Price: $12.95
- 4 magazines, 2 manuals, 1 declassified CIA report & photos
- PDF contains 850 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
June 1983
- U-2, Kelly Johnson’s High Flying Ghost
- Exclusive U-2 Pilot Interviews
- Mysterious X-19, Curtiss-Wright’s Last Airplane
July 1983
- Great U-2 Flights, Francis Gary Powers
- Enter the TR-1
- Underrated Polish Air Force of 1939
August 2005
- 50th anniversary of the U-2 Dragon Lady
- XB-70 Rollout and First Flight
- Aviation Advertising
September 2005
- 50th anniversary of the U-2
- Paul Mantz & Frank Tallman, Aviation’s Movie Legends
- F-100 Super Sabre Factory Fresh
- F-105 Color Portfolio
Manuals & Photos
- U2 Flight Handbook 1959
- U2 Flight Manual 1968
- The CIA and Overhead Reconnaissance: U-2 & Project OXCART 1954-1974 (Declassified)
- Over 250 Lockheed U-2 photos
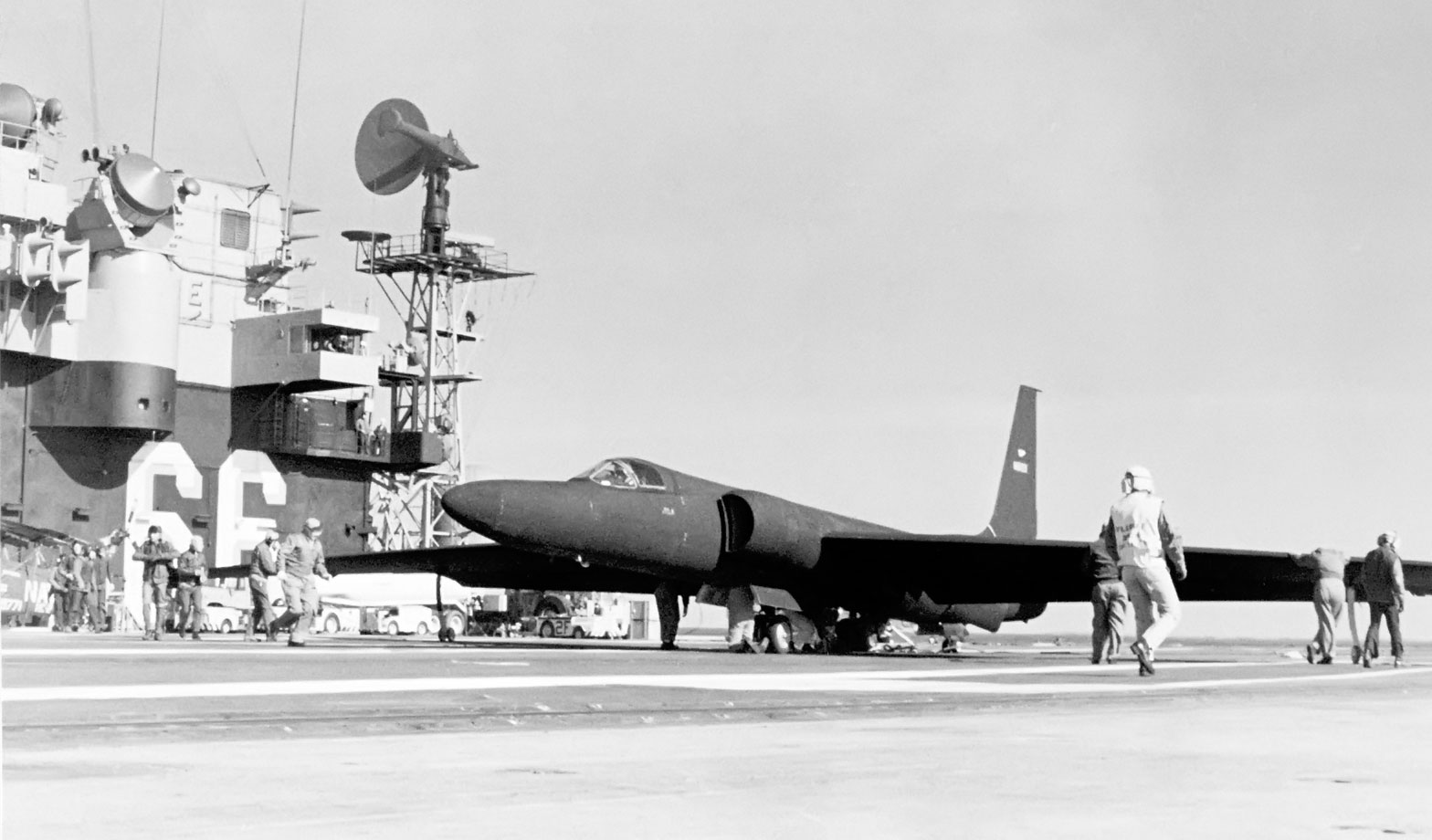
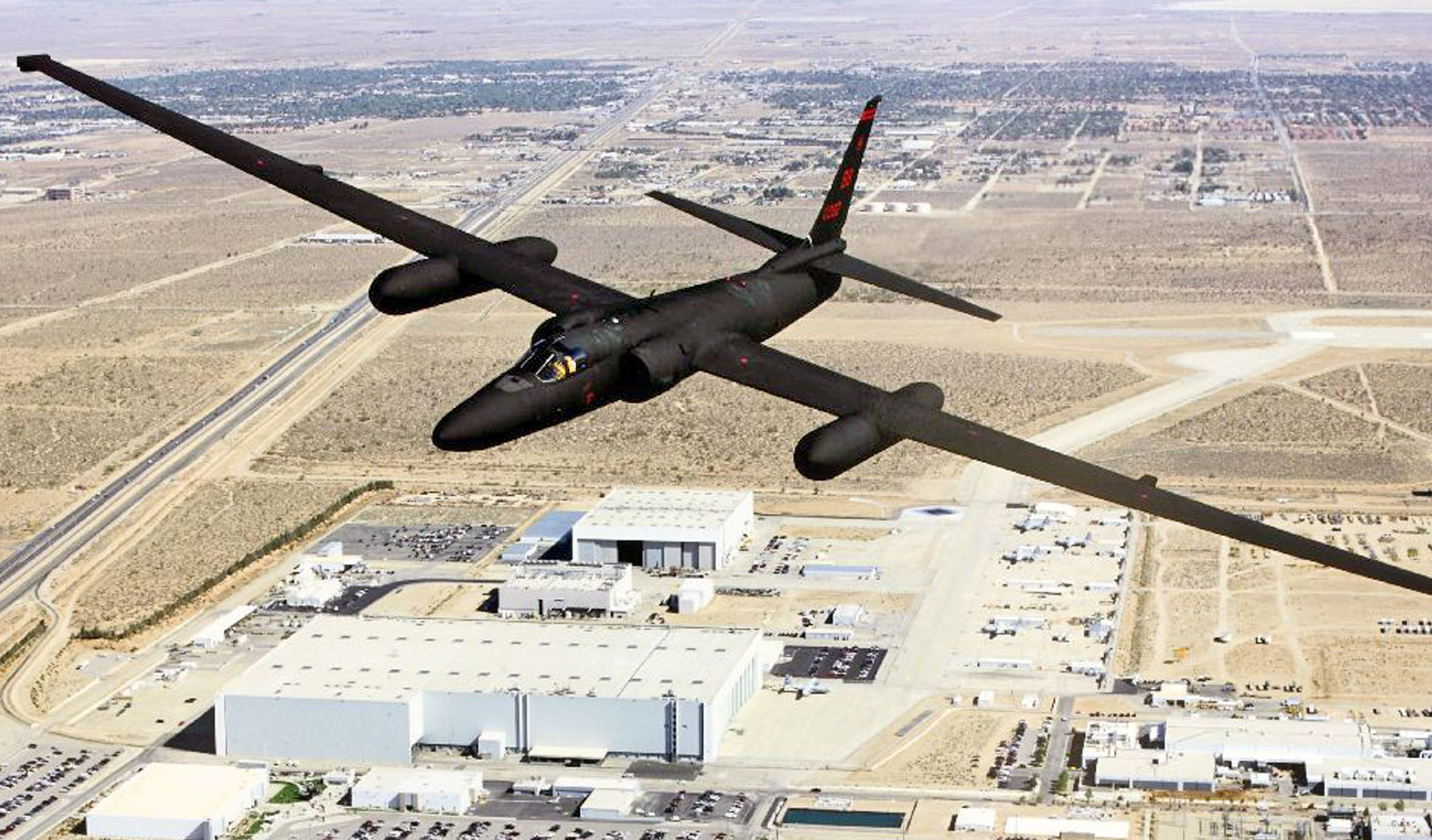
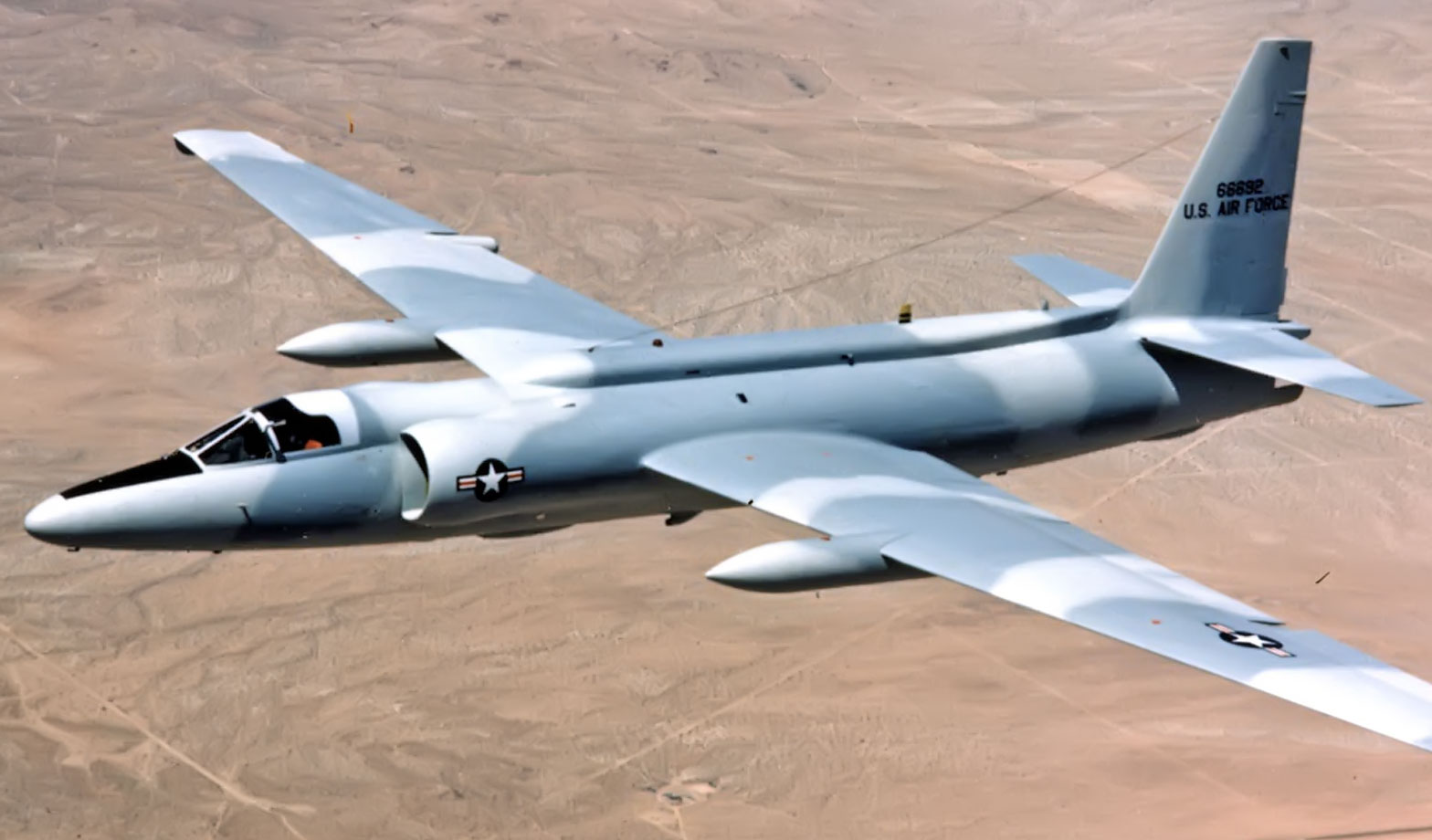
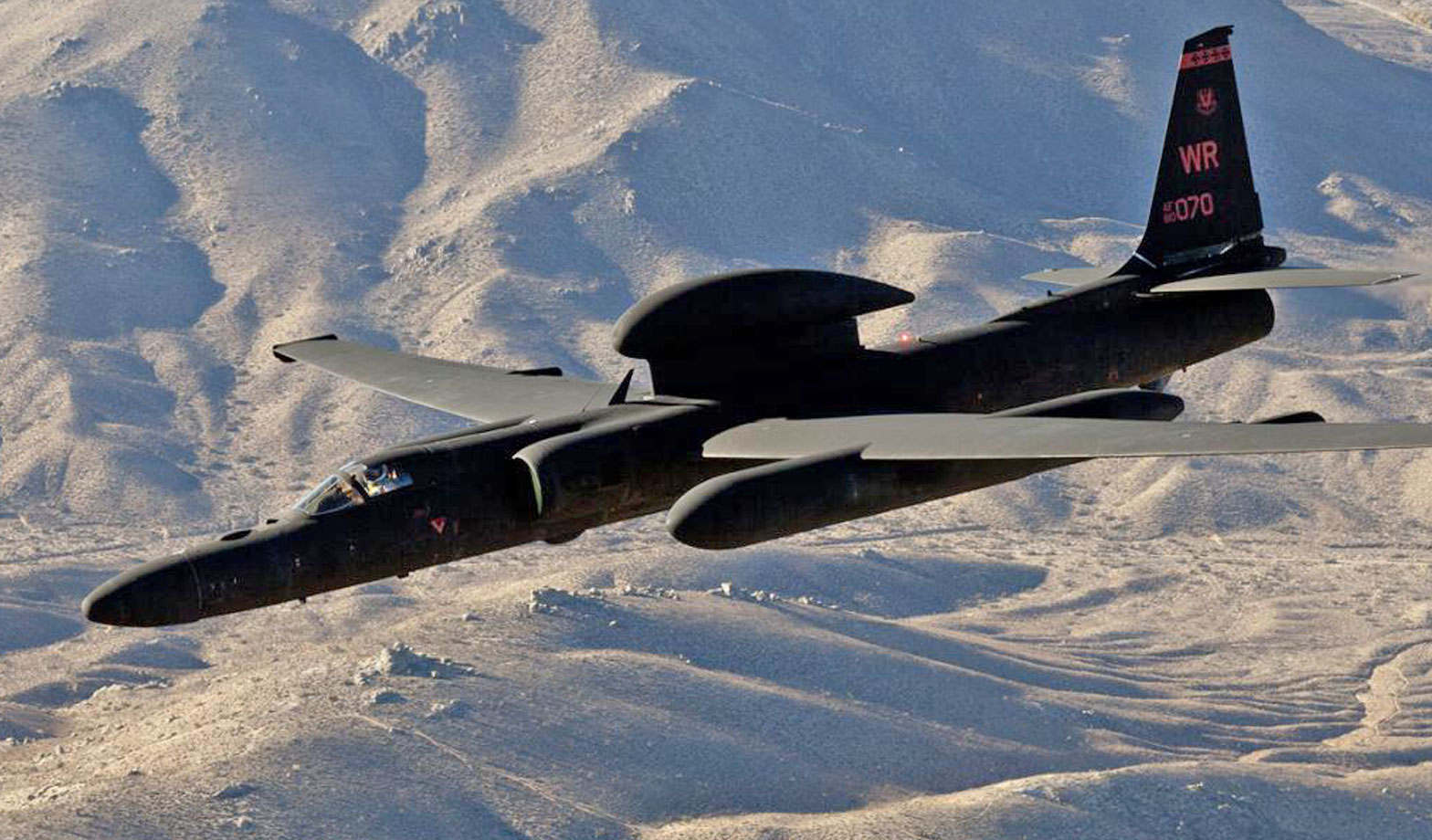
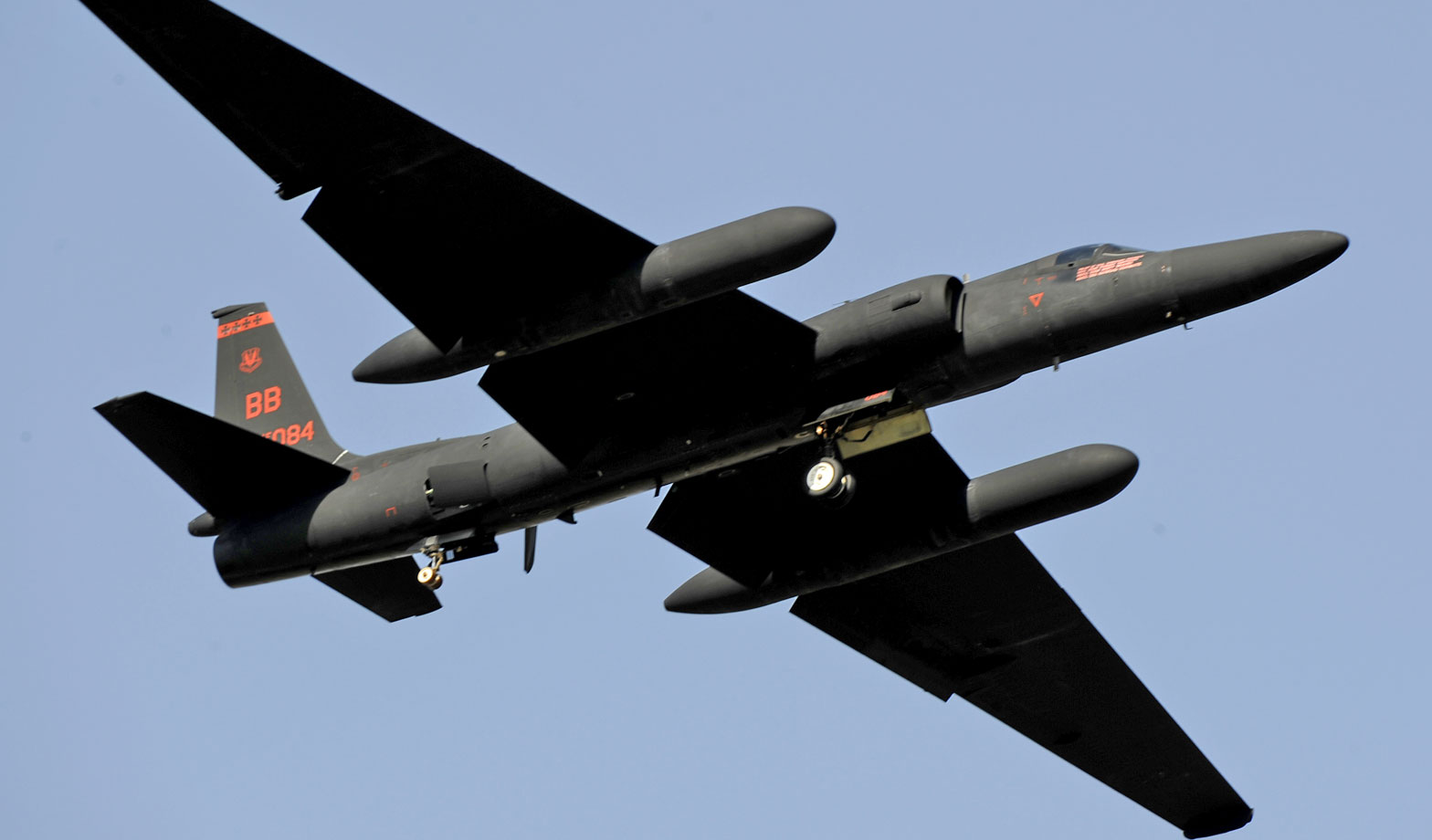
Lockheed U-2 Dragon Lady
U-2S Specifications
Variants
On Display
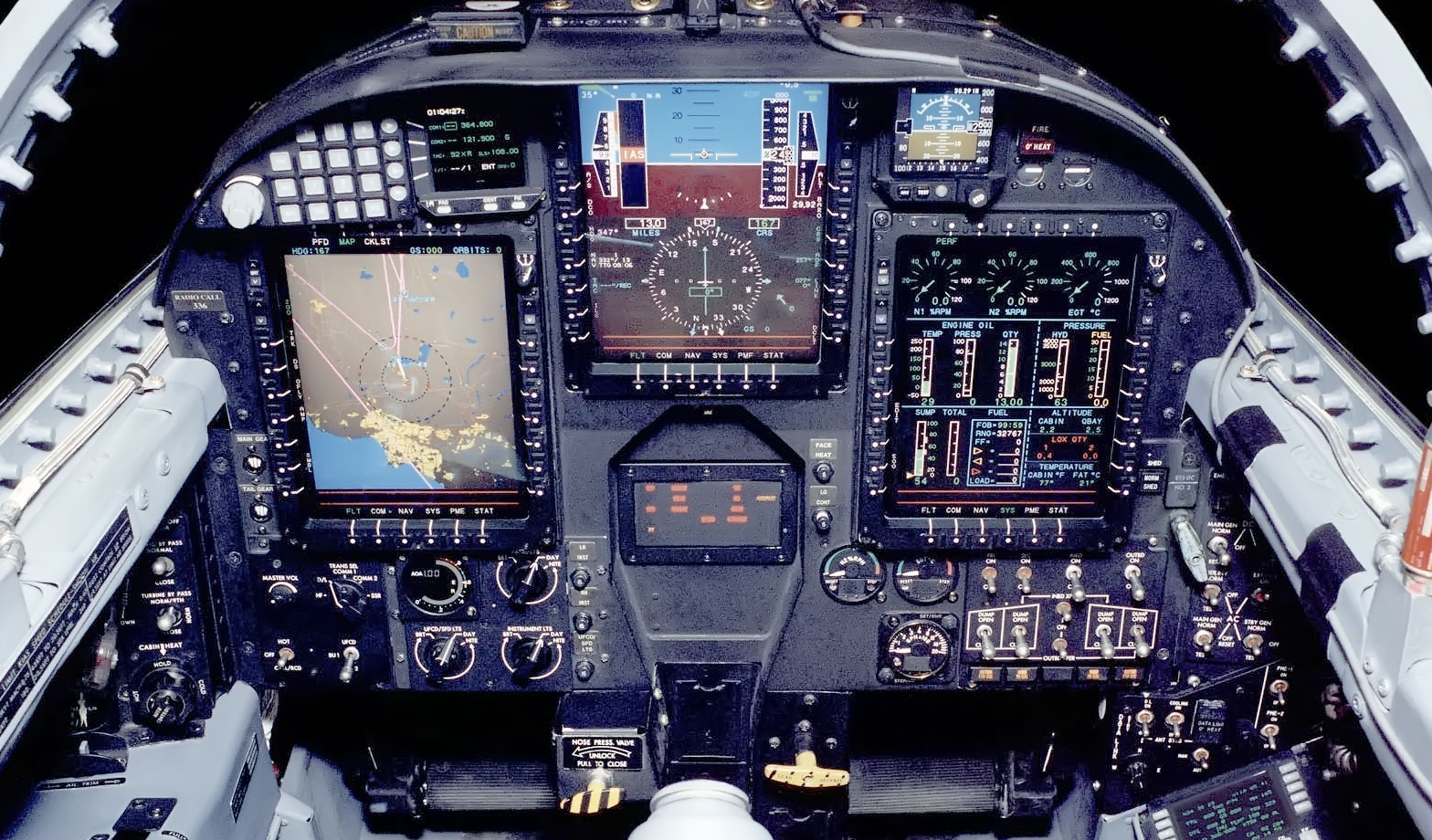
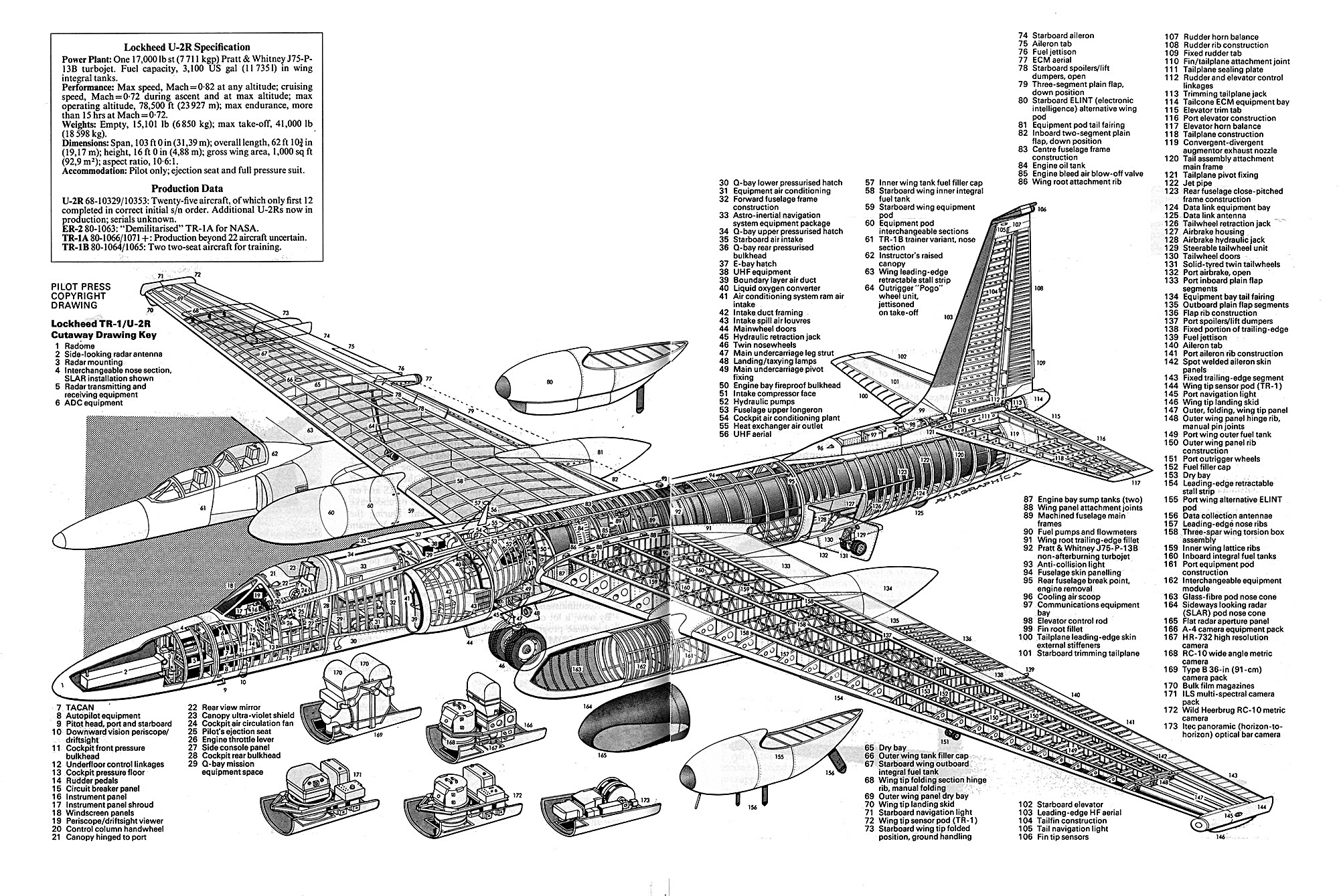
Cutaway
General Characteristics
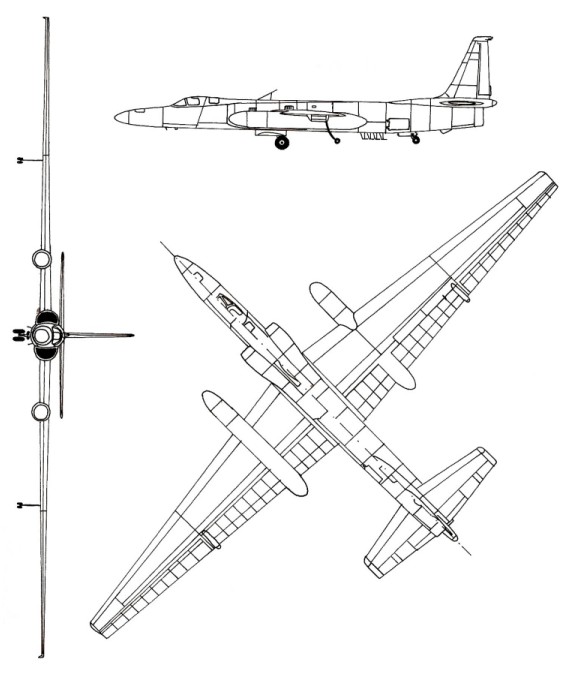
- Crew: One
- Length: 63 ft (19.2 m)
- Wingspan: 103 ft (31.4 m)
- Height: 16 ft (4.88 m)
- Wing area: 1,000 ft² (92.9 m²)
- Aspect ratio: 10.6
- Empty weight: 14,300 lb (6,760 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 40,000 lb (18,100 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × General Electric F118-101 turbofan, 19,000 lbf (85 kN)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 434 knots (Mach 0.67, 500 mph, 805 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 373 knots (Mach 0.56, 429 mph, 690 km/h)
- Range: 5,566 nmi (6,405 mi, 10,300 km)
- Service ceiling: 70,000+ ft (21,300+ m)
- Flight endurance: 12 hours
- U-2A – Initial production, single-seat; J57-P-37A engine; 48 built
- U-2B – Two-seat trainer; J57-P-31 engine; five built
- U-2C – Enhanced single-seat model with J75-P-13 engine and modified engine intakes
- U-2D – Enhanced two-seat trainer
- U-2CT – Enhanced two-seat trainer rebuilt from U-2D airframes with relocation of the seats; six known converted
- U-2E – Aerial refueling capable, J57-powered
- U-2F – Aerial refueling capable, J75-powered
- U-2G – A-models modified with reinforced landing gear, added arresting hook, and lift dump spoilers on the wings for U.S. Navy carrier operations; three converted
- U-2H – Aircraft carrier capable, aerial refueling capable
- U-2R – Re-designed enlarged airframes with underwing pods and increased fuel capacity; 14 built.
- U-2RT – Enhanced two-seat R-model trainer; one built.
- U-2EPX – Proposed U.S. Navy maritime surveillance R-model; two built
- TR-1A – A third production batch of U-2R aircraft built for high-altitude tactical reconnaissance missions with side-looking radar, new avionics, and improved ECM equipment; 33 built. Re-designated U-2S after the fall of the Soviet Union.
- TR-1B – Two TR-1A airframes completed as two-seat conversion trainers
- TU-2S – New redesignated TR-1B two-seat trainer with improved engine; five converted
- ER-2 – Two TR-1A airframes, AF Ser. No. 80-1063, and Ser. No. 80-1097, are modified as an Earth resources research aircraft, moved from USAF to NASA and operated by the NASA High-Altitude Missions Branch, Ames Research Center. NASA flies Ser. No. 80-1097 as N609NA and Ser. No. 80-1063 as N806NA
- U-2S – Redesignation of the TR-1A / U-2R; updated with a General Electric F118 engine, improved sensors, and addition of a GPS receiver; 31 converted
- WU-2 – Atmospheric/weather research WU-model
China
- U-2C
- 56-6691 – wreckage is on display at the Military Museum of the Chinese People’s Revolution, Beijing. It has been re-assembled and is on display in the aircraft exhibit hall. This airframe, flown by a pilot of the Republic of China Air Force, which was shot down on 10 January 1965, southwest of Beijing by a S-75 Dvina missile.
Cuba
- U-2F
- 56-6676 – wreckage is on display at three museums in Cuba. It was flown by Major Rudolf Anderson, USAF, and was shot down during the Cuban Missile Crisis on 27 October 1962 by a Soviet-supplied S-75 Dvina (NATO designation SA-2 Guideline) surface-to-air missile near Banes, Cuba. One of the engine intakes is at the Museo Girón at Girón village, in the province of Matanzas, at the entrance to Bahia de Cochinos, or Bay of Pigs. The engine and portion of the tail assembly from the U-2 is at the Museum of the Revolution in Havana. The right wing, a portion of the tail assembly, and front landing gear are at the Fortaleza de San Carlos de la Cabaña, or La Cabaña, Havana. The two latter groups of parts were previously displayed at the Museo del Aire, Havana.
Norway
- U-2C
- 56-6953 – Norwegian Aviation Museum, Bodø.
Russia
- U-2C
- 56-6693 – wreckage is on display at the Moscow Military Museum. It was flown by Francis Gary Powers and was shot down on 1 May 1960 near Sverdlovsk (now Ekaterinburg).
United Kingdom
- U-2CT
- 56-6692 – Imperial War Museum Duxford.
United States
- U-2A
- 56-6722 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio.
- U-2C
- 56-6680 – National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC.
- 56-6701 – Strategic Air and Space Museum, near Offutt AFB in Ashland, Nebraska.
- 56-6707 – Laughlin AFB, Texas.
- 56-6716 – Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona.
- U-2D
- 56-6682 – Museum of Aviation, Robins AFB, Georgia.
- 56-6714 – Beale AFB, California.
- 56-6721 – Production Flight Test Installation Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California.
- ER-2
- N806NA – NASA Museum, Moffett Field, California.