Price: $14.95
- 3 magazines, 3 manuals, & photos
- PDF contains 1,240 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
February 1974
- Fiat CR-32
- B-32 Dominator, Second String Superbomber
- Curtiss AT-9 Air Jeep
- Grumman’s F2F & F3F Flying Beer Barrels
- Loening’s Flying Shoehorns
June 1990
- USAF Big Iron bombers, 1940-1990
April 1993
- Clipped Wings, the Future of American Aerospace
- Supersonic Spearhead, Convair’s B-58 Hustler
- Flying Terminated Inventory
Manuals & Photos
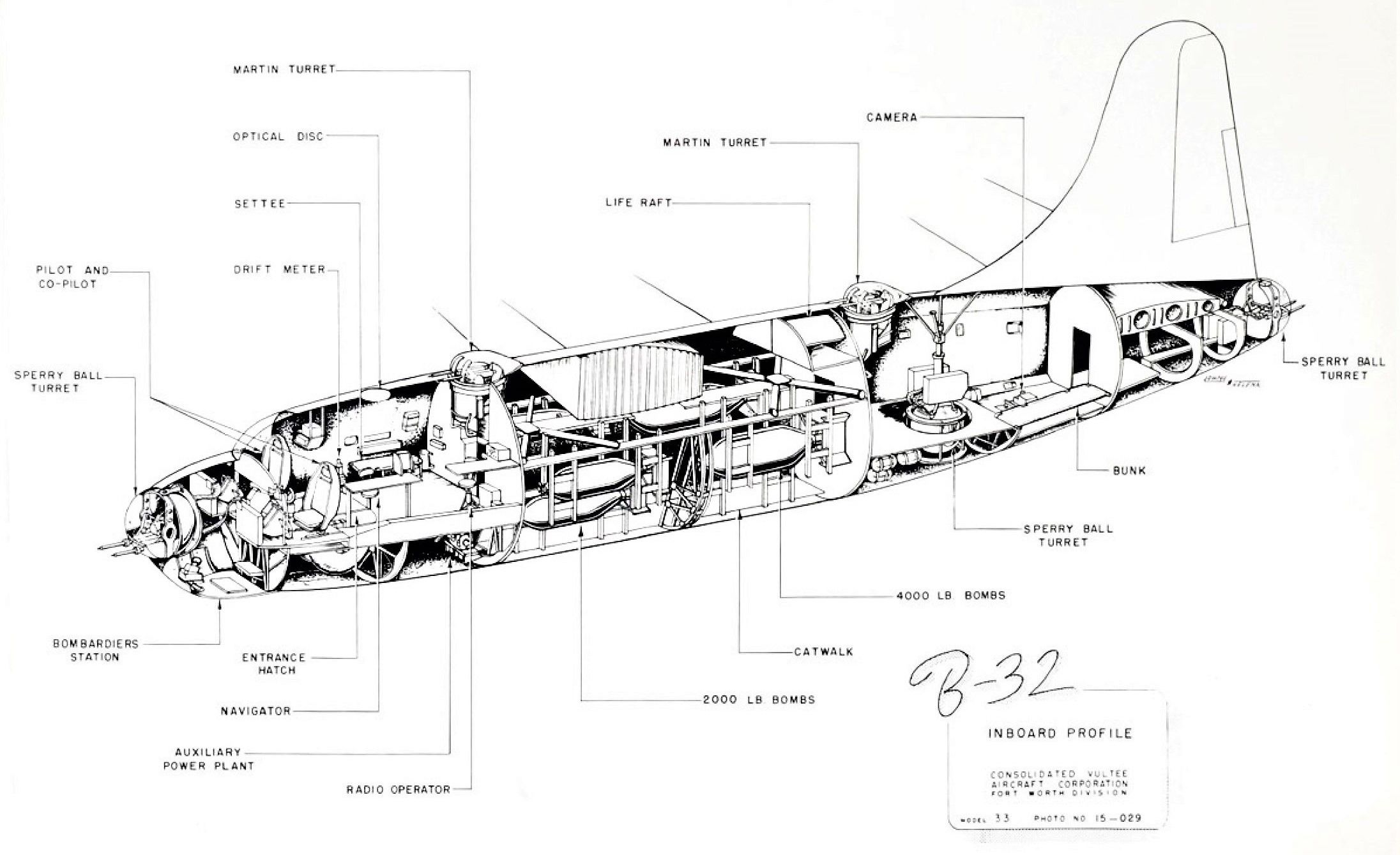
- B-32 Training Manual, 1945
- B-32 Operating Instructions, 1945
- B-32 Preliminary Erection & Maintenance Instructions
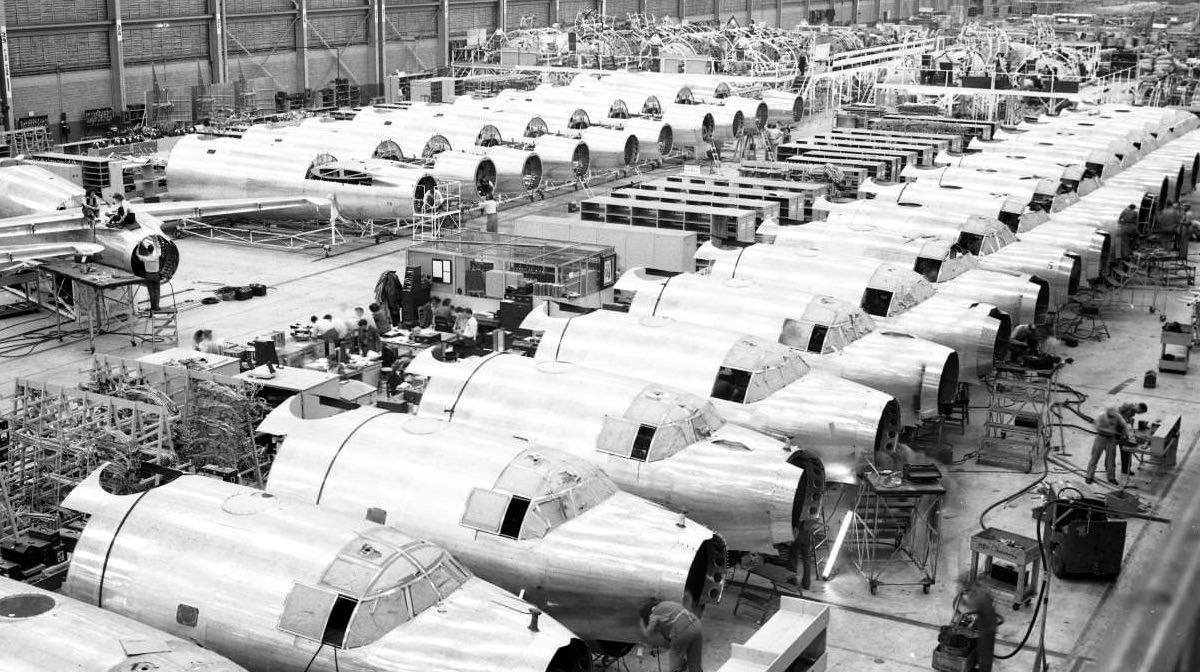
- Nearly 200 Consolidated B-32 Dominator photos
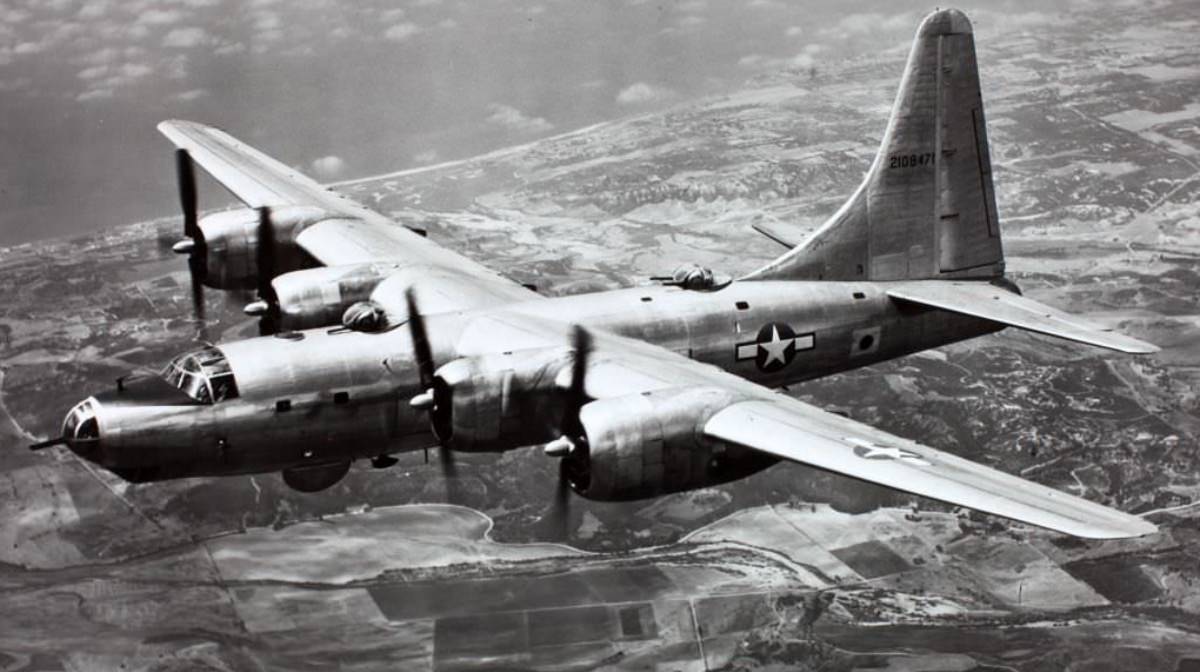
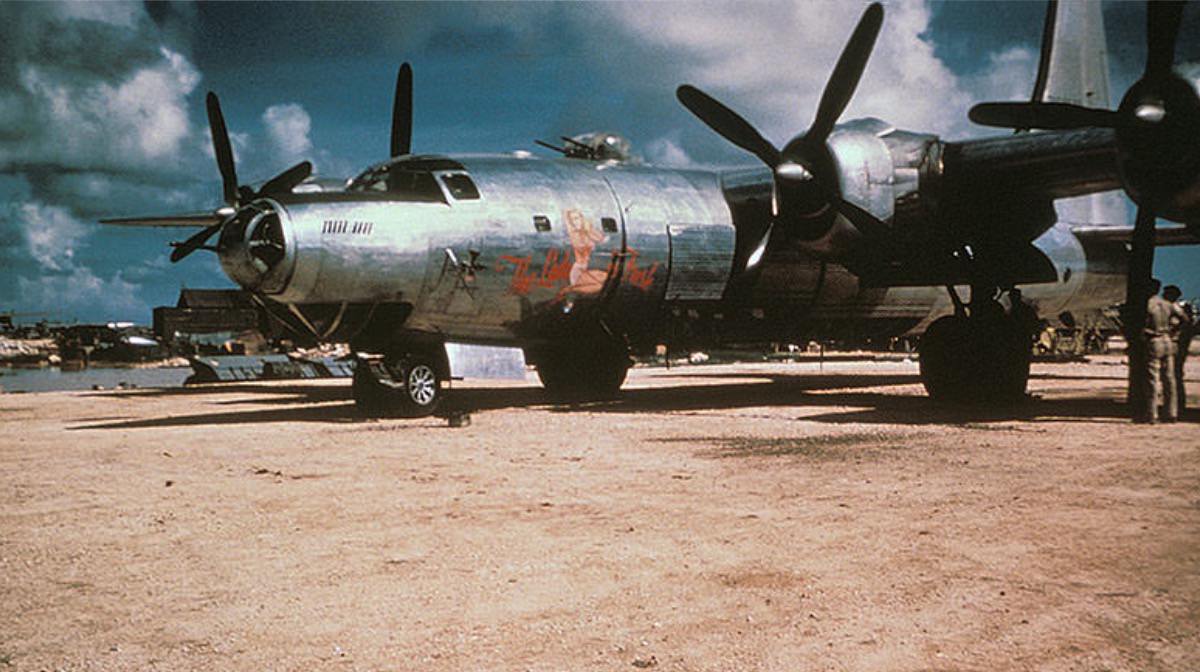
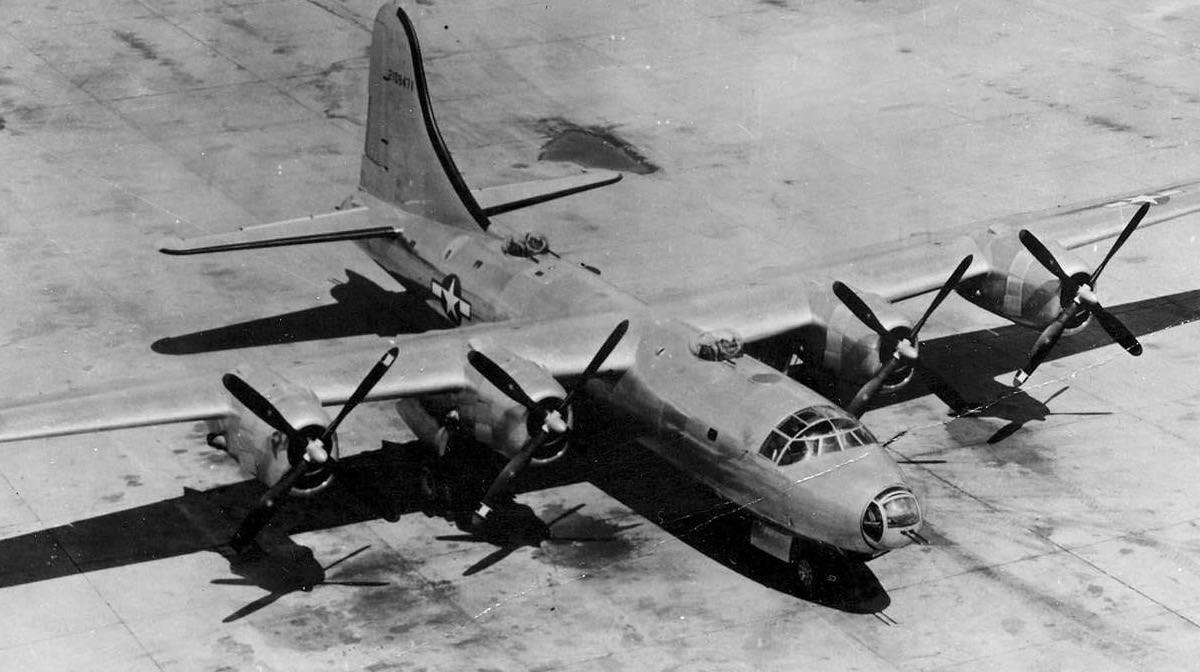
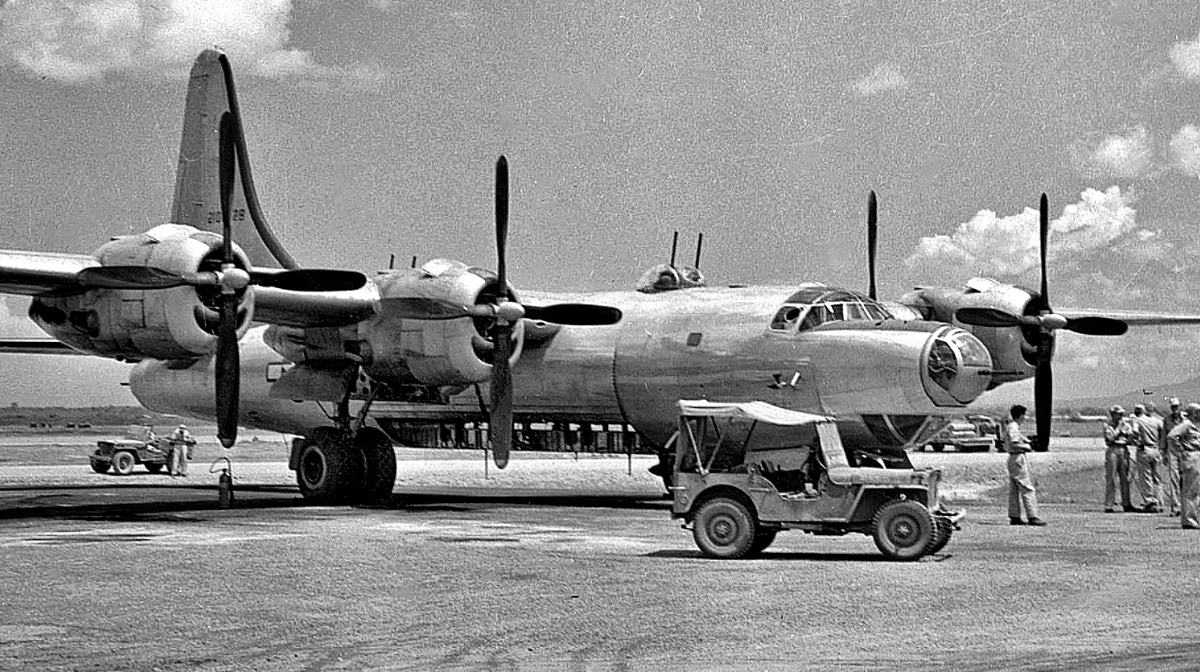
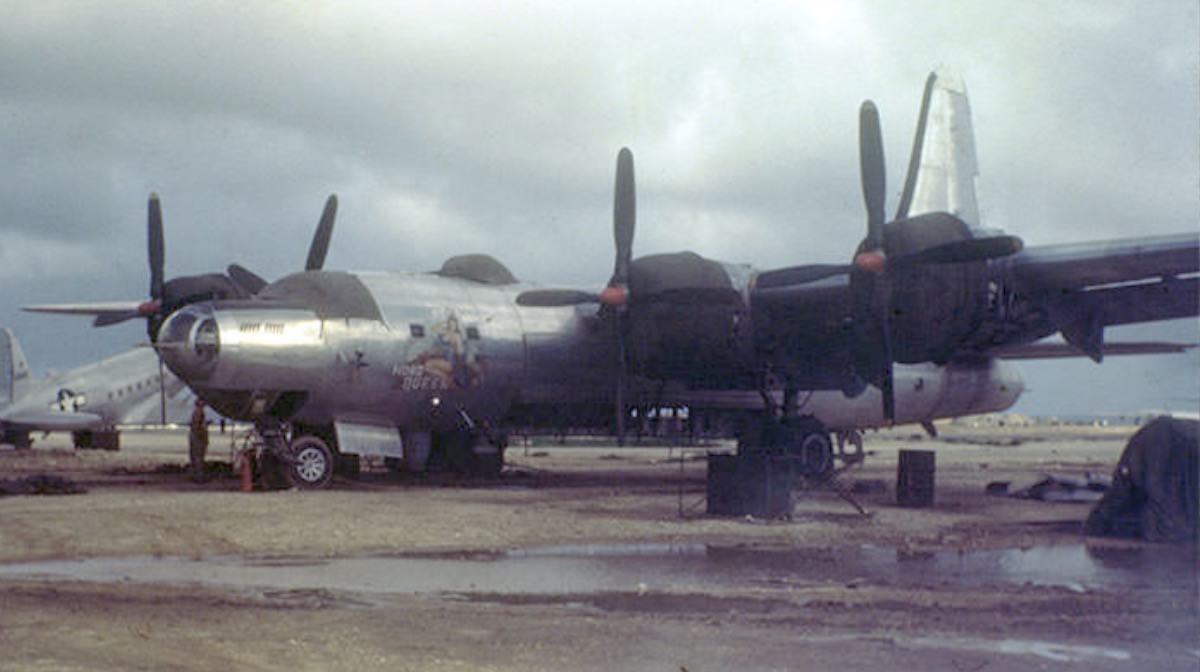
Consolidated B-32 Dominator
B-32 Specifications
Variants
On Display
Cutaway
Videos
General Characteristics
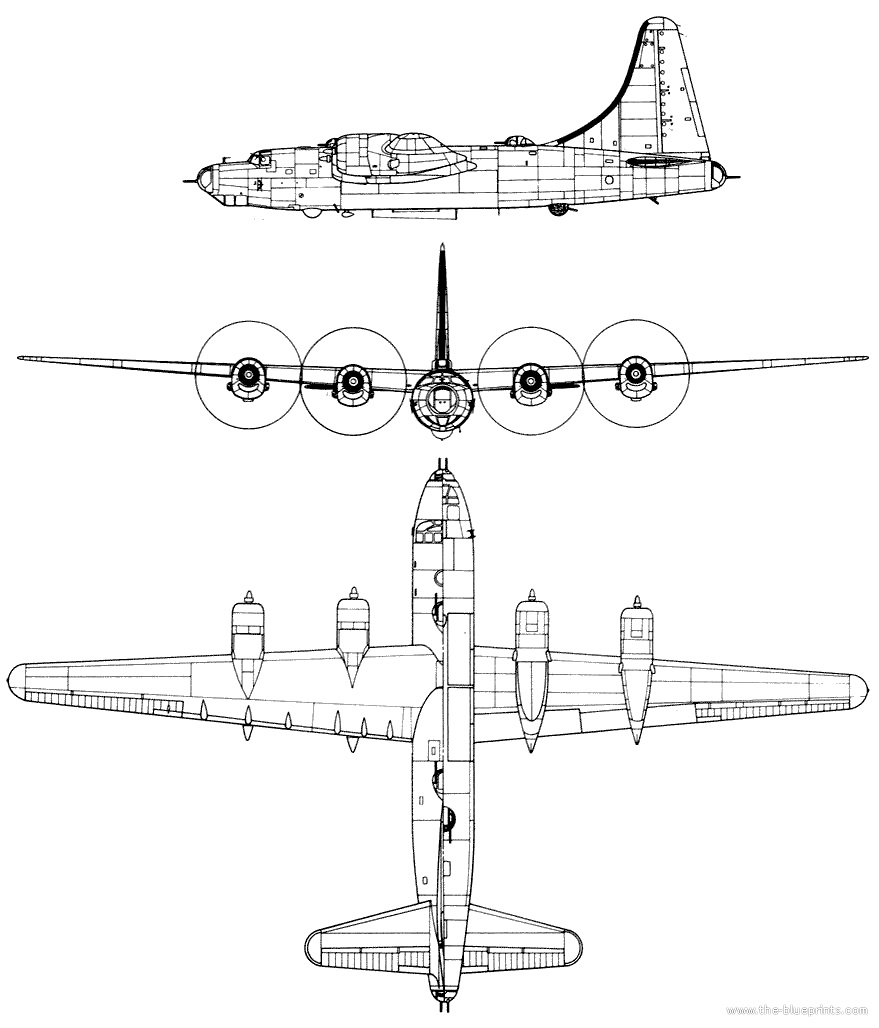
- Crew: 10
- Length: 82 ft 1 in (25.02 m)
- Wingspan: 135 ft 0 in (41.15 m)
- Height: 32 ft 2 in (9.80 m)
- Wing area: 1,422 sq ft (132.1 m2)
- Empty weight: 60,278 lb (27,342 kg)
- Gross weight: 100,800 lb (45,722 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 123,250 lb (55,905 kg)
- Powerplant: 4 × Wright R-3350-23A Duplex-Cyclone 18-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 2,200 hp (1,600 kW) each
- Propellers: 4-bladed constant-speed propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 357 mph (575 km/h, 310 kn) at 30,000 ft (9,144 m)
- Cruise speed: 290 mph (470 km/h, 250 kn)
- Range: 3,800 mi (6,100 km, 3,300 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 30,700 ft (9,400 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,050 ft/min (5.3 m/s)
Armament
- Guns: 10× .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns
- Bombs: 20,000 lb (9,100 kg)
- XB-32
- Company Designation Model 33, three built, on first aircraft: Wright R-3350-13 (inboard) and Wright R-3350-21 (outboard) engines, three-bladed propeller, rounded, glassed nose, first two aircraft had a twin tail configuration. Second prototype was pressurized and had remotely controlled retractable gun turrets in the dorsal ventral positions, with a manned tail “stinger”. Second and third prototypes had numerous tail variations installed, including a B-29 tail installation. First flown 7 September 1942.
- B-32-1-CF
- Model 34 flight testing aircraft first flown 5 August 1944. Wright R-3350-23 engines. First two aircraft initially had modified B-29 tails installed. Installation of armament, single rudder tabs, radar bombing equipment (AN/APQ-5B and AN/APQ-13) and long range navigation equipment, 10 built.
- B-32-5-CF
- Twin rudder tabs made standard. Last 11 aircraft converted to TB-32-5CF with deletion of all armament (openings faired over), deletion of radar bombing equipment, and deletion of long range navigation equipment, 15 built.
- TB-32-10-CF
- Redesigned bombardier’s entrance door, replacement of SCR-269-G Radio compass with AN/ARN-7 set, installation of engine fire extinguishers, 25 built.
- TB-32-15-CF
- Empennage de-icer boots, four built.
- B-32-20-CF
- Combat equipped aircraft. Pressurization system removed, scanning blister installed in rear fuselage, 21 built.
- B-32-21-CF
- One B-32-20-CF converted to paratroop conversion. All bombing equipment removed and benches installed in rear bomb bay and rear fuselage.
- B-32-25-CF
- Modified fuel system to allow auxiliary tanks in the bomb bay. AN/APN-9 LORAN, 25 built.
- B-32-30-CF
- Variant with a stabilized Sperry A-17A nose turret, installation of countermeasure equipment (AN/APQ-2, AN/APT-1 and AN/APT-2) and improved APQ-13A radar bombing equipment. Seven built, last three aircraft flown directly to storage and scrapped.
- B-32-35-CF
- Seven produced with increased ammunition; flown directly to storage and scrapped.
- B-32-40-CF
- A total of ten were built and flown directly to storage and then scrapped
- B-32-45/50-CF
- A total of 37 under construction. Partially assembled machines were stripped of all their government-furnished equipment and engines and were scrapped on site by the contractor.
- B-32-1-CO
- Three aircraft the same as the B-32-20CF but assembled by Consolidated – San Diego. One aircraft accepted with the remaining two units flown directly to storage and scrapped.
A total of 300 B-32s ordered, 118 delivered, 130 flyable, 170 cancelled, orders for a further 1,099 B-32-CFs and 499 B-32-COs were cancelled after VJ-Day.
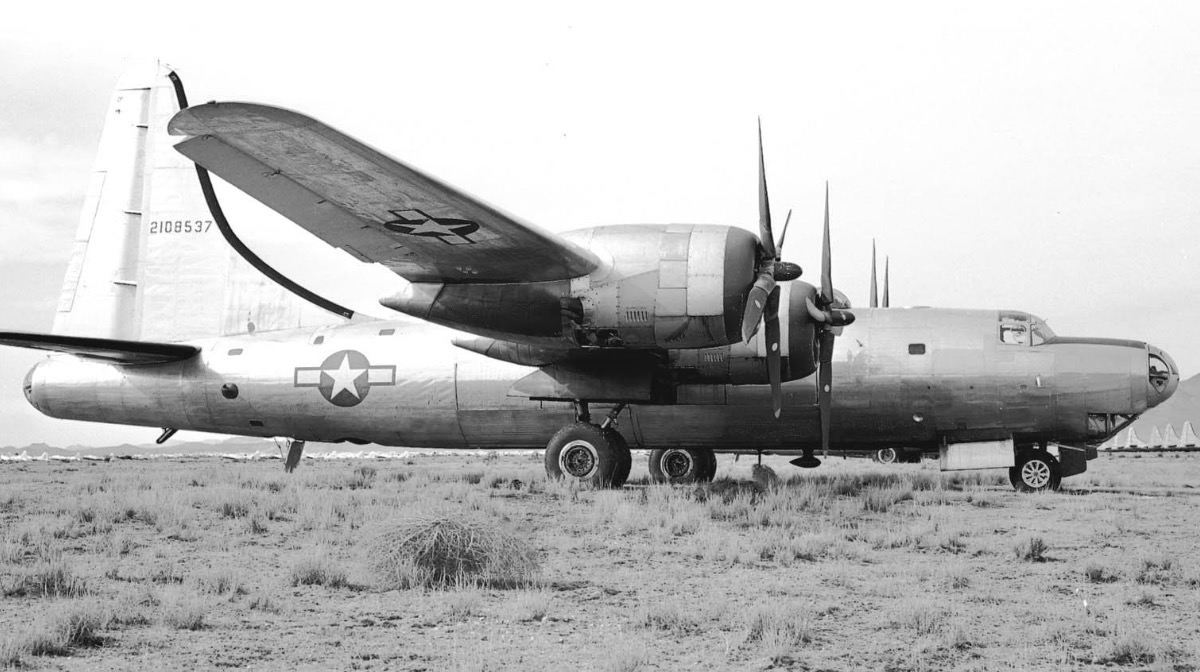
No examples of a B-32 remain today. The XB-32 (AAF Ser. No. 41-18336) was used as a ground instructional airframe for fire fighting training. Others were written off after suffering major damage in operational accidents. Excess inventories were flown either to Walnut Ridge Army Airfield, Arkansas, to be scrapped by the Texas Railway Equipment Company, or to Kingman Army Airfield, Arizona to be scrapped by the Wunderlich Construction Company.
One of the few portions of a B-32 surviving is a wing panel removed from a static test model and erected at the Montgomery Memorial near San Diego, California as a monument to aviation pioneer John J. Montgomery.
Several Sperry A-17 nose/tail turrets, unique to the B-32, survive in various U.S. locations. These included the National Air & Space Museum, the National Museum of the U.S. Air Force, the Commemorative Air Force, the National Warplane Museum in Geneseo, New York and at least four others in private collections.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OZKhiNGv9dE