Price: $14.95
- 3 magazines, 3 manuals, & photos
- PDF contains 1,274 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
May 1981
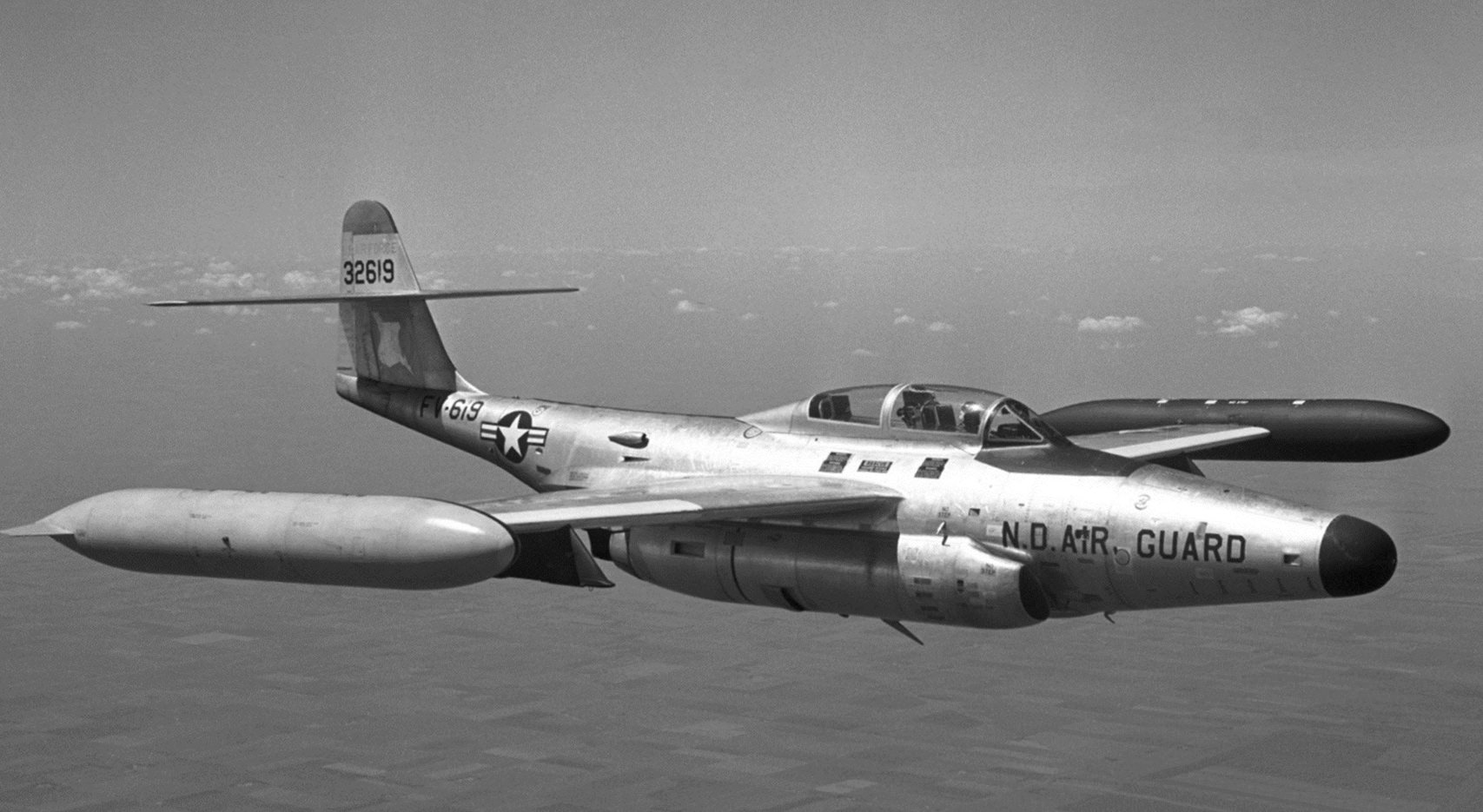
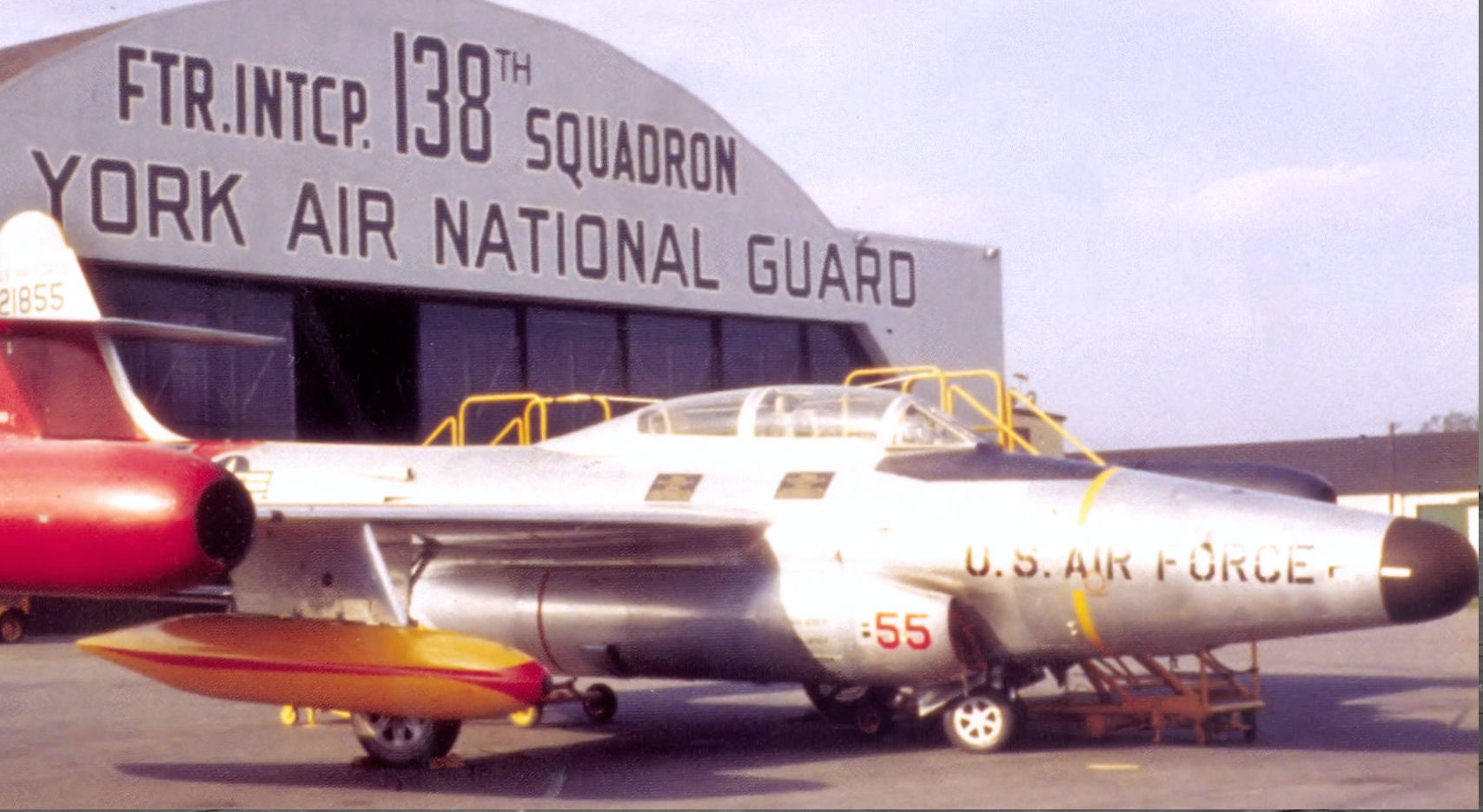
- Northrop’s F-89 Scorpion Long Range Interceptor
July 1998
- Rocket-powered Kamakazes, Japan’s last ditch suicide flying bombs
- XP-56 Black Bullet, Prototype Mustang
- Flying Wing Bombers
- F-89 Scorpion
- SM-62 Snark
October 2006
- F-89 Scorpion – Potent subsonic sting
- Aircraft cutaways – An inside look
- Gulfstreams – From twin-turboprop to globe-spanning luxury jet
Manuals & Photos
- F-89D Flight Handbook
- F-89 B&C Flight Manual
- F-89H Flight Manual
- 98 F-89 Scorpion photos
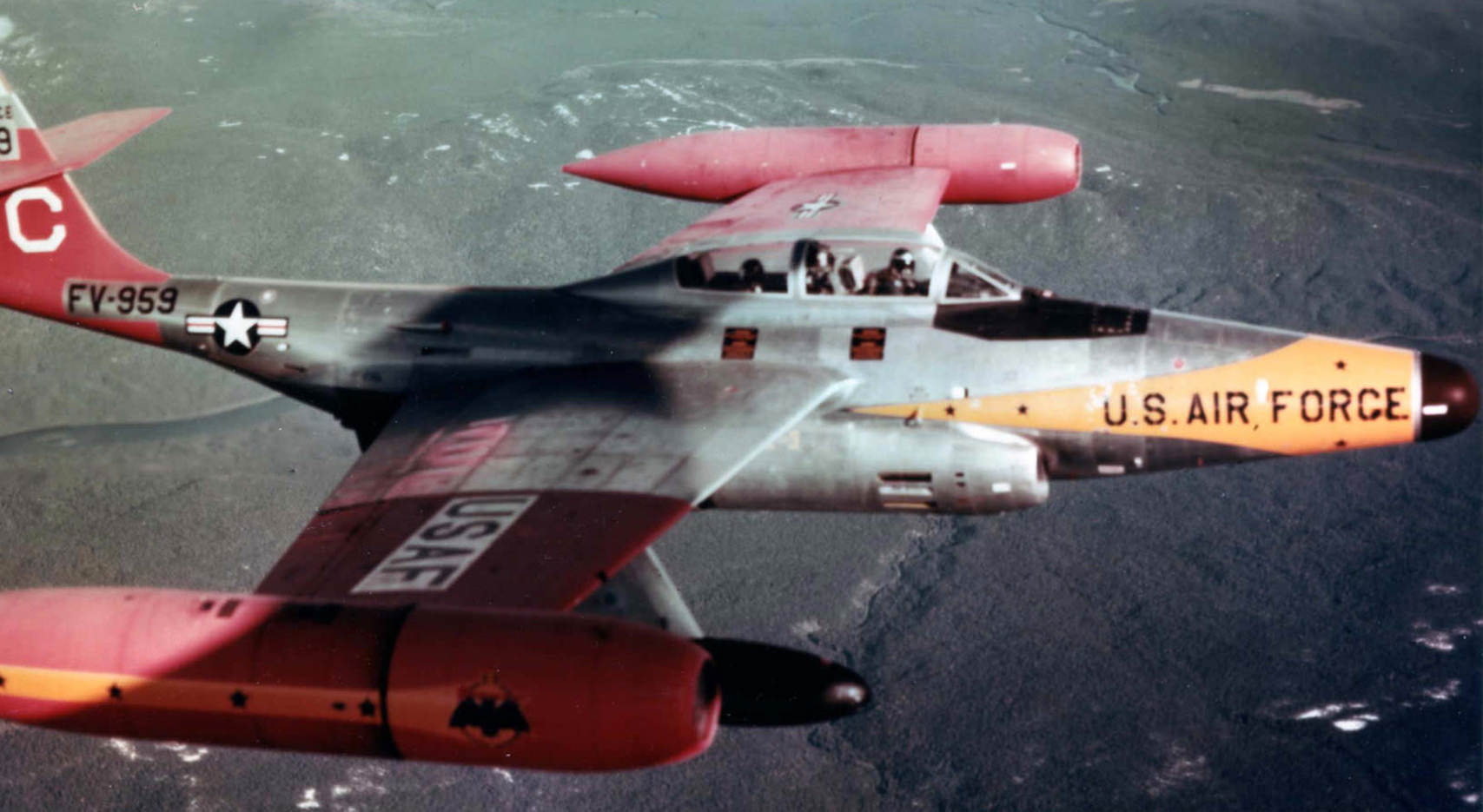
Northrop F-89 Scorpion
F-89D Specs
Variants
On Display
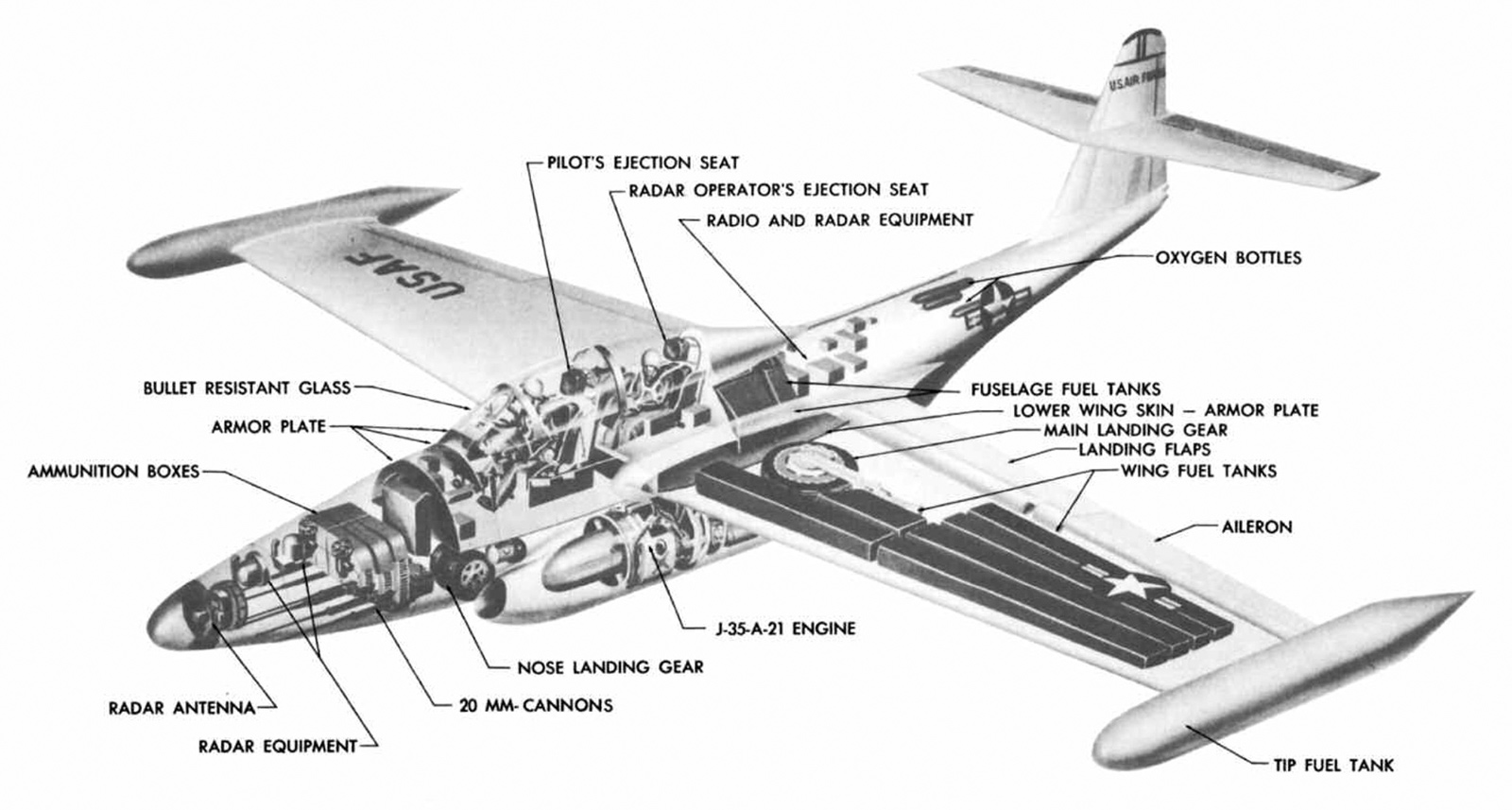
Cutaway
Videos
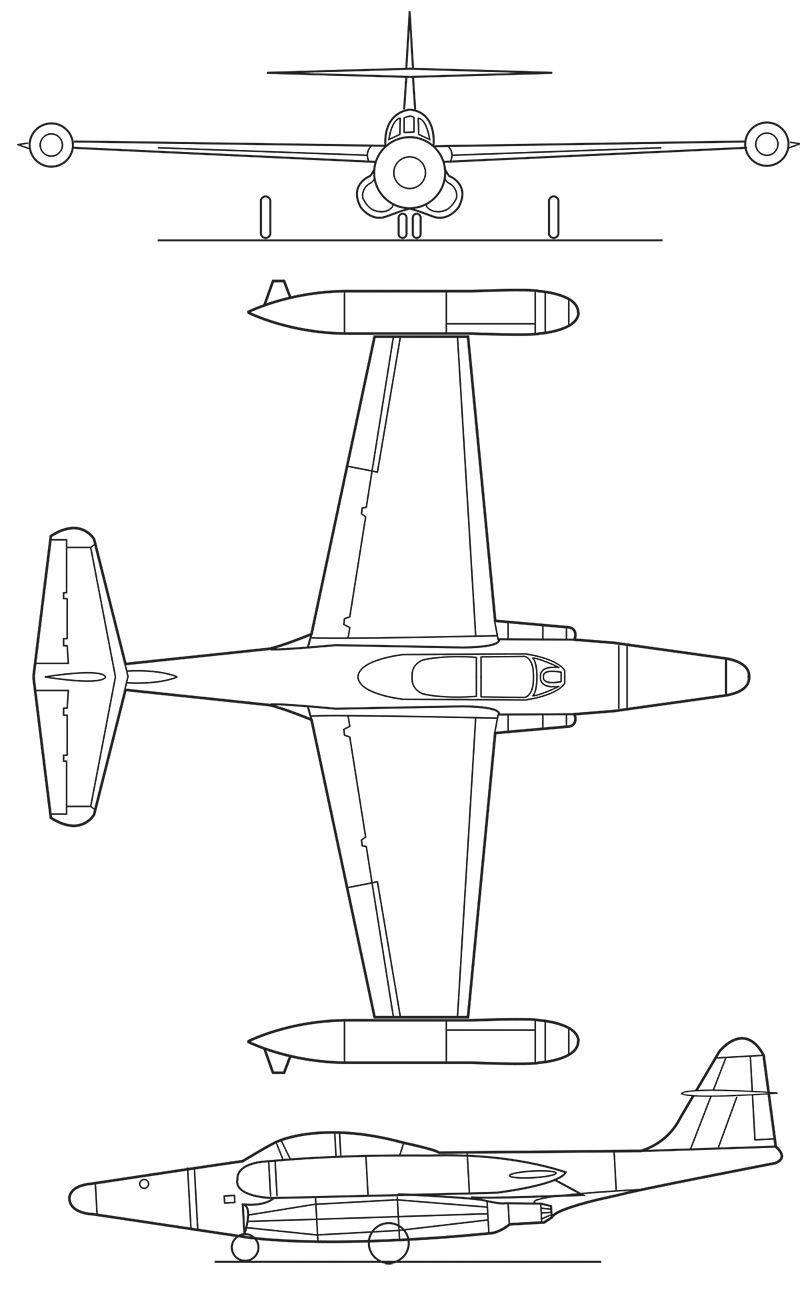
General Characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 53 ft 9.5 in (16.396 m)
- Wingspan: 59 ft 8.5 in (18.199 m)
- Height: 17 ft 6 in (5.33 m)
- Wing area: 606 sq ft (56.3 m2)
- Aspect ratio: 5.88
- Airfoil: NACA 0009-64
- Empty weight: 25,194 lb (11,428 kg)
- Gross weight: 37,190 lb (16,869 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 42,241 lb (19,160 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Allison J35-A-35 afterburning turbojet engines, 5,440 lbf (24.2 kN) thrust each dry, 7,200 lbf (32 kN) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 645 mph (1,038 km/h, 560 kn) at 10,600 ft (3,231 m)
- Ferry range: 1,366 mi (2,198 km, 1,187 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 49,200 ft (15,000 m)
- Rate of climb: 7,440 ft/min (37.8 m/s)
Armament
- F-89A
- 6 × 20 mm (0.79 in) T-31 cannon with 200 rpg
- 16 × 5 in (130 mm) aerial rockets
- F-89D
- 2 × pods of 52 2.75 in (70 mm) “Mighty Mouse” Mk 4/Mk 40 Folding-Fin Aerial Rockets, for a total of 104.
- F-89H
- 6 × Hughes GAR-1/GAR-2 Falcon missiles
- 42 “Mighty Mouse” Mk 4/Mk 40 Folding-Fin Aerial Rockets
- F-89J
- 2 × MB-1 (later AIR-2) Genie nuclear armed rocket
- 4 × Hughes GAR-1/GAR-2 Falcon missiles
Avionics
- F-89A
- Hughes E-1 fire-control system
- AN/APG-33 radar
- F-89D
- Hughes E-6 fire-control system
- AN/APG-40 radar
- AN/APA-84 computer
- F-89H
- Hughes E-9 fire-control system
- XF-89
- First prototype, powered by two 4,000 lbf (17.79 kN) Allison J35-A-9 engines.
- XF-89A
- Second prototype. Fitted with more powerful 5,100 lbf (22.69 kN) dry (6,800 lbf (30.25 kN) wet) Allison J35-A-21A engines and revised, pointed nose with cannon armament.
- F-89A
- First production version, eight built. Fitted with revised tailplane and six cannon armament.
- DF-89A
- F-89As converted into drone control aircraft.
- F-89B
- Second production version with upgraded avionics. 40 built.
- DF-89B
- F-89Bs converted into drone control aircraft.
- F-89C
- Third production version with more powerful 5,600 lbf (24.91 kN) dry (7,400 lbf (32.92 kN) wet) Allison J35-A-33 engines. 164 built.
- YF-89D
- Conversion of one F-89B to test new avionics and armament of F-89D.
- F-89D
- Main production version which saw deletion of the six 20-millimeter cannon in favor of 104 rockets in wing pods, installation of new Hughes E-6 fire-control system, AN/APG-40 radar and the AN/APA-84 computer. This new system allowed the use of a lead-collision attack in place of the previous lead-pursuit-curve technique. A total of 682 built.
- YF-89E
- One-off prototype to test the 7,000 lbf (31.14 kN) dry (9,500 lbf (42.26 kN) wet) Allison YJ71-A-3 engine, converted from an F-89C.
- F-89F
- Proposed version with revised fuselage and wings, powered by 10,200 lbf (45.37 kN) dry (14,500 lbf (64.50 kN) wet) Allison J71-A-7 engines, never built.
- F-89G
- Proposed version equipped with Hughes MA-1 fire control and GAR-1/GAR-2 Falcon air-to-air missiles, never built.
- YF-89H
- Modified F-89D to test features of F-89H. Three converted.
- F-89H
- Version with E-9 fire control system, six Hughes GAR-1/GAR-2 Falcon missiles and 42 Folding Fin Aircraft Rockets (FFAR). 156 built.
- F-89J
- Conversion of F-89D with underwing hardpoints for two MB-1 (later AIR-2) Genie nuclear armed rocket and four Falcon missiles, and carrying either the standard F-89D rocket/fuel pod or pure fuel tanks. A total of 350 were converted from F-89Ds.
- F-89B
- 49-2457 – Lakeview Park, Nampa, Idaho.
- F-89D
- 52-1862 – Elmendorf AFB, Anchorage, Alaska. Marked as 53-2453 (actual 53-2453 is a F-89J below)
- 53-2463 – Museum of Aviation, Robins Air Force Base, Georgia.
- 53-2494 – home base of the 158th Fighter Wing, Vermont Air National Guard, Burlington Air National Guard Base, Vermont.
- 53-2519 – Planes of Fame Museum, Chino, California.
- 53-2536 – EAA AirVenture Museum, Oshkosh, Wisconsin.
- 53-2610 – Air Force Armament Museum, Eglin Air Force Base, Florida.
- 53-2646 – Friendship Park, Smithfield, Ohio.
- 53-2674 – Pima Air & Space Museum (adjacent to Davis-Monthan Air Force Base), Tucson, Arizona.
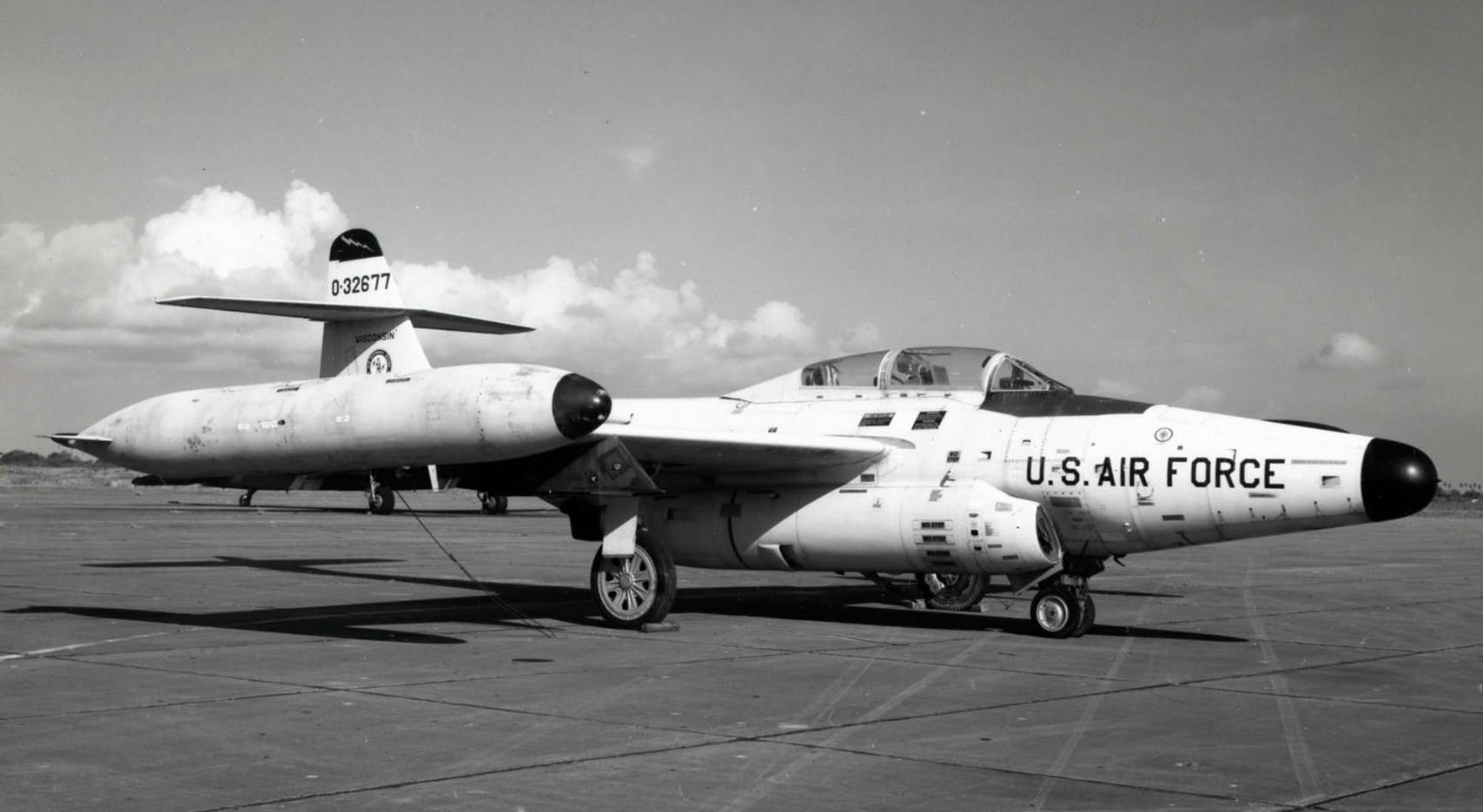
- 53-2677 – Minnesota Air National Guard Museum, Minneapolis, Minnesota.
- F-89H
- 54-0298 – Dyess Linear Air Park, Dyess Air Force Base, Texas.
- 54-0322 – Hill Aerospace Museum, Hill Air Force Base, Utah.
- F-89J
- 52-1856 – Bangor International Airport / Bangor Air National Guard Base (former Dow AFB), Maine.
- 52-1896 – New England Air Museum, Windsor Locks, Connecticut.
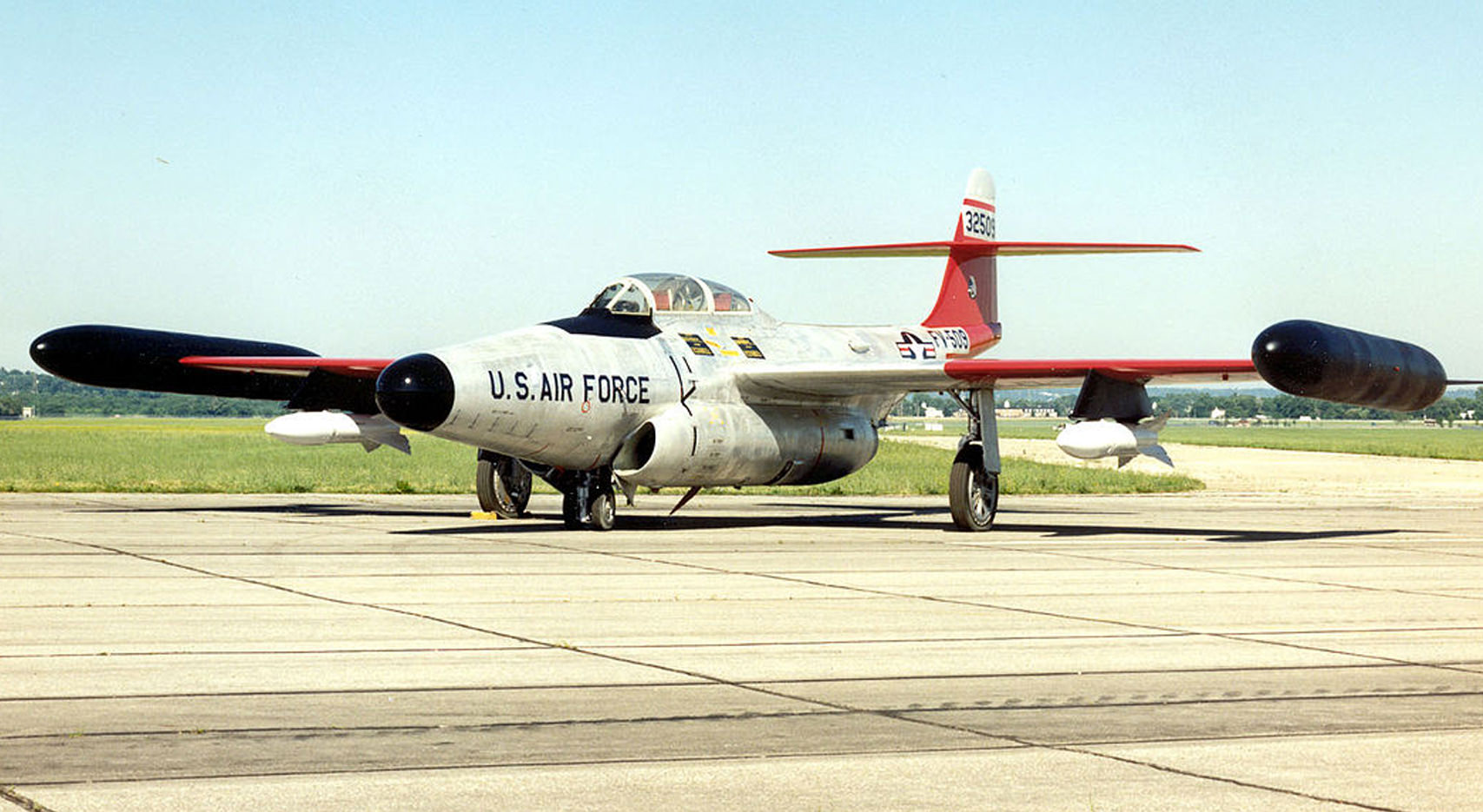
- 52-1911 (painted as 53-2509) – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio. This aircraft was the last F-89 remaining in service when it was transferred to the Museum from the Maine Air National Guard in July 1969.
- 52-1927 – Castle Air Museum (former Castle AFB), Atwater, California.
- 52-1941 – Peterson Air and Space Museum, Peterson Air Force Base, Colorado.
- 52-1949 – March Field Air Museum, March Air Reserve Base (former March AFB), Riverside, California.
- 52-2129 – Air Power Park and Museum (near Langley Air Force Base), Hampton, Virginia.
- 53-2547 – 120th Fighter Wing of the Montana Air National Guard at Great Falls Air National Guard Base, Great Falls International Airport, Montana. It is the only F-89 to have ever fired a Genie rocket with a live nuclear warhead, having done so as part of Operation Plumbob.
- 53-2453 – Heritage Flight Museum, Bellingham, Washington. (note: see 52-1862 above, falsely marked as 53-2453)
- 53-2604 – 119th Wing of the North Dakota Air National Guard, Fargo Air National Guard Base / Hector Field, Fargo, North Dakota.