Municipal Airport, Faulkton, South Dakota.
- 69-6241 – Brooke County Veterans Memorial Park, Weirton, West Virginia.
- 69-6242 – Greeley Weld County Airport, Greeley, Colorado.
- 70-0931 – South Dakota ANGB – 114th FW, Sioux Falls, South Dakota.
- 70-0937 – Correctionville, Iowa.
- 70-0963 – American Legion Post 307, Martin Field, South Sioux City, Nebraska.
- 70-0964 – Chico Air Museum, Chico, California. This aircraft donated from the collection of George Ford and was purchased at Auction from the Merle Maine Estate Ontario Oregon.
- 70-0966 – Virginia Aviation Museum, Richmond International Airport, Richmond, Virginia.
- 70-0970 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Dayton, Ohio.
- 70-0973 – Pima Air & Space Museum, Tucson, Arizona.
- 70-0982 – Wisconsin National Guard Memorial Library and Museum, Volk Field, Camp Douglas, Wisconsin.
- 70-0996 – South Dakota National Guard Museum, Pierre, South Dakota.
- 70-0998 – Aerospace Museum of California, McClellan AFB, McClellan, California
- 70-1001 – Buckley AFB (North-West Side), Denver, Colorado.
- 70-1008 – Monoma County Veterans Memorial & Museum, Onawa, Iowa.
- 70-1012 – Huron Regional Airport, Huron, South Dakota.
- 70-1019 – Myrtle Beach AFB, South Carolina.
- 70-1028 – Oklahoma ANGB – 138th FG, Tulsa, Oklahoma
- 70-1035 – Memorial Park, McEntire ANGB, Columbia, South Carolina.
- 70-1040 – Firefighting Training Center, Helena, Montana.
- 70-1046 – Wyoming ANGB – 153th AG, Cheyenne, Wyoming.
- 70-1050 – Great Plains Airport, Sioux Falls, South Dakota.
- 70-1055 – Montrose County Airport, Montrose, Colorado.
- 71-0334 – Sam Wise Youth Complex, Altoona, Iowa.
- 71-0337 – 37th Training Wing HQ Parade Ground, Kelly Field (formerly Kelly AFB), San Antonio, Texas.
- 71-0342 – Miracle of America Museum, Polson, Montana.
- 71-0347 – American Legion Post 50, Blue Island, Illinois.
- 71-0360 – Ohio ANG, Blue Ash Air Station, Blue Ash, Ohio.
- 72-0117 – Kirtland AFB, Albuquerque, New Mexico.
- 72-0175 – Heritage Museum, Tinker AFB (north side), Oklahoma City, Oklahoma.
- 72-0178 – Ohio ANG, Springfield, Ohio.
- 72-0188 – Commemorative Air Force – Highland Lakes Squadron, Burnet, Texas.
- 72-0211 – Ohio ANG, Toledo Express Airport, Toledo, Ohio.
- 72-0213 – Iowa Aviation Museum, Greenfield, Iowa.
- 72-0230 – Moody Heritage Park, Moody AFB, Valdosta, Georgia.
- 72-0245 – New Mexico ANG, Santa Rosa Route 66 Airport, Santa Rosa, New Mexico.
- 72-0247 – Naval Air Reserve Facility, Rickenbacker Airport, Columbus, Ohio.
- 72-0254 – Arthur N Neu Airport, Carroll, Iowa.
- 72-0261 – Selfridge Military Air Museum and Air Park, Selfridge AFB, Michigan
- 73-0996 – Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum, Denver, Colorado.
- 73-0999 – Rickenbacker ANGB, Ohio ANG – 121st ARW, Rickenbacker Airport, Columbus, Ohio.
- 73-1002 – Pennsylvania ANGB – 171st ARW, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
- 73-1006 – MOTTS Military Museum, Columbus, Ohio.
- 73-1009 – Mid-America Air Museum, Liberal, Kansas.
- 73-1010 – Veterans Memorial Park, Alexander City, Alabama.
- 74-1739 – South Dakota Air and Space Museum, Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota.
- 74-1741 – Arizona Military Museum, Phoenix, Arizona.
- 74-1746 – National Guard Armory, Farmington, New Mexico.
- 74-1756 – 45th Infantry Museum, Oklahoma City, Oklahoma.
- 74-1760 – Airport, Salinas, Puerto Rico.
- 75-0394 – Arizona ANGB, Tucson, Arizona.
- 75-0400 – Grimes ANG – Iowa ANG – 132nd FW, Des Moines Airport, Iowa.
- 75-0403 – Iowa Gold Star Military Museum, Camp Dodge, Johnston, Iowa.
- 75-0406 – Iowa Air National Guard – 185th Fighter Wing, Sioux City, Iowa.
- 75-0408 – Quonset Air Museum, North Kingstown, Rhode Island.
-
A-7E
- 156804 – stored outside at the National Naval Aviation Museum, NAS Pensacola, Florida.
- 157435 – Watertown Municipal Airport, Watertown, South Dakota.
- 157452 – Aviation Wing of the Marietta Museum of History, Dobbins ARB (formerly Atlanta NAS), Atlanta, Georgia.
- 157455 – War Eagles Air Museum, Santa Teresa, New Mexico.
- 157506 – Air Power Park, Hampton, Virginia.
- 157586 (displayed as 157503) – Camp Blanding AAF/NG – Museum and Memorial Park, Camp Blanding, Jacksonville, Florida.
- 158003 – Brothers Welcome Airport, Lake City, Florida.
- 158026 – Heritage in Flight Museum, Lincoln, Illinois.
- 158657 (displayed as 158857) – New Century Air Center, Olathe, Kansas.
- 158662 – NAS Oceana (South Side), Virginia Beach, Virginia.
- 158819 – Tillamook Air Museum, Tillamook, Oregon.
- 158842 – Air Classics Museum, Sugar Grove, Illinois.
- 159261 – Veterans Memorial Park, University Mall, Tuscaloosa, Alabama.
- 159268 – MAPS Air Museum, Canton, Ohio.
- 159278 – Southern Museum of Flight, Birmingham, Alabama.
- 159291 – Patriots Point Naval & Maritime Museum, Charleston, South Carolina.
- 159301 – Oakland Aviation Museum, Oakland, California.
- 159303 – Edwardsville Township Park, Edwardsville, Illinois.
- 159647 – Fallon Auto Mall, Fallon, Nevada.
- 159971 – Carolinas Aviation Museum, Charlotte, North Carolina.
- 159974 – New Orleans NAS JRB, New Orleans, Louisiana.
- 160613 – Empire State Aerosciences Museum, Glenville, New York.
- 160614 – Mountain Home High School, Mountain Home, Arkansas.
- 160713 – Pima Air & Space Museum, Tucson, Arizona.
- 160714 – National Naval Aviation Museum, NAS Pensacola, Florida.
- 160715 – Heritage Park, NAS Jacksonville, Jacksonville, Florida.
- 160724 – Louisiana Veterans Memorial, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
- 160869 – Veterans Museum, Halls, Tennessee.
-
YA-7F
- 70-1039 – Hill Aerospace Museum, Hill AFB, Utah.
- 71-0344 – Air Force Flight Test Center Museum, Edwards AFB, California.
-
A-7K
- 80-0288 – Celebrity Row, Davis-Monthan AFB (North Side), Tucson, Arizona.
- 81-0073 – Iowa Gold Star Military Museum, Camp Dodge, Johnston, Iowa.
General Characteristics

- Crew: 1
- Payload: 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) of weapons
- Length: 54 ft 3 in (16.53 m)
- Wingspan: 35 ft 8 in (10.87 m)
- Height: 15 ft 9 in (4.80 m)
- Wing area: 375 ft² (34.8 m²)
- Airfoil: NACA 65A006 mod root, NACA 65A005 mod tip
- Aspect ratio: 3.4
- Empty weight: 17,541 lb (7,956 kg)
- Loaded weight: 29,000 lb (13,000 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 34,000 lb (15,000 kg)
- Zero-lift drag coefficient: 0.0133
- Drag area: 5.0 ft² (0.46 m²)
- Fuel capacity: 1,325 US gal (5,020 L)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney J57-P-20A afterburning turbojet
- Dry thrust: 10,700 lbf (47.6 kN)
- Thrust with afterburner: 18,000 lbf (80.1 kN)
Performance
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.86 (1,225 mph, 1,975 km/h) at 36,000 ft (11,000 m)
- Cruise speed: 495 kn (570 mph, 917 km/h)
- Combat radius: 450 mi (730 km)
- Ferry range: 1,735 mi (2792 km) () with external fuel
- Service ceiling: 58,000 ft (17,700 m)
- Rate of climb: 19,000 ft min (96.52 m/s)
- Wing loading: 77.3 lb/ft² (377.6 kg/m²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.62
- Lift-to-drag ratio: 12.8
Armament
- Guns: 4× 20 mm (0.79 in) Colt Mk 12 cannons in lower fuselage, 125 rpg
- Hardpoints: 2× side fuselage mounted Y-pylons (for mounting AIM-9 Sidewinders and Zuni rockets) and 2× underwing pylon stations with a capacity of 4,000 lb (2,000 kg) and provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets: 2× LAU-10 rocket pods (each with 4× 5 inch (127mm) Zuni rockets)
- Missiles:
- 4× AIM-9 Sidewinder or Matra Magic (French Navy only) air-to-air missiles
- 2× AGM-12 Bullpup air-to-surface missiles
- Bombs:
- 12× 250 lb (113 kg) Mark 81 bombs or
- 8× 500 lb (227 kg) Mark 82 bombs or
- 4× 1,000 lb (454 kg) Mark 83 bombs or
- 2× 2,000 lb (907 kg) Mark 84 bombs
Avionics
- Magnavox AN/APQ-84 or AN/APQ-94 Fire-control radar
- XF8U-1 (XF-8A) (V-383) – the two original unarmed prototypes.
- F8U-1 (F-8A) – first production version, J57-P-12 engine replaced with more powerful J57-P-4A starting with 31st production aircraft, 318 built.
- YF8U-1 (YF-8A) – one F8U-1 fighter used for development testing.
- YF8U-1E (YF-8B) – one F8U-1 converted to serve as an F8U-1E prototype.
- F8U-1E (F-8B) – added a limited all-weather capability thanks to the AN/APS-67 radar, the unguided rocket tray was sealed shut because it was never used operationally, first flight: 3 September 1958, 130 built.
- XF8U-1T – one XF8U-2NE used for evaluation as a two-seat trainer.
- F8U-1T (TF-8A) (V-408) – two-seat trainer version based on F8U-2NE, fuselage stretched 2 ft (0.61 m), internal armament reduced to two cannon, J57-P-20 engine, first flight 6 February 1962. The Royal Navywas initially interested in the Rolls-Royce Spey-powered version of TF-8A but chose the Phantom II instead. Only one TF-8A was built, although several retired F-8As were converted to similar two-seat trainers.
- YF8U-2 (YF-8C) – two F8U-1s used for flight testing the J57-P-16 turbojet engine.
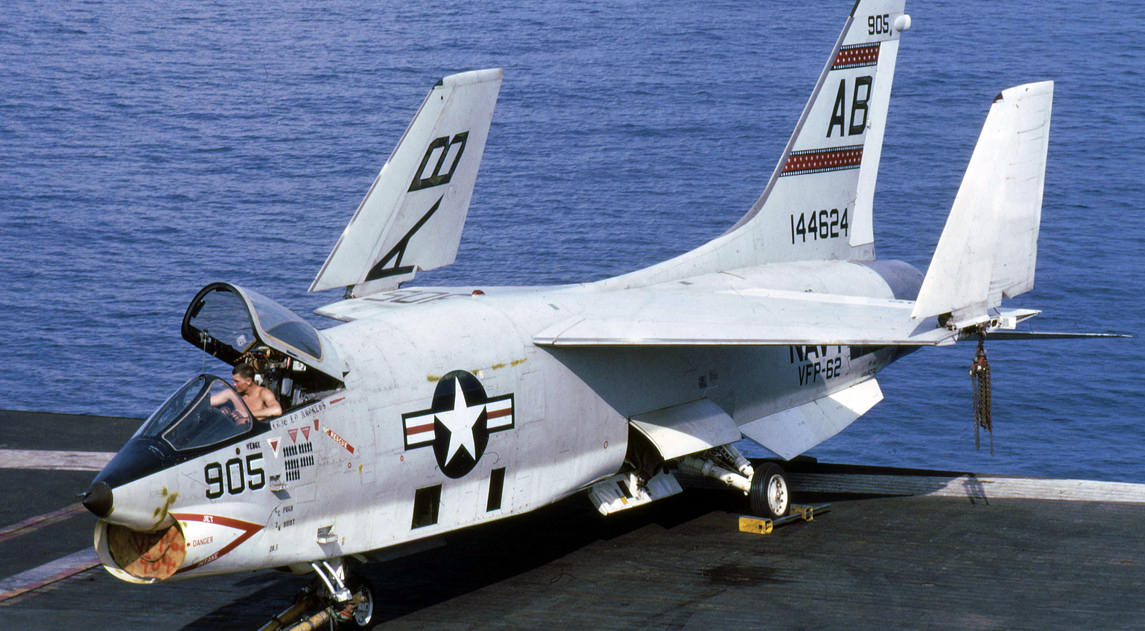
- F8U-2 (F-8C) – J57-P-16 engine with 16,900 lbf (75 kN) of afterburning thrust, ventral fins added under the rear fuselage in an attempt to rectify yaw instability, Y-shaped cheek pylons allowing two Sidewinder missiles on each side of the fuselage, AN/APQ-83 radar retrofitted during later upgrades. First flight: 20 August 1957, 187 built. This variant was sometimes referred to as Crusader II.
- F8U-2N (F-8D) – all-weather version, unguided rocket pack replaced with an additional fuel tank, J57-P-20 engine with 18,000 lbf (80 kN) of afterburning thrust, landing system which automatically maintained present airspeed during approach, incorporation of AN/APQ-83 radar. First flight: 16 February 1960, 152 built.
- YF8U-2N (YF-8D) – one aircraft used in the development of the F8U-2N.
- YF8U-2NE – one F8U-1 converted to serve as an F8U-2NE prototype.
- F8U-2NE (F-8E) – J57-P-20A engine, AN/APQ-94 radar in a larger nose cone, dorsal hump between the wings containing electronics for the AGM-12 Bullpup missile, payload increased to 5,000 lb (2,270 kg), Martin-Baker ejection seat, AN/APQ-94 radar replaced AN/APQ-83 radar in earlier F-8D. IRSTsensor blister (round ball) was added in front of the canopy. First flight: 30 June 1961, 286 built.
- F-8E(FN) – air superiority fighter version for the French Navy, significantly increased wing lift due to greater slat and flap deflection and the addition of a boundary layer control system, enlarged stabilators, incorporated AN/APQ-104 radar, an upgraded version of AN/APQ-94. A total of 42 built.
- F-8H – upgraded F-8D with strengthened airframe and landing gear, with AN/APQ-84 radar. A total of 89 rebuilt.
- F-8J – upgraded F-8E, similar to F-8D but with wing modifications and BLC like on F-8E(FN), “wet” pylons for external fuel tanks, J57-P-20A engine, with AN/APQ-124 radar. A total of 136 rebuilt.
- F-8K – upgraded F-8C with Bullpup capability and J57-P-20A engines, with AN/APQ-125 radar. A total of 87 rebuilt.
- F-8L – F-8B upgraded with underwing hardpoints, with AN/APQ-149 radar. A total of 61 rebuilt.
- F-8P – 17 F-8E(FN) of the Aéronavale underwent a significant overhaul at the end of the 1980s to stretch their service life another 10 years. They were retired in 1999.
- F8U-1D (DF-8A) – several retired F-8A modified to controller aircraft for testing of the SSM-N-8 Regulus cruise missile. DF-8A was also modified as drone (F-9 Cougar) control which were used extensively by VC-8, NS Roosevelt Rds, PR; Atlantic Fleet Missile Range.
- DF-8F – retired F-8A modified as controller aircraft for testing of missiles including at the USN facility at China Lake.
- F8U-1KU (QF-8A) – retired F-8A modified into remote-controlled target drones
- YF8U-1P (YRF-8A) – prototypes used in the development of the F8U-1P photo-reconnaissance aircraft – V-392.
- F8U-1P (RF-8A) – unarmed photo-reconnaissance version of F8U-1E, 144 built.
- RF-8G – modernized RF-8As.
- LTV V-100 – revised “low-cost” development based on the earlier F-8 variants, created in 1970 to compete against the F-4E Phantom II, Lockheed CL-1200 and F-5-21 in a tender for U.S. Military Assistance Program (MAP) funding. The unsuccessful design was ultimately only a “paper exercise.”
- XF8U-3 Crusader III (V-401) – new design loosely based on the earlier F-8 variants, created to compete against the F-4 Phantom II; J75-P-5A engine with 29,500 lbf (131 kN) of afterburning thrust, first flight: 2 June 1958, attained Mach 2.39 in test flights, canceled after five aircraft were constructed because the Phantom II won the Navy contract.
France
-
F-8E(FN)
- 151732 (French Navy Side Number 1) – Musee des Avions de Chasse, Beaune.
- 151750 (French Navy Side Number 19) – Musée des Ailes Anciennes, Toulouse.
-
F-8P
- 151733 (French Navy Side Number 3) – Lann Bihoue Airport, Le Meneguen.
- 151735 (French Navy Side Number 4) – Musee Europeen de lAviation de Chasse, Montelimar-Ancone.
- 151738 (French Navy Side Number 7) – Aeronavale Base, Landivisau.
- 151741 (French Navy Side Number 10) – Musee de l air et de l Espace, (The Air and Space Museum), Paris, France.
- 151742 (French Navy Side Number 11) – Musee de l aeronautique navale, Rochefort.
- 151754 (French Navy Side Number 23) – Aeronavale Base, Landivisau.
- 151760 (French Navy Side Number 29) – Aeronavale Base, Landivisau.
- 151767 (French Navy Side Number 36) – Musee des Avions de Chasse, Beaune.
- 151768 (French Navy Side Number 37) – Airport in Cuers.
- 151770 (French Navy Side Number 39) – Aeronavale Base, Landivisau.
Philippines
-
F-8H
- 147056 – Philippine Air Force Aerospace Museum, Villamor Air Base, Manila.
- 147060 – Basa Air Base, Floridablanca, Pampanga.
- 148661 – Clark Air Base, Angeles.
- 148696 – Fort Del Pilar, Baguio City.
United States
-
XF8U-1 (XF-8A)
- 138899 – Museum of Flight in Seattle, Washington.
-
XF8U-2 (XF-8B)
- 140448 – McAuliffe-Shepard Discovery Center in Concord, New Hampshire.
-
F8U-1 (F-8A)
- 141351 – NAS Jacksonville Heritage Park, Naval Air Station Jacksonville, Florida (relocated from former NAS Cecil Field).
- 141353 – Edwards AFB, California.
- 143703 – USS Hornet Museum, former Naval Air Station Alameda, Alameda, California.
- 143755 – Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, California.
- 143806 – Wings of Freedom Aviation Museum, former Naval Air Station Willow Grove, Willow Grove, Pennsylvania.
- 144427 – Pima Air and Space Museum adjacent to Davis-Monthan AFB in Tucson, Arizona.
- 145336 – Planes of Fame at Chino, California.
- 145347 – National Naval Aviation Museum at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
- 145349 – Pueblo Weisbrod Aircraft Museum, Pueblo, Colorado.
- 145397 – Naval Air Engineering Station Lakehurst, Lakehurst, New Jersey.
-
F8U-2 (F-8C)
- 145546 – Edwards AFB, California.
- 146963 – Marine Corps Air Station Beaufort, South Carolina.
- 146973 – Marine Corps Air Station Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii
- 147034 – (nose section only) USS Hornet Museum, former NAS Alameda, Alameda, California.
- 149150 – NAS Oceana Aviation Heritage Park, Naval Air Station Oceana, Virginia.
- BUNO unknown – N.A.D. Park, Bremerton, Washington.
-
F8U-2N (F-8D)
- 148693 – Mid America Air Museum in Liberal, Kansas.
F8U-2NE (F-8E)
- 150920 – Flying Leatherneck Aviation Museum at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, California
-
F8U-1P (RF-8G)
- 144617 – Flying Leatherneck Aviation Museum at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, California
- 144618 – Celebrity Row, Davis-Monthan AFB (North Side), Tucson, Arizona.
- 145607 – Castle Air Museum (formerly Castle AFB), Atwater, California.
- 145608 – (nose section only) Pacific Coast Air Museum, Santa Rosa, California.
- 145609 – National Museum of Naval Aviation, Naval Air Station Pensacola, Pensacola, Florida.
- 145645 – USS Alabama Battleship Memorial Park, Mobile, Alabama.
- 146860 – Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Virginia, adjacent to Dulles International Airport.
- 146858 – in storage at Flying Leatherneck Aviation Museum at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, California
- 146882 – Frontiers of Flight Museum in Dallas, Texas.
- 146898 – Fort Worth Aviation Museum in Fort Worth, Texas.
-
F-8H
- 147909 – NAD Soroptimist Park, Kitsap Lake, Bremerton, Washington, about 1 mile away from Naval Hospital Bremerton. Aircraft is on loan from the National Naval Aviation Museum, Pensacola, Florida.
-
F-8J
- 150904 – Air Zoo in Kalamazoo, Michigan.
-
F8U-2 (F-8K)
- 145550 – USS Intrepid Museum in New York City, New York.
- 146931 – Estrella Warbirds Museum in Paso Robles, California.
- 146939 – Patriots Point Naval & Maritime Museum aboard ex-USS Yorktown (CV-10), Mount Pleasant, South Carolina.
- 146983 – Marine Corps Air Station Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii.
- 146985 – Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum at Space Coast Regional Airport in Titusville, Florida
- 146995 – Pacific Coast Air Museum, adjacent to the Sonoma County Airport in Santa Rosa, California
- 147030 – USS Midway Museum in San Diego, California.
-
F-8L
- 145449 – Naval Air Station Fallon, Fallon, Nevada.