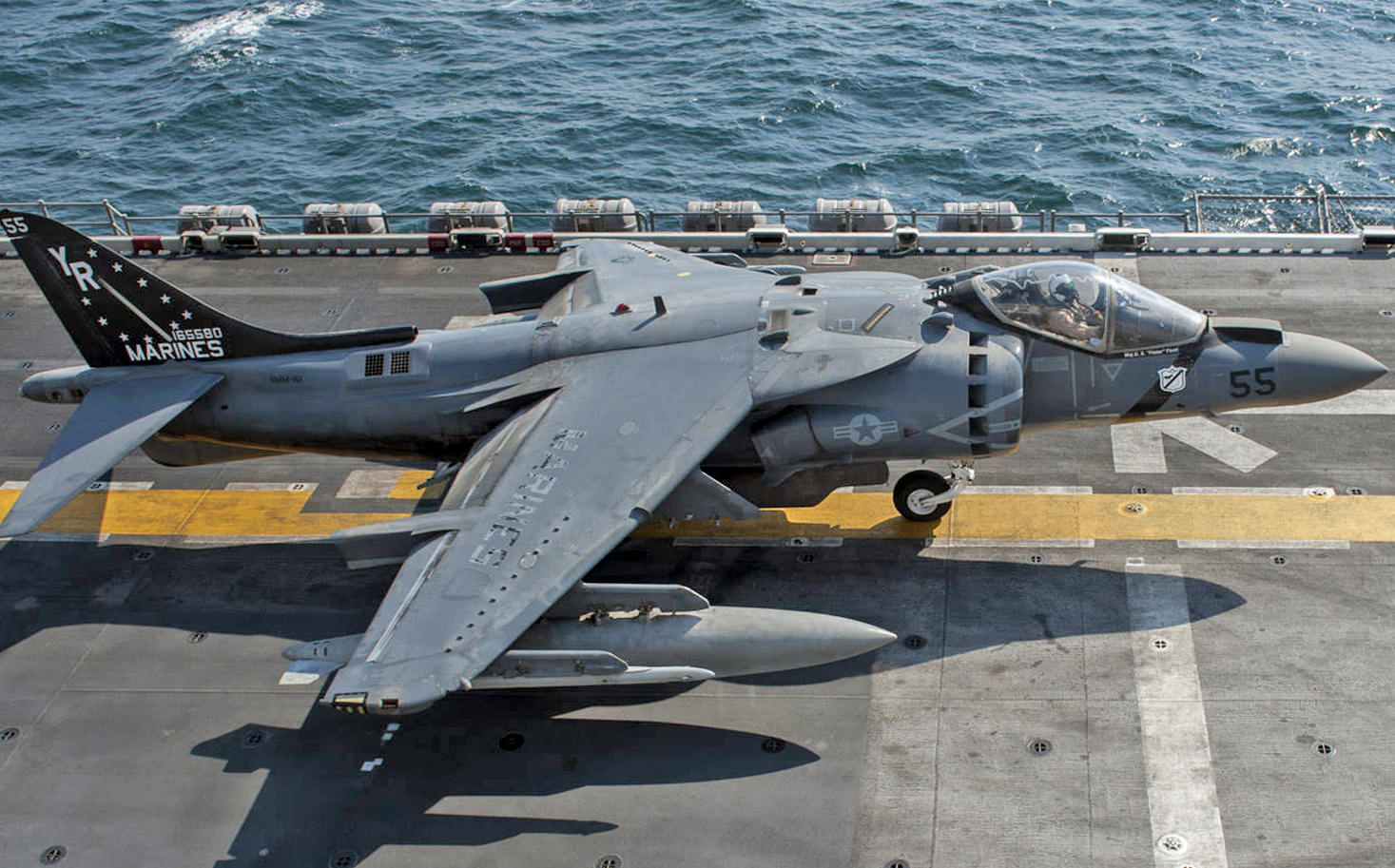
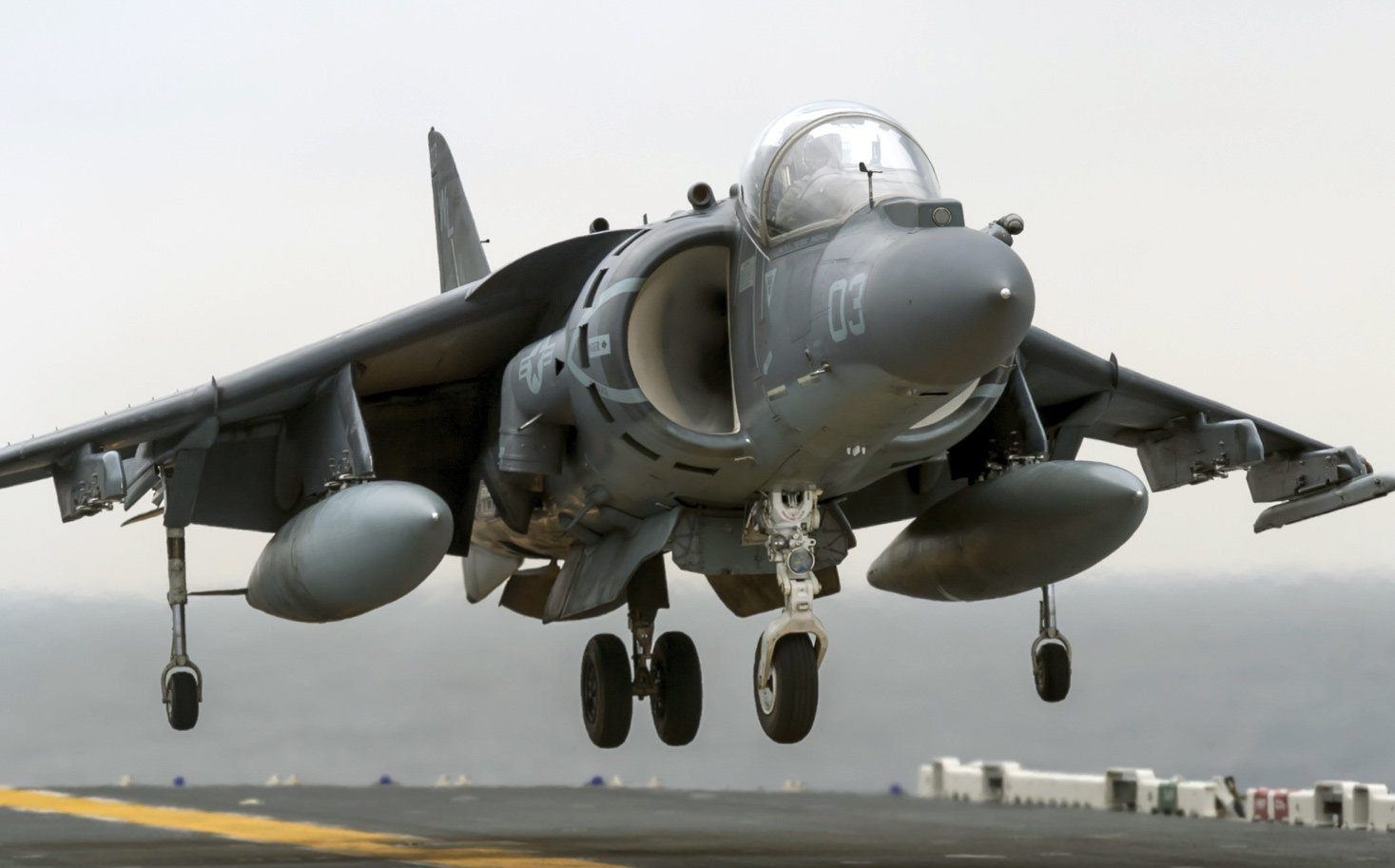
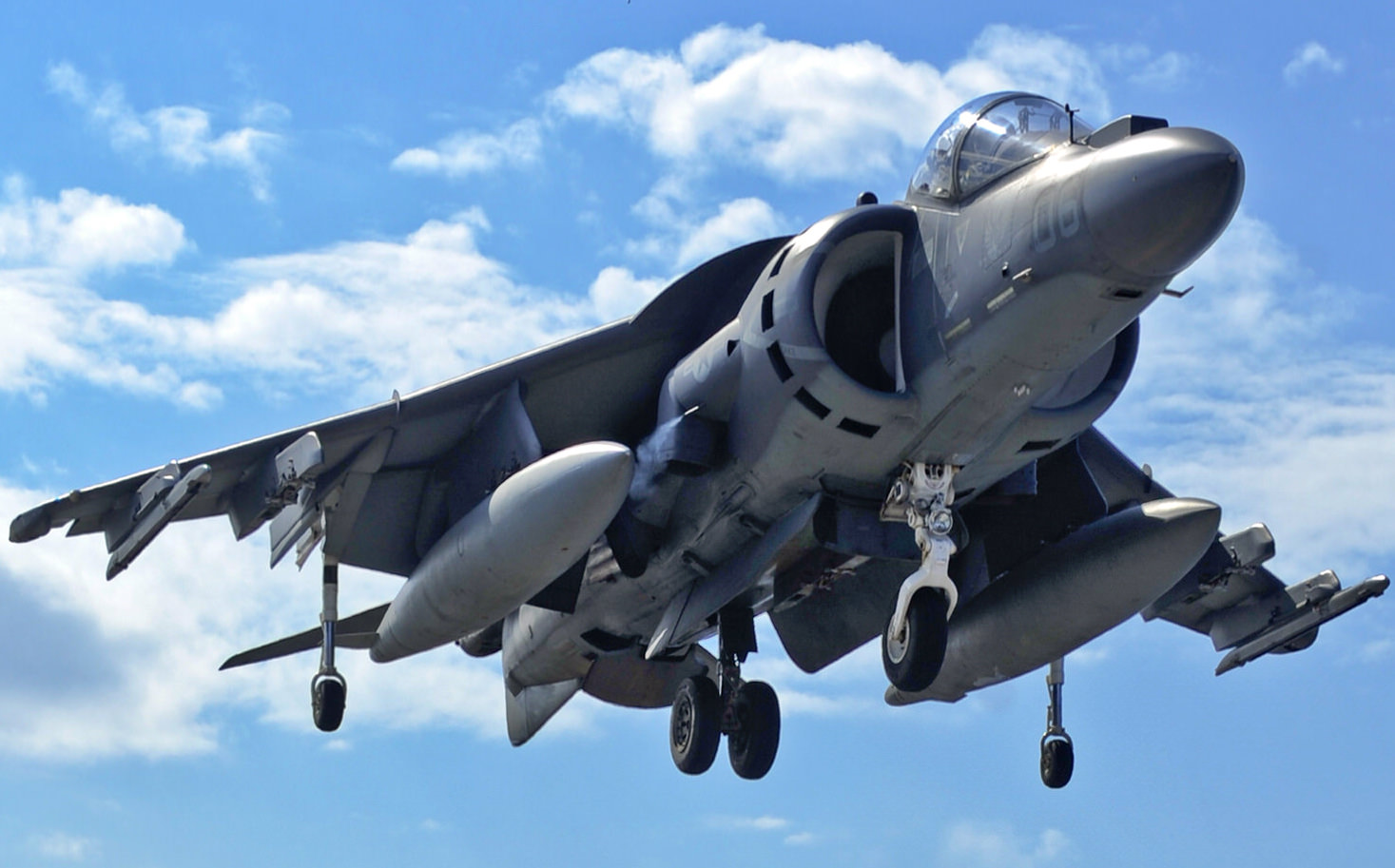
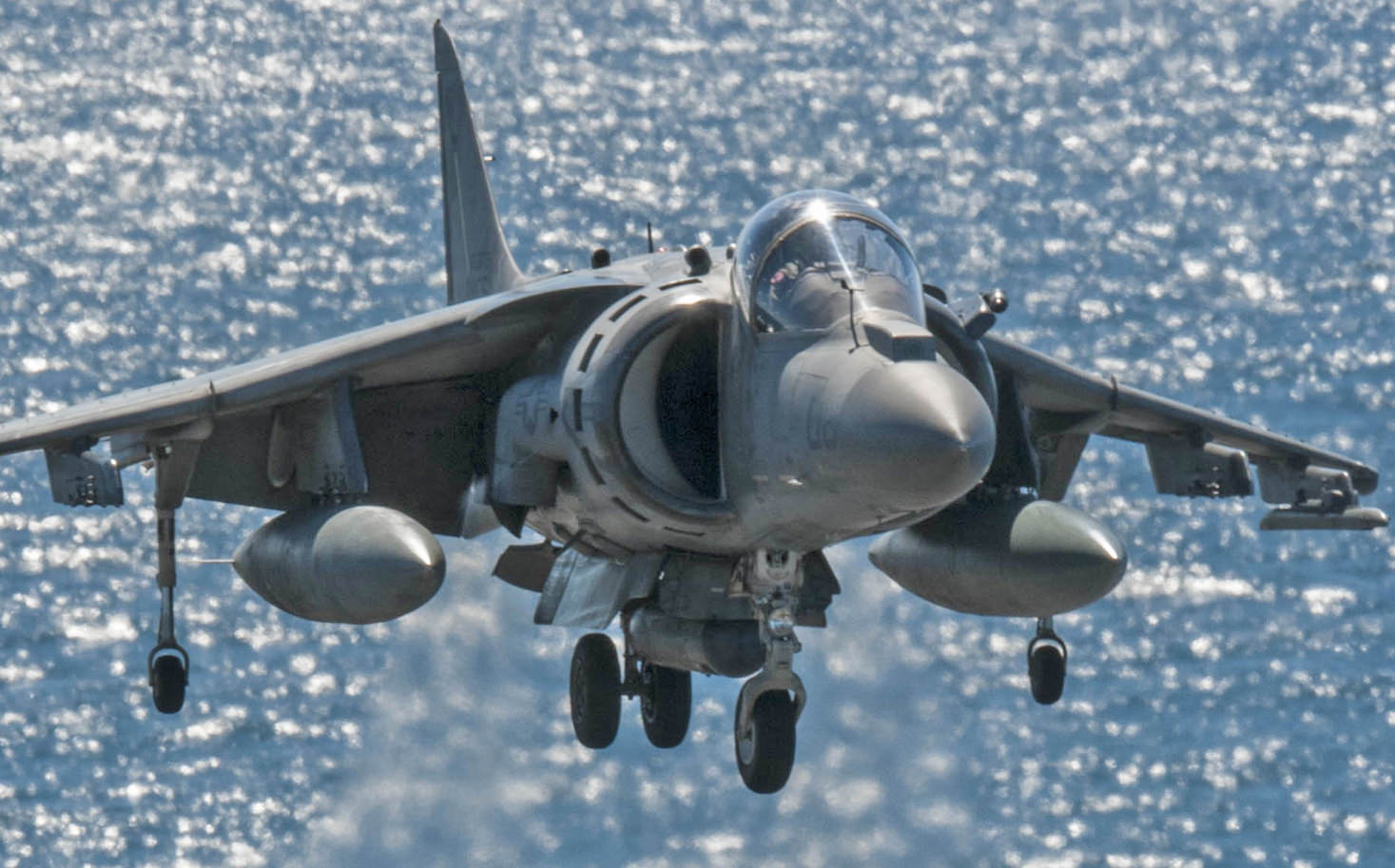
Price: $34.95
- 3 magazines, 14 manuals, & photos
- PDF contains 5,651 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
January 1985
- McDonnell F-85 “Goblin” – Fighter on a Trapeze
- F-14 to F-20, Handicapping the Best of the West
- Today’s Combat Fighters, Rules of the Dogfight
- Hollywood’s Wartime Flying Films
April 1986
- 21st Century Carriers, Aircraft, and Strategy
- USS Constellation, Super Carrier at Sea!
July 2004
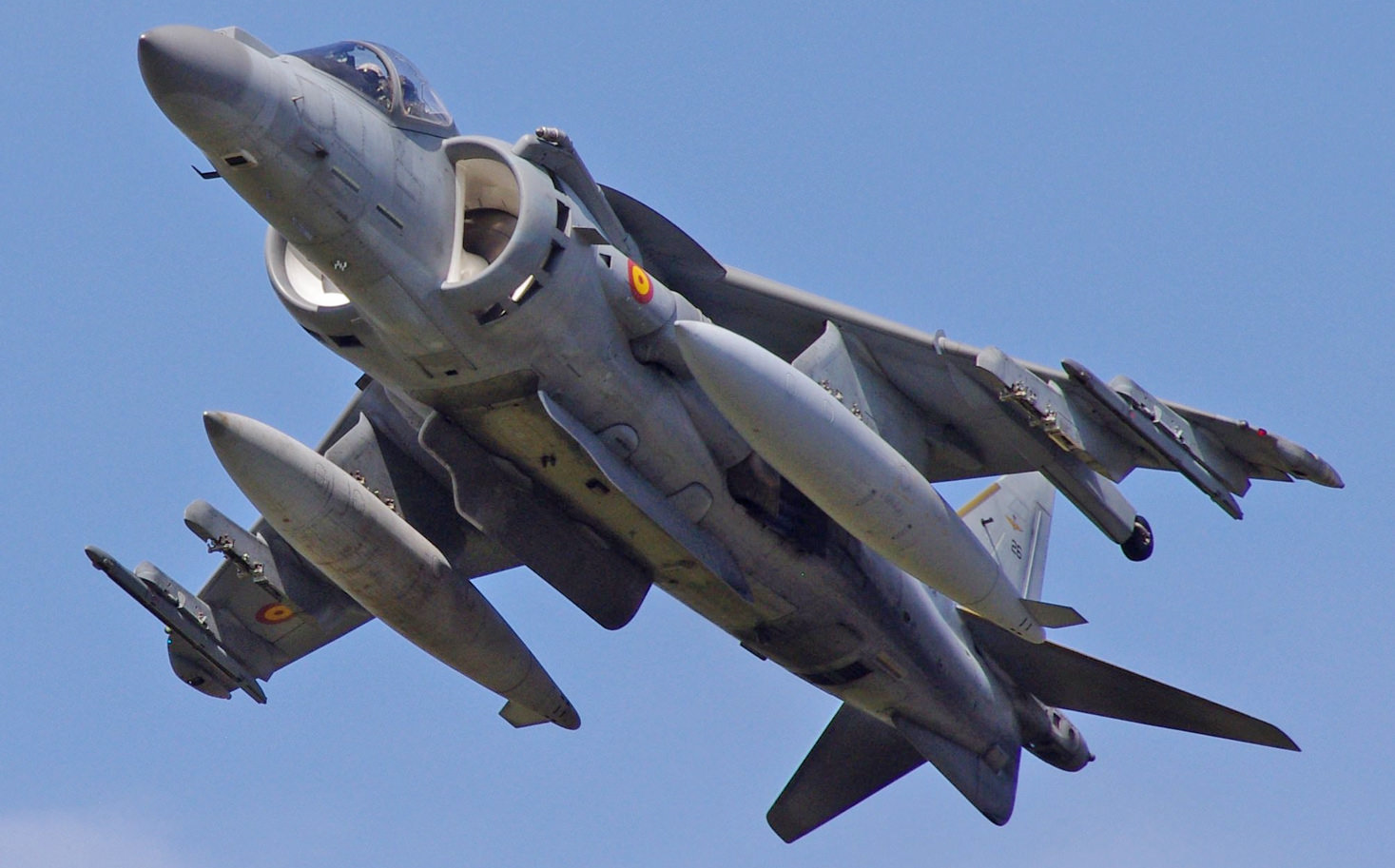
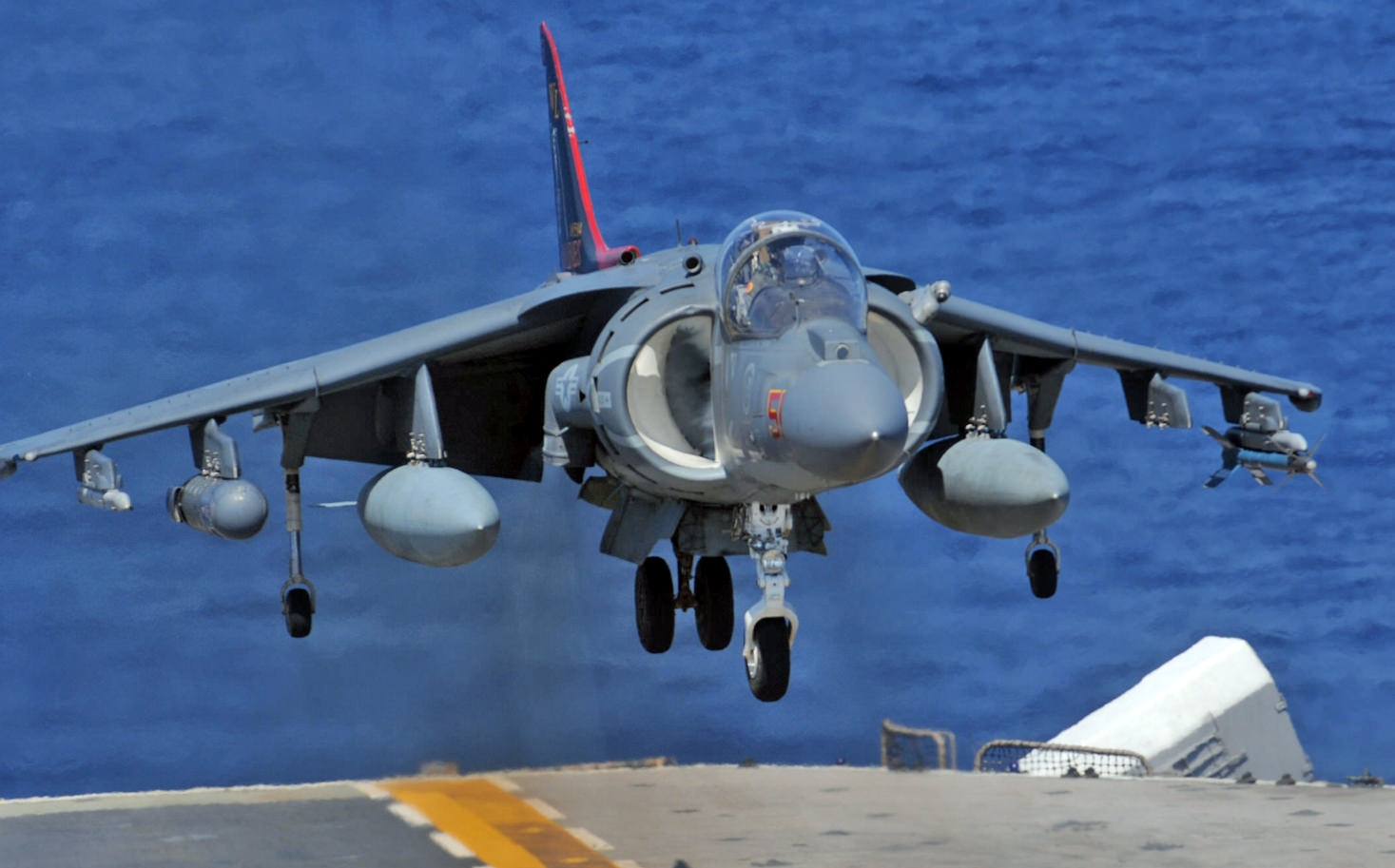
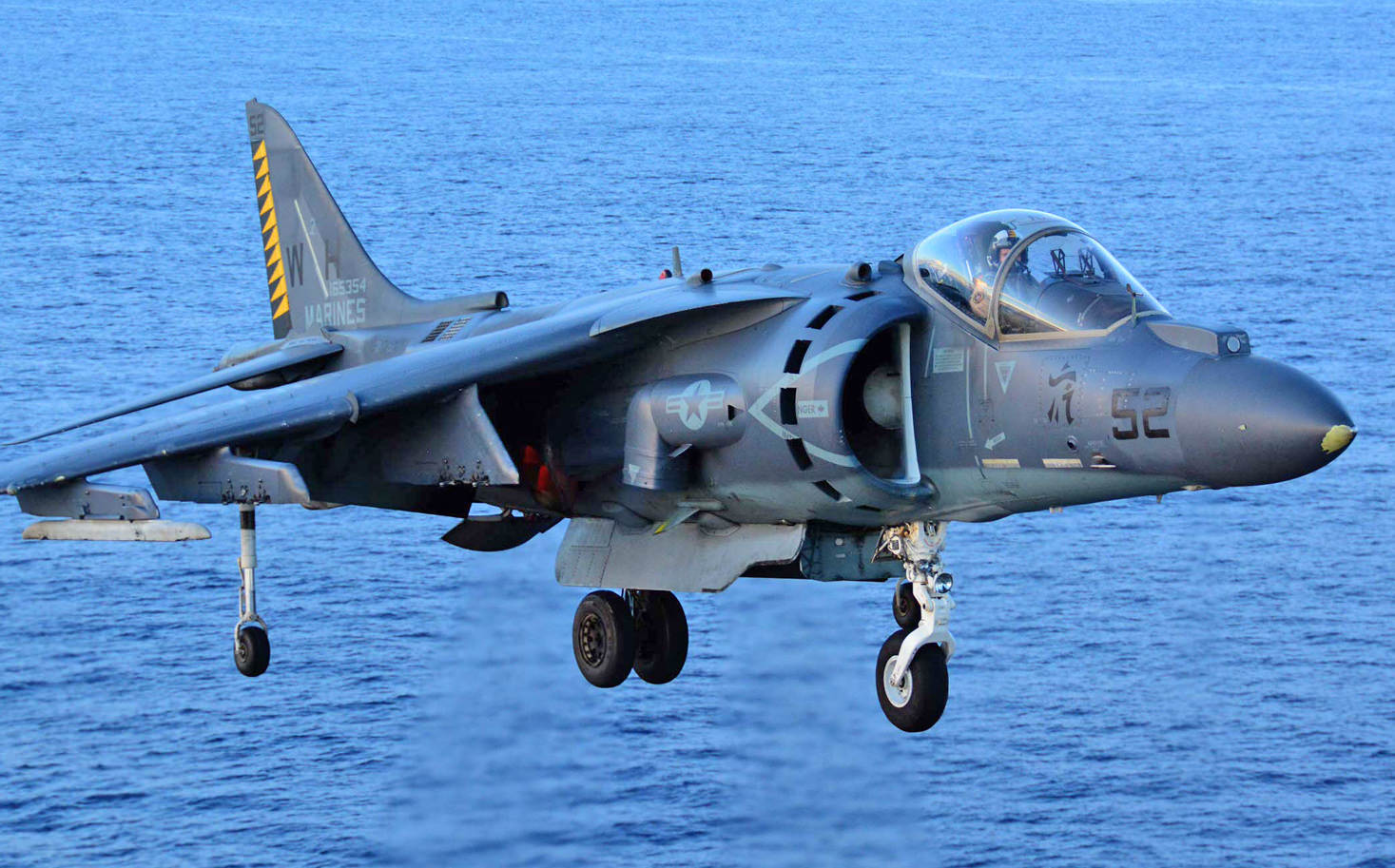
- Marine Corps Harriers – The Hunter Killers
- C-46s of Air America – Secret ops in Southeast Asia
- Piper – He gave America wings
- Factory Fresh – DC-7 Golden Falcon
Manuals & Photos
- AV-8A Flight Manual, 1973
- AV-8A Harrier Flight Manual, 1975
- AV-8A Weapons Stores Loading Manual, 1972
- AV-8B Executive Summary Report, 1981
- AV-8 Tactical Manual Vol.1, 2002
- AV-8 Tactical Manual Vol.2, 1998
- AV-8B Flight Handbook, 1984
- AV-8B Flight Manual, 2008
- AV-8B Maintainable by Design, 1981
- AV-8B / TAV-8B Flight Manual, 2011
- AV-8B / TAV-8B Performance Charts, 2003
- AV-16A Pegasus 15 Report No. A2908, 1974
- TAV-8B Environmental Control System, 2004
- TAV-8B Executive Summary
- Over 400 photos of the AV-8 Harrier VTOL Jump Jet
AV-8 Harrier VTOL Jump Jet
AV-8B Specs
GR.3 Specs
P.1127 Specs
On Display
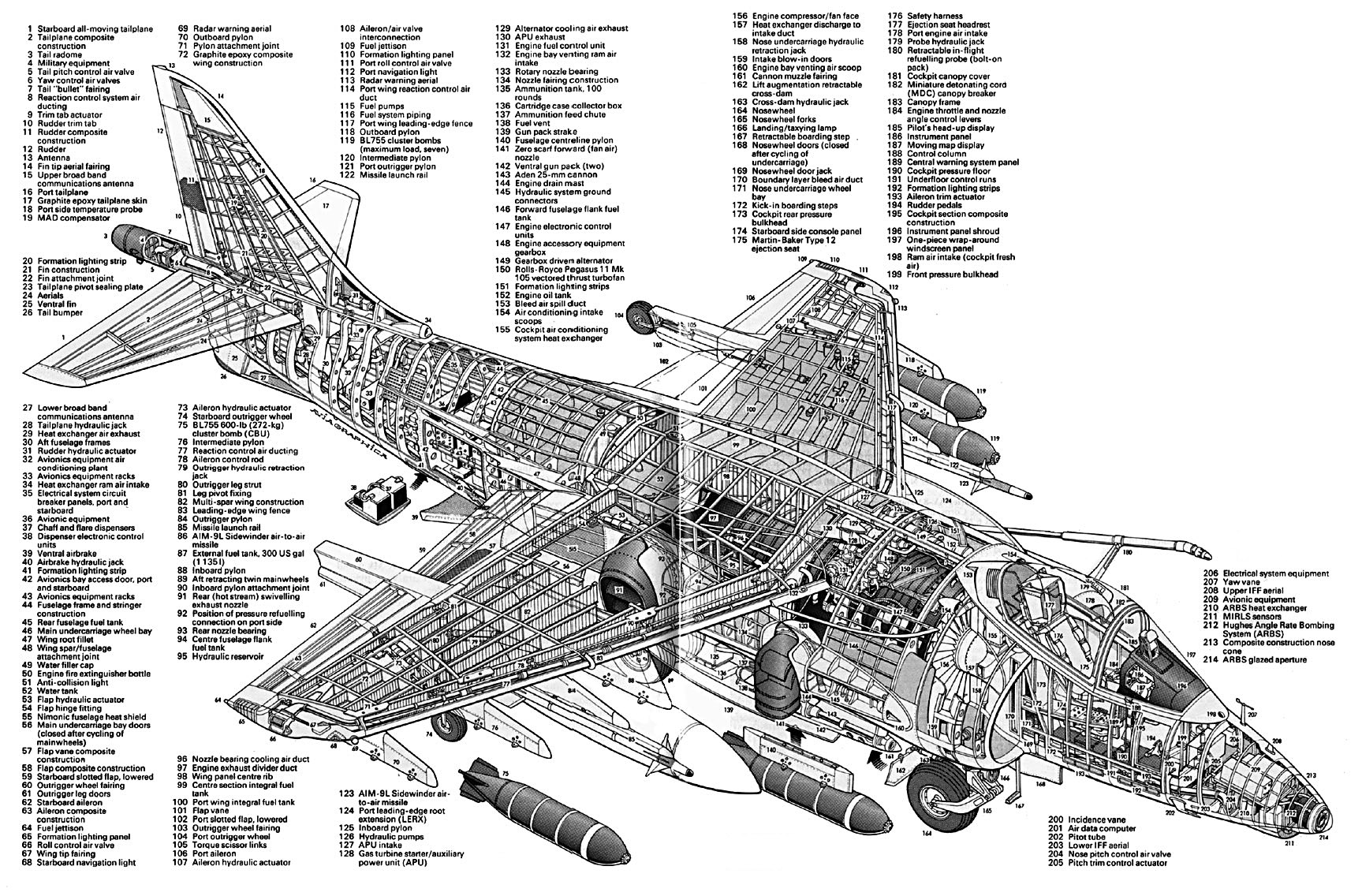
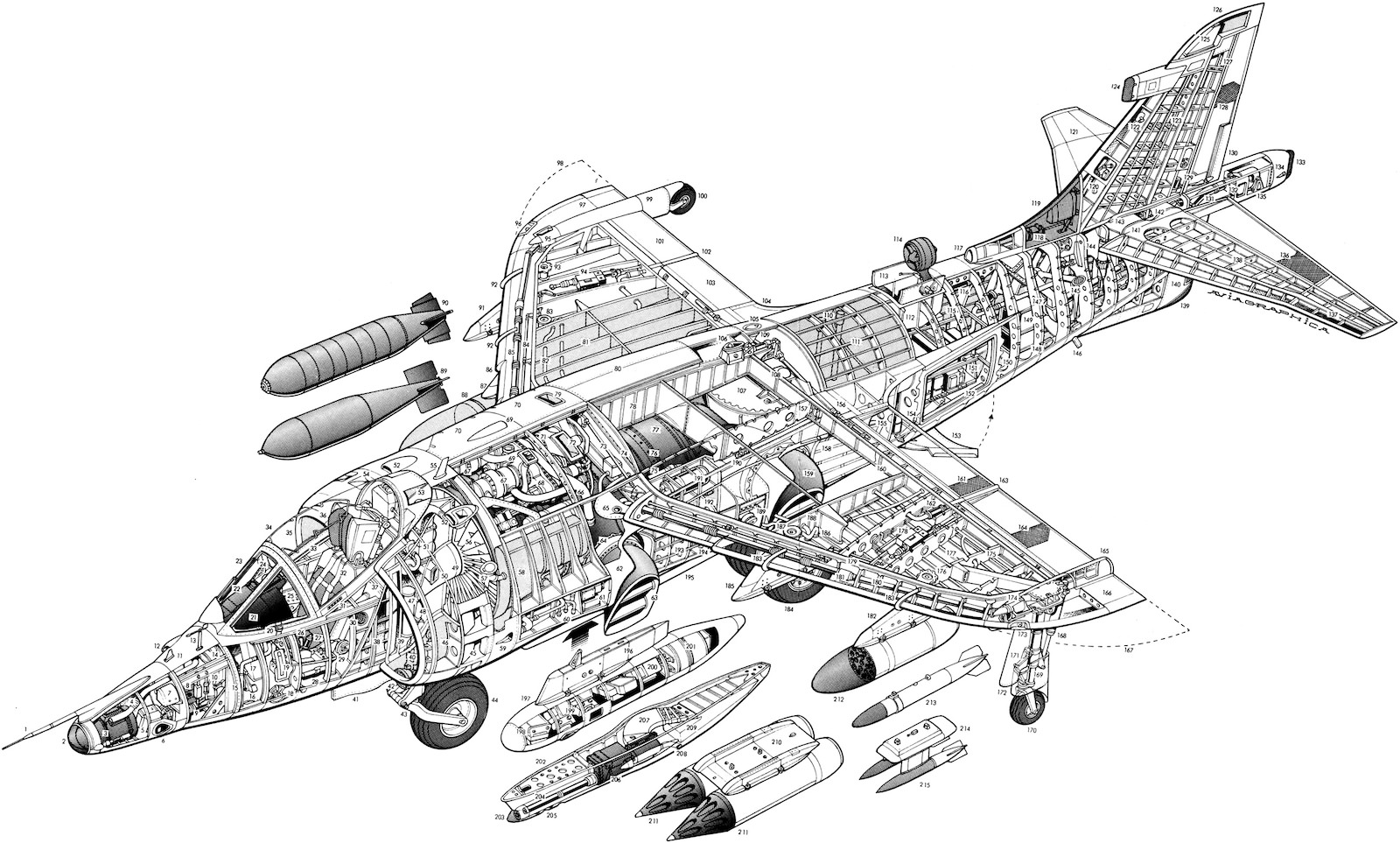
Cutaway
Videos
Boeing AV-8B Harrier II Plus
General Characteristics
- Crew: 1 pilot
- Length: 46 ft 4 in (14.12 m)
- Wingspan: 30 ft 4 in (9.25 m)
- Height: 11 ft 8 in (3.55 m)
- Wing area: 243.4 sq ft (22.61 m²)
- Airfoil: supercritical airfoil
- Empty weight: 13,968 lb (6,340 kg)
- Loaded weight: 22,950 lb (10,410 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: **
- Rolling: 31,000 lb (14,100 kg)
- Vertical: 20,755 lb (9,415 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Rolls-Royce Pegasus F402-RR-408 (Mk 107) vectored-thrust turbofan, 23,500 lbf (105 kN)
Performance
- Maximum speed: Mach 0.9 (585 knots, 673 mph, 1,083 km/h)
- Range: 1,200 nmi (1,400 mi, 2,200 km)
- Combat radius: 300 nmi (350 mi, 556 km)
- Ferry range: 1,800 nmi (2,100 mi, 3,300 km)
- Rate of climb: 14,700 ft/min (75 m/s)
- Wing loading: 94.29 lb/(sq ft) (460.4 kg/m²)
Armament
- Guns: 1× General Dynamics GAU-12 Equalizer 25 mm (0.984 in) 5-barreled Rotary cannon mounted under-fuselage in the left pod, with 300 rounds of ammunition in the right pod
- Hardpoints: 6× under-wing pylon stations holding up to 9,200 lb (4,200 kg) of payload:
- Rockets: ** 4× LAU-5003 rocket pods (each with 19× CRV7 or APKWS 70 mm rockets)
- Missiles: ** Air-to-air missiles:
-
- 4× AIM-9 Sidewinder or similar-sized infrared-guided missiles
- 6× AIM-120 AMRAAM (on radar equipped AV-8B Plus variants)
- Air-to-surface missiles:
- 6× AGM-65 Maverick; or
- 2× AGM-84 Harpoon; or
- 2× AGM-88 HARM
-
- Bombs:
- CBU-100 cluster bombs (CBUs)
- Mark 80 series of unguided bombs (including 3 kg [6.6 lb] and 14 kg [31 lb] practice bombs)
- Paveway series of laser-guided bombs (LGBs)
- Joint Direct Attack Munitions (GBU-38, GBU-32, and GBU-54)
- Mark 77 fire bomb
- B61 nuclear bomb
- Others:
- up to 4× 300/330/370 US Gallon drop tanks (pylon stations No. 2, 3, 4, & 5 are wet plumbed)
- Intrepid Tiger II electronic jammer
Avionics
- Raytheon APG-65 radar
- AN/AAQ-28V LITENING targeting pod (on AV-8B Night Attack and radar-equipped AV-8B Plus variants)
Variants
- YAV-8B – Two prototypes converted in 1978 from existing AV-8A airframes (BuNos 158394 and 158395).
- AV-8B Harrier II sans suffix – The initial “day attack” variant.
- AV-8B Harrier II Night Attack – Improved version with a forward-looking infrared (FLIR) camera, an upgraded cockpit with night-vision goggle compatibility, and the more powerful Rolls Royce Pegasus 11 engine. This variant was originally planned to be designated AV-8D.
- AV-8B Harrier II Plus – Similar to the Night Attack variant, with the addition of an APG-65 radar and separate targeting pod. It is used by the USMC, Spanish Navy, and Italian Navy. Forty-six new-built aircraft were assembled from 1993 to 1997.
- TAV-8B Harrier II – Two-seat trainer version.
- EAV-8B Matador II – Company designation for the Spanish Navy version.
- EAV-8B Matador II Plus – The AV-8B Harrier II Plus, ordered for the Spanish Navy.
- Harrier GR5, GR7, GR9
Hawker Siddeley GR.3 Harrier
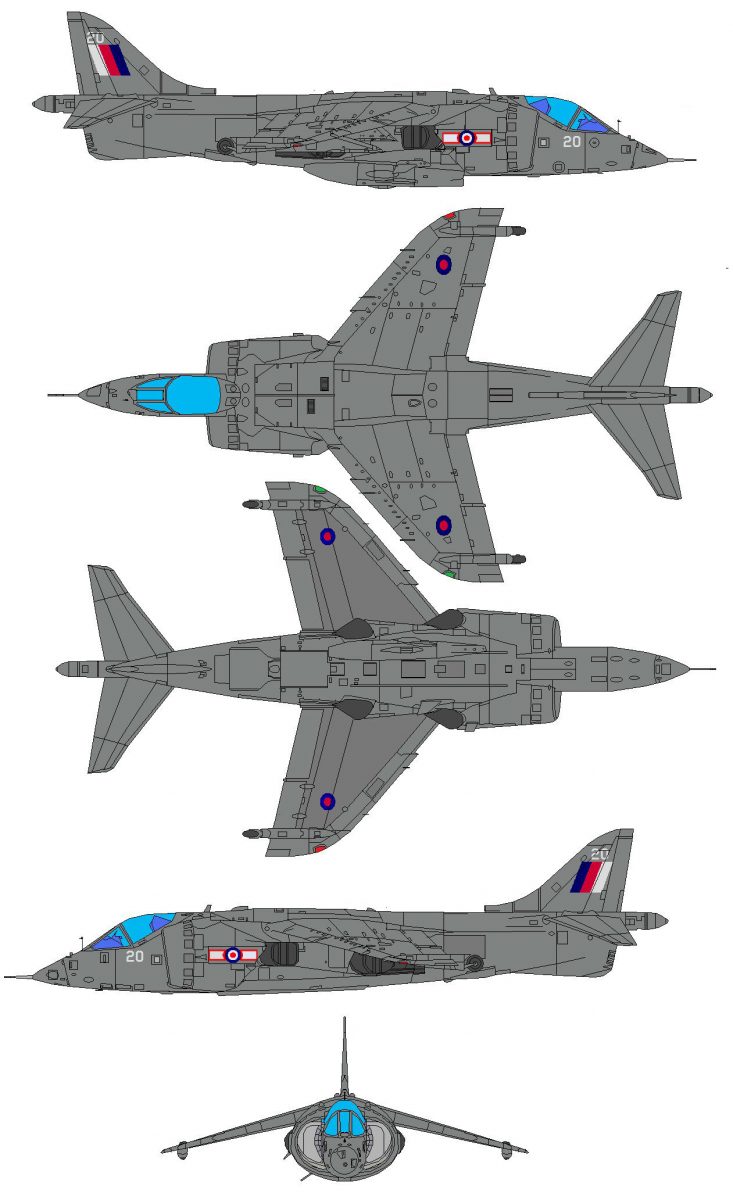
General Characteristics
- Crew: One
- Length: 46 ft 10 in (14.27 m)
- Wingspan: 25 ft 3 in (7.70 m)
- Height: 11 ft 11 in (3.63 m)
- Wing area: 201.1 ft² (18.68 m²)
- Empty weight: 13,535 lb (6,140 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 25,200 lb (11,430 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Rolls-Royce Pegasus 103 turbofan with four swivelling nozzles, 21,500 lbf (95.6 kN) Four vertical flight puffer jets use engine bleed air, mounted in the nose, wingtips, and tail.
Performance
- Maximum speed: 730 mph (635 knots, 1,176 km/h) at sea level
- Combat radius: 230 mi (200 nmi, 370 km) lo-lo-lo with 4,400 lb (2,000 kg) payload
- Ferry range: 2,129 mi (1,850 nmi, 3,425 km)
- Endurance: 1 hr 30 min (combat air patrol – 115 mi (185 km) from base)
- Service ceiling: 51,200 ft (15,600 m)
- Time to climb to 40,000 ft (12,200 m): 2 min 23 s
Armament
- Guns: 2× 30 mm (1.18 in) ADEN cannon pods under the fuselage
- Hardpoints: 4× under-wing & 1× under-fuselage pylon stations with a capacity of 5,000 lb (2,268 kg) and provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets: 4× Matra rocket pods with 18× SNEB 68 mm rockets each
- Missiles: 2× AIM-9 Sidewinders Air-to-air missiles
- Bombs: A variety of unguided iron bombs, BL755 cluster bombs or laser-guided bombs
- Others:
- 1× Reconnaissance pod
- 2× drop tanks for extended range/loitering time
Variants
- Harrier GR.1, GR.1A, GR.3 – Single-seat versions for the RAF. The RAF ordered 118 of the GR.1/GR.3 series, with the last production aircraft delivery in December 1986. 122 built.
- AV-8A, AV-8C Harrier – Single-seat versions for the US Marine Corps. The USMC ordered 102 AV-8As (company designation: Harrier Mk. 50). The AV-8C was an upgrade to the AV-8A. 110 built.
- AV-8S Matador – Export version of the AV-8A Harrier for the Spanish Navy, who designated them as VA-1 Matador; later sold to the Royal Thai Navy. 10 built.
- Harrier T.2, T.2A, T.4, T.4A – Two-seat training versions for the RAF, with a stretched body and taller tail fin. 25 built.
- Harrier T.4N, T.8, T.60 – Two-seat training versions for the Royal Navy and Indian Navy with avionics based on the Sea Harrier.
- TAV-8A Harrier – Two-seat training version for the USMC, powered by a Pegasus Mk 103.
- TAV-8S Matador – Two-seat training version for the Spanish Navy and later sold to the Royal Thai Navy.
Hawker Siddeley Kestrel FGA.1
General Characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 42 ft 6 in (12.95 m)
- Wingspan: 22 ft 11 in (6.99 m)
- Height: 10 ft 9 in (3.28 m)
- Empty weight: approximately 9,800 lb (4,445 kg)
- Loaded weight: for VTO 14,500 lb (6,580 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: for STO, approximately 17,000 lb (7,700 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Bristol Siddeley Pegasus 5 vectored-thrust turbofan, 15,000 lbf (67 kN)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 710 mph, Mach 0.92 (1,142 km/h) at sea level
- Service ceiling: (service) approximately 55,000 ft (16,750 m)
- Rate of climb: approximately 30,000 ft/min (150 m/s)
- Thrust/weight: 1.04
Variants
- P.1127 – Experimental V/STOL fighter, two prototypes and four development aircraft.
- Kestrel FGA.1 – Aircraft for the tripartite evaluation squadron, nine built, six later transferred to the United States where they were designated XV-6A.
- P.1127 (RAF) – Development V/STOL ground attack and reconnaissance fighter, six built as pre-production evaluation aircraft before the type was ordered into production as the Harrier GR.1. First aircraft flew from Dunsfold on 31 August 1966.
- XV-6A – United States military designation for the six Kestrel FGA.1 transferred to the U.S.
- VZ-12 – U.S. Army designation for two P.1127 development aircraft, not delivered.
On Display
- P.1127 XP831 on display at The Science Museum, London, England.
- P.1127 XP980 (fitted with a Harrier GR.1 wing) is on display at the Fleet Air Arm Museum, Yeovilton, England
- P.1127 XP984 (temporarily fitted with an earlier P.1127 wing) is on display at the Brooklands Museum, Surrey, England.
- Kestrel FGA.1 XS695 on display at the Royal Air Force Museum Cosford England.
- P.1127(RAF) XV277 on display at the National Museum of Flight, Scotland.
- P.1127(RAF) XV278 on display at the Luftwaffenmuseum, Germany.
- XV-6A Kestrel 64-18262 on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force at Wright Patterson AFB, Ohio, United States.
- XV-6A Kestrel 64-18263 with NASA livery on display at the Virginia Air and Space Center, Hampton, Virginia, United States
- XV-6A Kestrel 64-18264 formerly held in storage by the United States Army Aviation Museum, Alabama, United States; now on display at the Pima Air & Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona.
- XV-6A Kestrel 64-18266 with NASA livery on display at Air Power Park, Hampton, Virginia, United States.
Canada
- AV-8A
- 158966 – Canada Aviation and Space Museum, Ottawa, Ontario
China
- GR.3
- XZ965 – Beijing Aviation Museum (?????)
Germany
- GR.1
- XV278 – Luftwaffenmuseum der Bundeswehr, Gatow
- GR.3
- XZ998 – Flugausstellung Hermeskeil at Hermeskeil
Poland
- GR.3
- XW919 – Polish Aviation Museum, Kraków, Poland
New Zealand
- GR.3
- XZ129 – Ashburton Aviation Museum, Ashburton, New Zealand
Thailand
- AV-8S
- 3109 – Royal Thai Air Force Museum
United Kingdom
- GR.1
- XV277 – National Museum of Flight, East Fortune
- GR.3
- XV744 – Tangmere Military Aviation Museum, Chichester, West Sussex
- XV748 – Yorkshire Air Museum, Elvington
- XV751 – Gatwick Aviation Museum, Surrey
- XV752 – South Yorkshire Aircraft Museum, Doncaster, South Yorkshire
- XV753 – Classic Air Force, St Mawgan, Newquay, Cornwall
- XV779 – RAF Wittering (Gate Guardian)
- XZ133 – Imperial War Museum, Duxford
- XZ968 – Muckleburgh Collection, Norfolk
- XZ997 – RAF Museum, Hendon[161]
- ZD667 – Bentwaters Cold War Museum, Suffolk
- Mk.52 G-VTOL
- ZA250 – Brooklands Museum, Surrey
- T.2
- XW269 – Airworld Aviation Museum Caernarfon Wales
- T.4
- XW934 – Farnborough Air Sciences Trust, Farnborough, Hampshire
- XW268 – City of Norwich Aviation Museum, Norfolk
- AV-8A
- 159233 – Imperial War Museum North
United States
- AV-8A
- 158695 – Air Park, Yuma MCAS, Yuma, Arizona
- 159239 – San Diego Air and Space Museum, San Diego, California
- 158963 – Craven County Regional Airport, Grantham, North Carolina
- 158976 – City of Havelock, Havelock, North Carolina
- Cockpit on display at Moffett Historical Museum, Moffett Federal Airfield, California
- TAV-8A
- 159381 – Oakland Aviation Museum, Oakland, California
- 159382 – Pima Air & Space Museum, Tucson, Arizona
- AV-8C
- 158387 – Flying Leatherneck Aviation Museum, Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego, California
- 158710 – Quonset Air Museum, North Kingstown, Rhode Island
- 158959 – Pacific Coast Air Museum, Santa Rosa, California
- 158975 – National Naval Aviation Museum, NAS Pensacola, Pensacola, Florida
- 158977 – Museum of Flight, Seattle, Washington
- 159232 – Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum, New York City, New York
- 159238 – Hangar 25 Museum, Webb AFB (formerly), Big Spring, Texas
- 159241 – Pima Air & Space Museum, Tucson, Arizona
- 159247 – Naval Inventory Control Point (NAVICP) Philadelphia, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
- 159249 – United States Naval Museum of Armament and Technology, NCC China Lake (North), Ridgecrest, California
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aTSPeHvaHYo