Price: $14.95
- 2 magazines, 4 manuals, & photos
- PDF contains 1,110 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
March 1980
- Typhoon, Tornado, Tempest
- F-86F Sabres
- Hunter / Killer (Grumman AF-2S Guardian)
- Sky Soldiers, Vietnam War As Seen From Cockpit Of A Bell UH-1 Gunship!
October 2003
- Bring in the Choppers! Evolution of the large military helicopter.
- Alaskan Twin Mustangs: North American F-82 Twin Mustang
- Pete Bowers Remember: 1946 National Air Races in Cleveland, Ohio.
Manuals & Photos
- CH-54A Operator’s Manual, 1977
- CH-54B Operator’s Manual, 1977
- CH-47, CH-54 Reliability & Maintainability Problems & Deficiencies, 1972
- CH-54 Operational Statistics, 1976
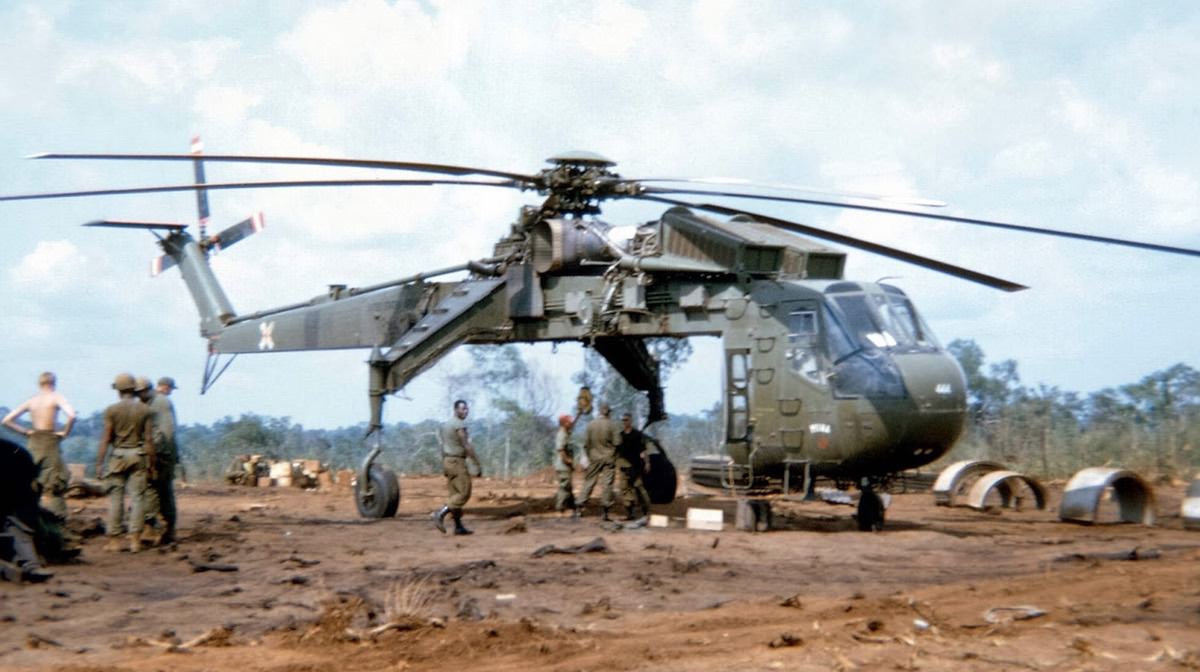
- Over 70 Sikorsky CH-54 Tarhe / S-64 Skycrane photos
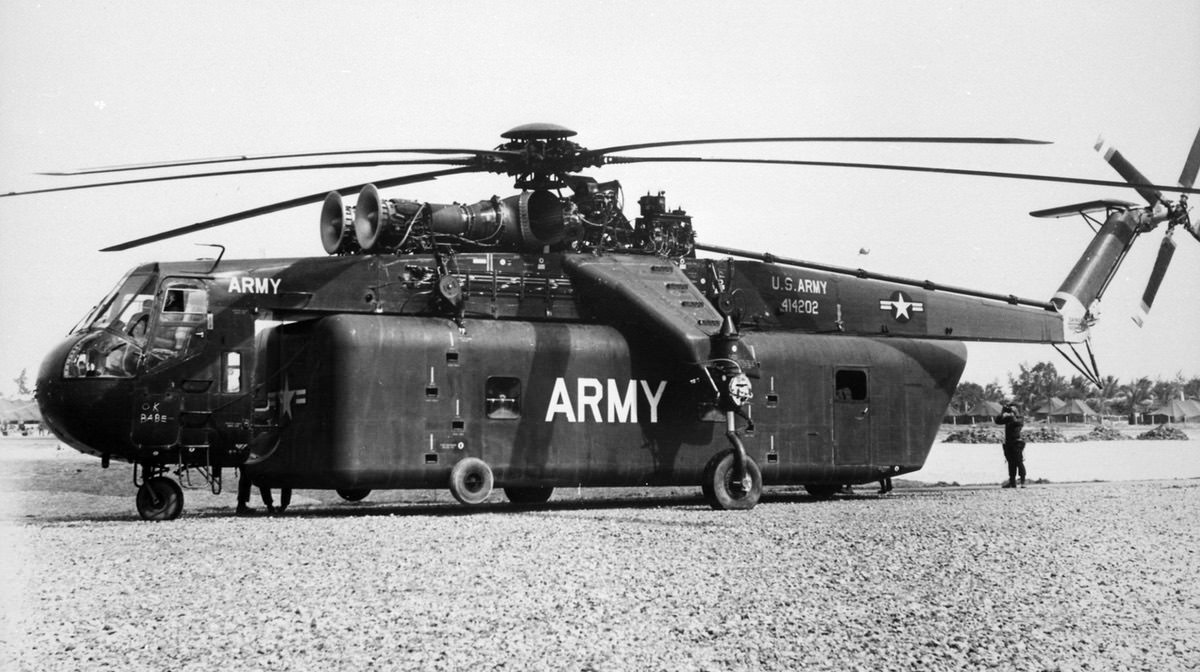
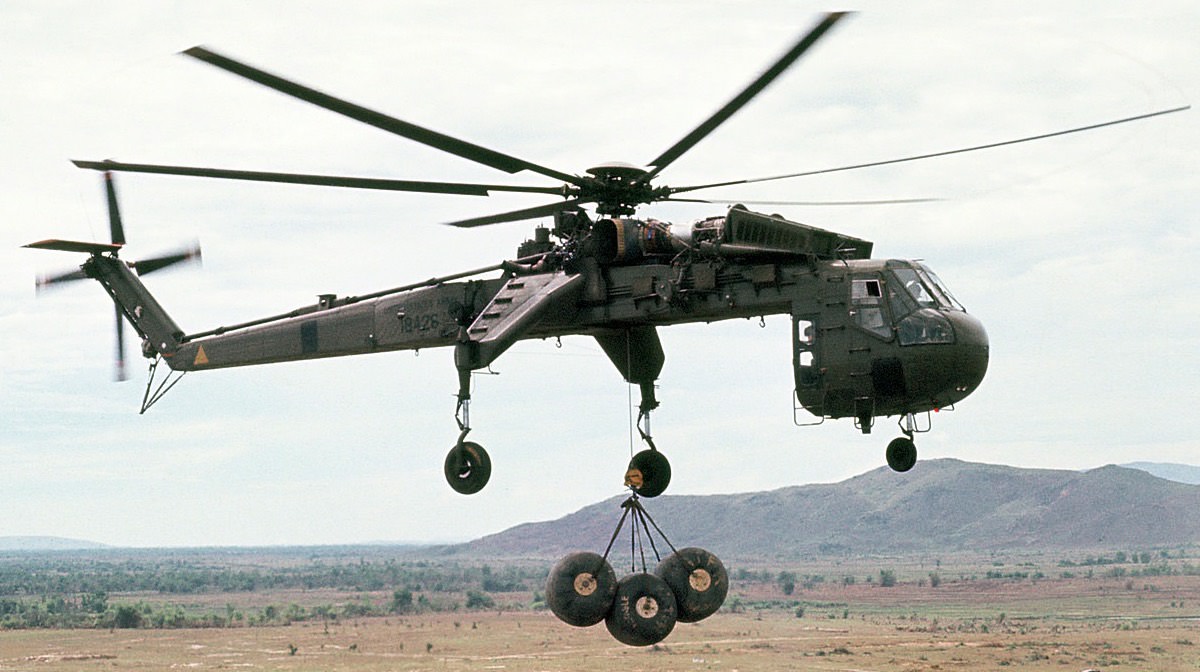
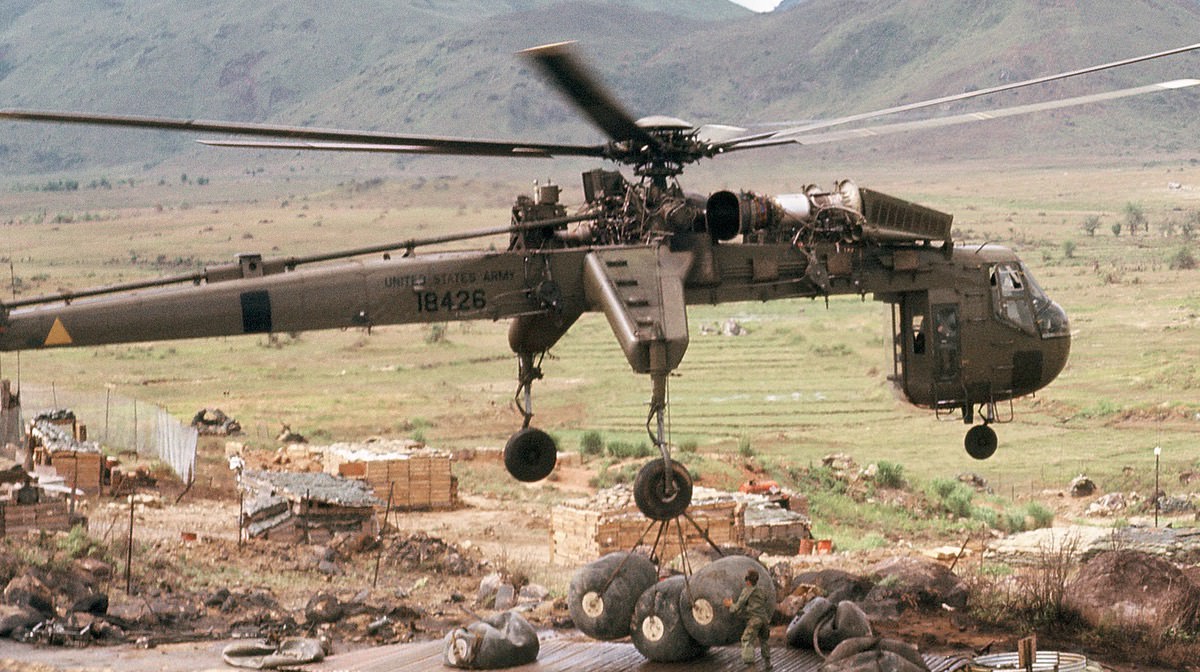
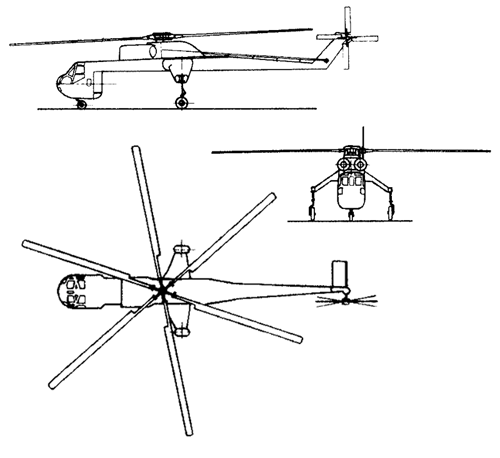
Sikorsky CH-54 Tarhe / S-64 Skycrane
CH-54B Specifications
Variants
On Display
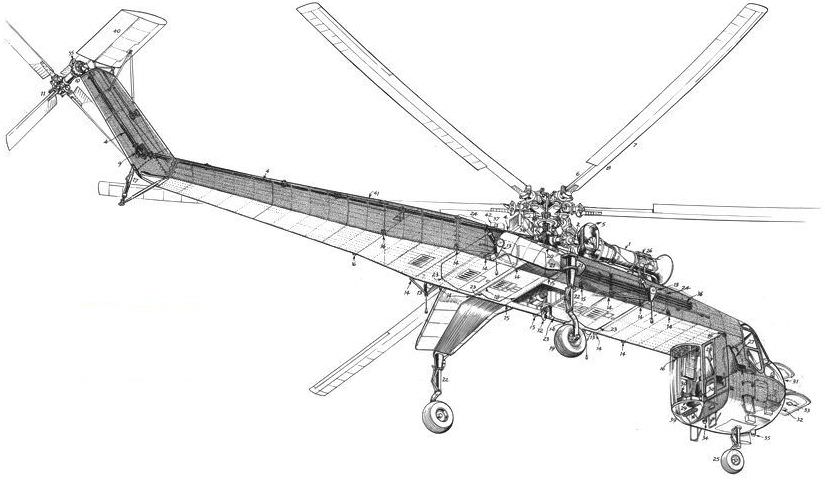
Cutaway
General Characteristics
- Crew: 3
- Capacity: 20,000 lb (9,072 kg) payload
- Length: 88 ft 6 in (26.97 m)
- Height: 25 ft 5 in (7.75 m)
- Empty weight: 19,800 lb (8,981 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 47,000 lb (21,319 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 Pratt & Whitney T73-P-700 turboshaft engines, 4,800 shp (3,600 kW) each
- Main rotor diameter: 72 ft 0 in (21.95 m)
- Main rotor area: 4,071.5 sq ft (378.25 m2) *
- Blade section: NACA 0011 mod
Performance
- Maximum speed: 130 kn (150 mph, 240 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 100 kn (120 mph, 190 km/h)
- Range: 200 nmi (230 mi, 370 km)
- Rate of climb: 1,330 ft/min (6.8 m/s)
- YCH-54A – Preproduction aircraft, six built.
- CH-54A – Production model powered by two 4,500 shp (3,400 kW) Pratt & Whitney T73-P-1 turboshafts, 54 built.
- CH-54B – Heavier version of the CH-54A with two 4,800 shp (3,600 kW) T73-P-700 turboshafts and twin-wheeled main undercarriage, 37 ordered, 29 built.
- S-64B – In 1968, Sikorsky proposed a three-engined growth version with upgraded rotor and gearbox. This was not proceeded with but did form the basis for the CH-53E Super Stallion.
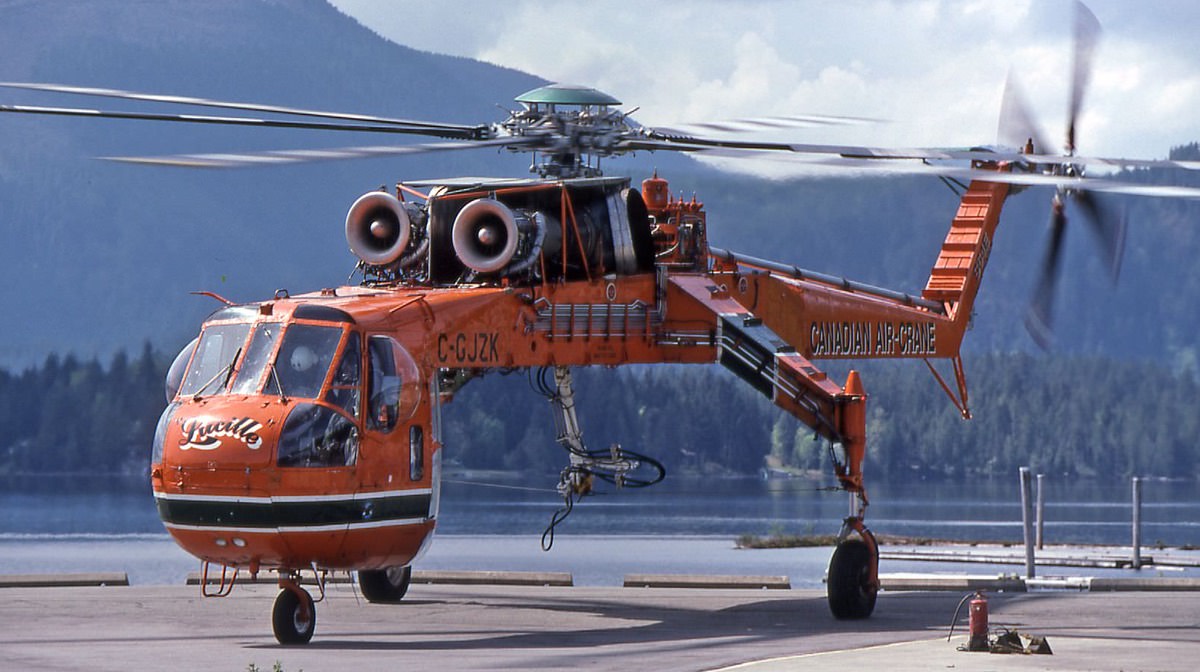
Airworthy
CH-54A
- 67-18427 – N793HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
- 67-18429 – N429C privately owned in Yuba City, California.
- 67-18430 – N7095B operated by Siller Helicopter in Yuba City, California.
- 68-18447 – N792HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
- 68-18455 – N9125M operated by Siller Helicopter in Yuba City, California.
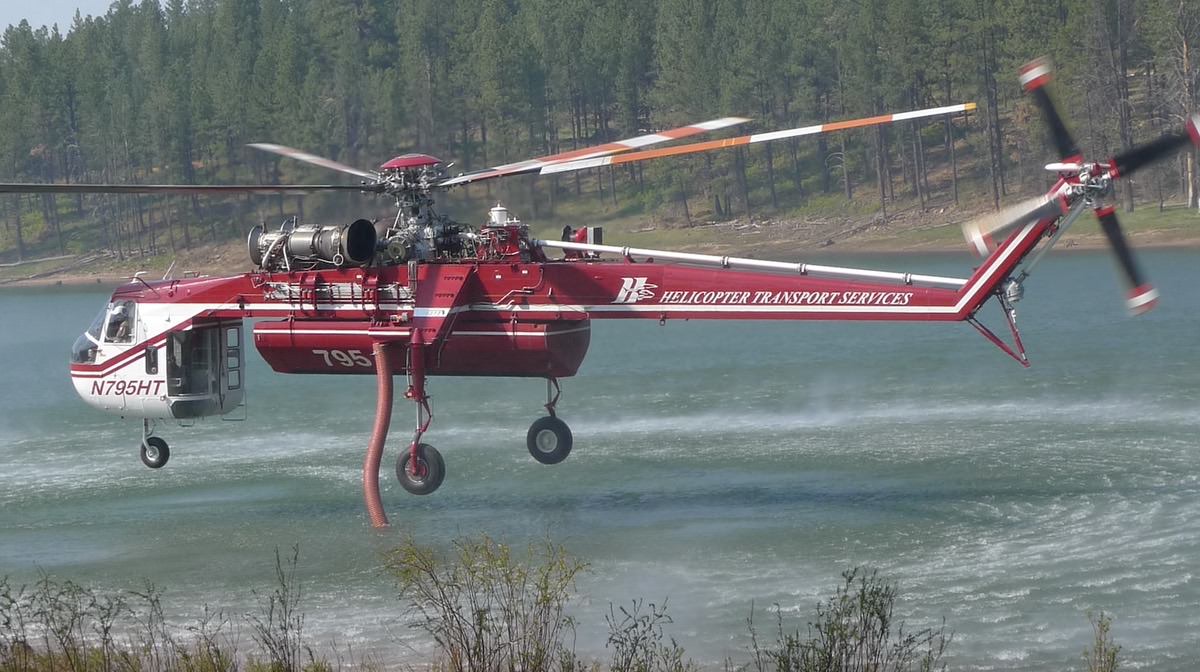
- 68-18458 – N795HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
CH-54B
- 69-18463 – N720HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
- 69-18466 – N721HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
- 69-18467 – N718HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
- 69-18468 – N722HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
- 69-18469 – N719HT privately owned in Wilmington, Delaware.
- 69-18470 – N715HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
- 69-18484 – N716HT operated by Helicopter Transport Services in Aurora, Oregon.
On display
YCH-54A
- 64-14203 – United States Army Transportation Museum at Fort Eustis near Newport News, Virginia.
CH-54A
- 66-18409 – 1st Cavalry Division Museum at Fort Hood in Killeen, Texas.
- 67-18418 – Stead Army National Guard Base in Reno, Nevada.
- 67-18424 – Combat Air Museum in Topeka, Kansas.
- 68-18437 – Pima Air & Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona.
- 68-18438 – United States Army Aviation Museum at Fort Rucker near Daleville, Alabama.
- 68-18439 – Museum of the Kansas National Guard in Topeka, Kansas.
CH-54B
- 68-18434 – Mississippi Armed Forces Museum at Camp Shelby near Hattiesburg, Mississippi.
- 69-18465 – New England Air Museum in Windsor Locks, Connecticut.
- 69-18479 – Birmingham Air National Guard Base in Birmingham, Alabama.
- 70-18486 – Russell Military Museum in Zion, Illinois.
- 70-18488 Isabell – Camp Denali at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson in Anchorage, Alaska.