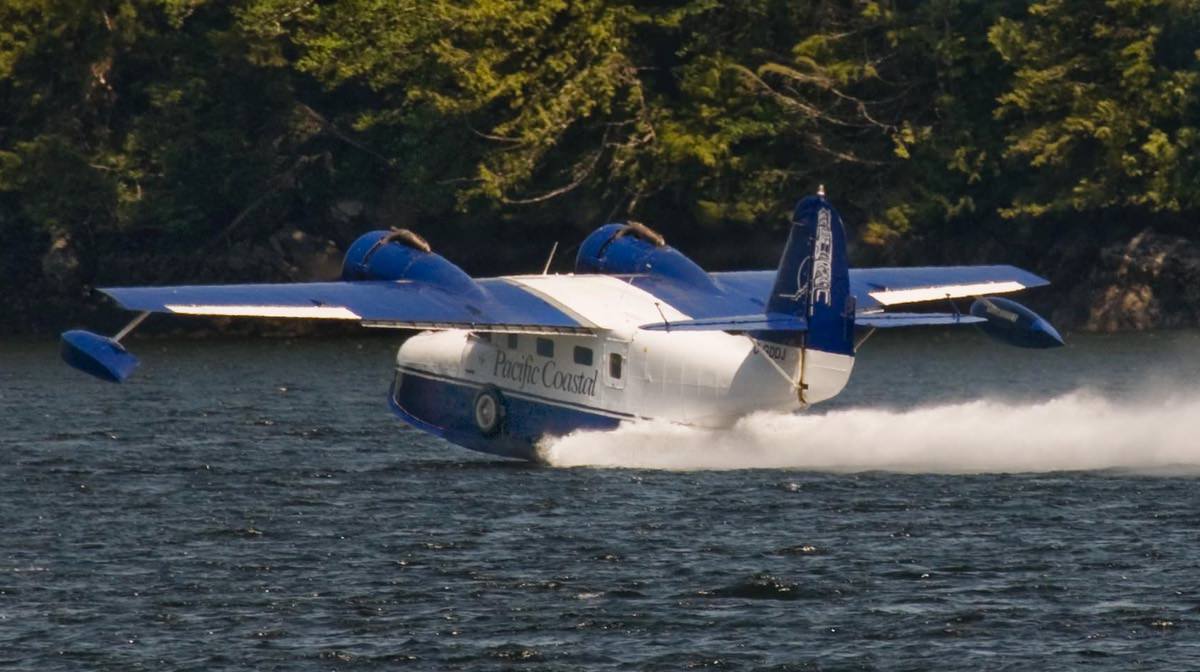
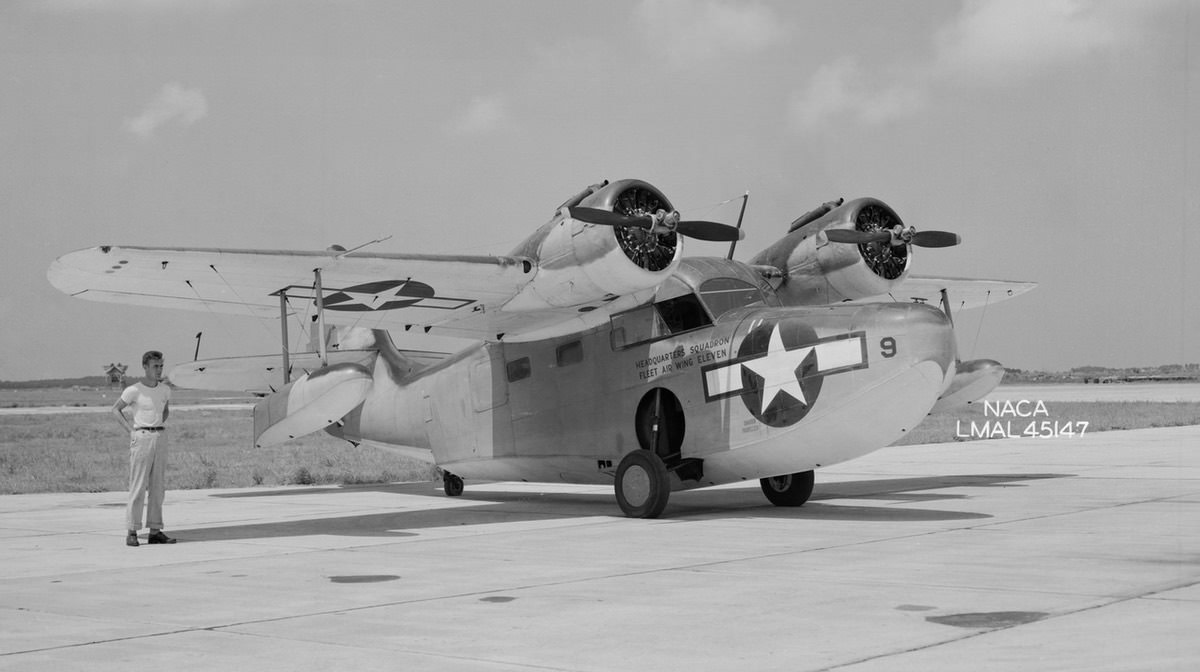
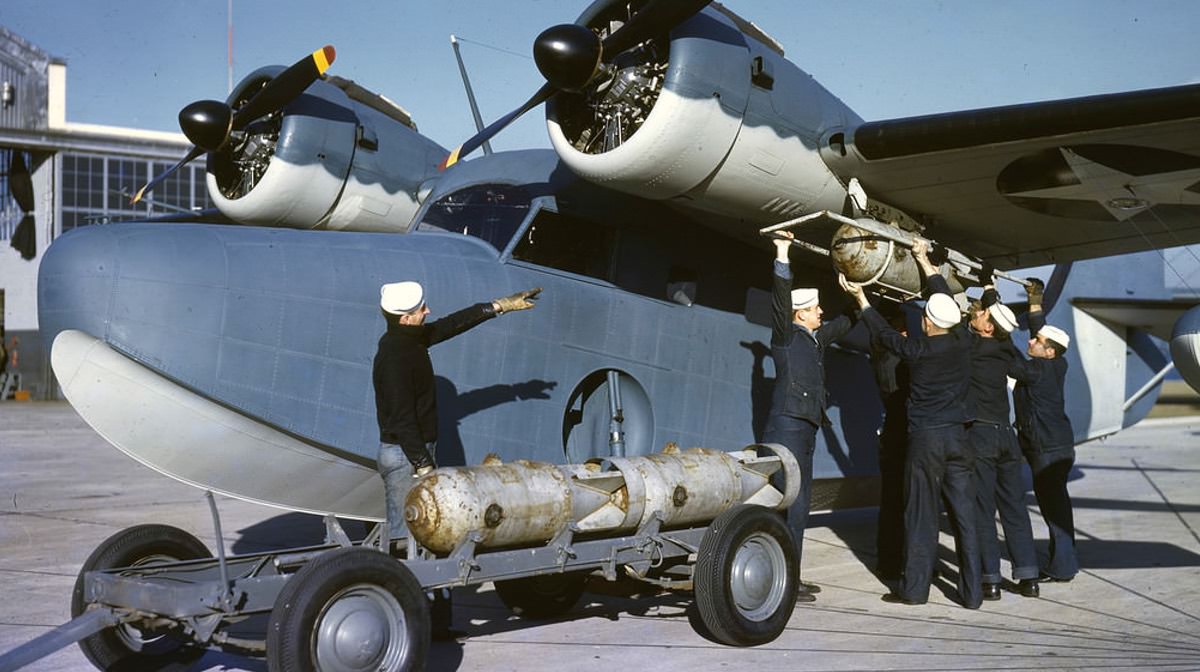
Price: $24.95
- 5 magazines, 5 manuals, & photos
- PDF contains 560 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
August 1994
- Three Generations of Combat Corsairs – O2U, F4U, A-7
- Seabirds of the Navy, Grumman’s Mighty Ducks – Geese & Widgeons
April 1996
- Replacing SAC Air Combat Command
- How Spitfire & Typhoon were Converted for Tactical Close Support
February 1997
- US Carrier Aviation Special Edition
- From Biplanes to WWII to the Dawn of the Jet Age
September 1997
- Grumman’s F6F Carrier Fighter
- Combat Coverage of B-17s over Fortress Europe!
- Army Seaplanes Part II
August 2003
- THE UGLY DUCKLING: The Grumman JF/J2F aircraft contributed most to the Allied Victory in World War II.
- GOLDEN AGE OF AVIATION ADVERTISING: World War II to the Space Age.
- DOUBLE YOUR PLEASURE: A two-place F-86 Sabre?
- DAYLIGHT BOMBING: From Schweinfurt to Baghdad
Manuals & Photos
- JRF-5 Pilot’s Handbook, 1945
- JRF-6B Pilot’s Handbook 1
- JRF-6B Pilot’s Handbook 2
- JRF-4 Basic Weight Checklist & Loading Data, 1945
- G-21 Erection & Maintenance Instructions
- Over 100 photos of the Grumman JRF/G-21 Goose
JRF-5 Specifications
Variants
On Display
Videos
General Characteristics
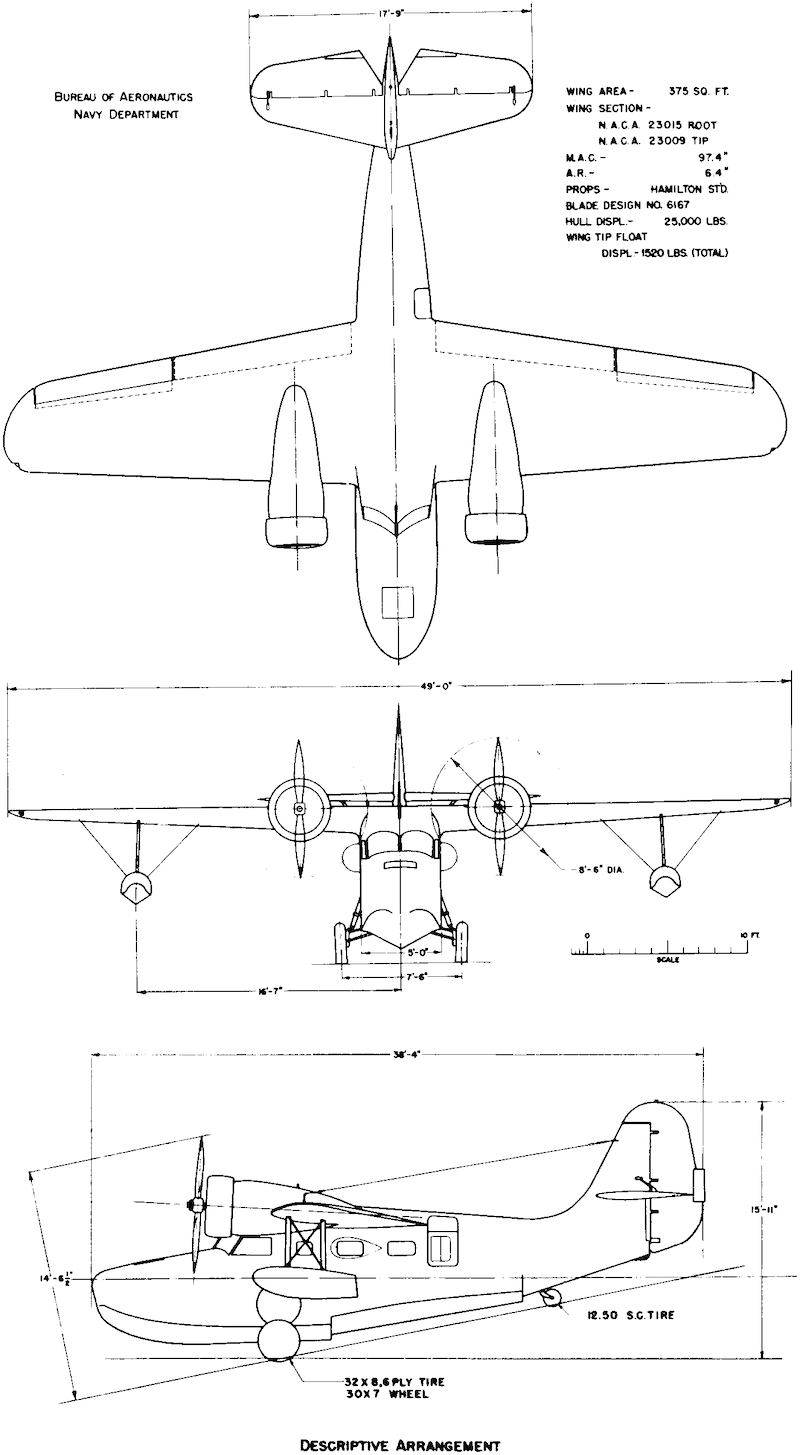
- Crew: 1-3
- Capacity: 5-7
- Length: 38 ft 6 in (11.73 m)
- Wingspan: 49 ft 0 in (14.94 m)
- Height: 16 ft 2 in (4.93 m)
- Wing area: 375 sq ft (34.8 m2)
- Airfoil: root: NACA 23015; tip: NACA 23009
- Empty weight: 5,425 lb (2,461 kg)
- Gross weight: 8,000 lb (3,629 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Pratt & Whitney R-985-AN-6 Wasp Junior 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 450 hp (340 kW) each
- Propellers: 3-bladed variable-pitch propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 201 mph (323 km/h, 175 kn) at 5,000 ft (1,524 m)
- Cruise speed: 191 mph (307 km/h, 166 kn) at 5,000 ft (1,524 m)
- Range: 640 mi (1,030 km, 560 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 21,300 ft (6,500 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,100 ft/min (5.6 m/s)
- Wing loading: 21.3 lb/sq ft (104 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.11 hp/lb (0.18 kW/kg)
Armament
- Bombs: 2 × 325 lb (147 kg) depth charges or 2 × 250 lb (110 kg) GP bombs
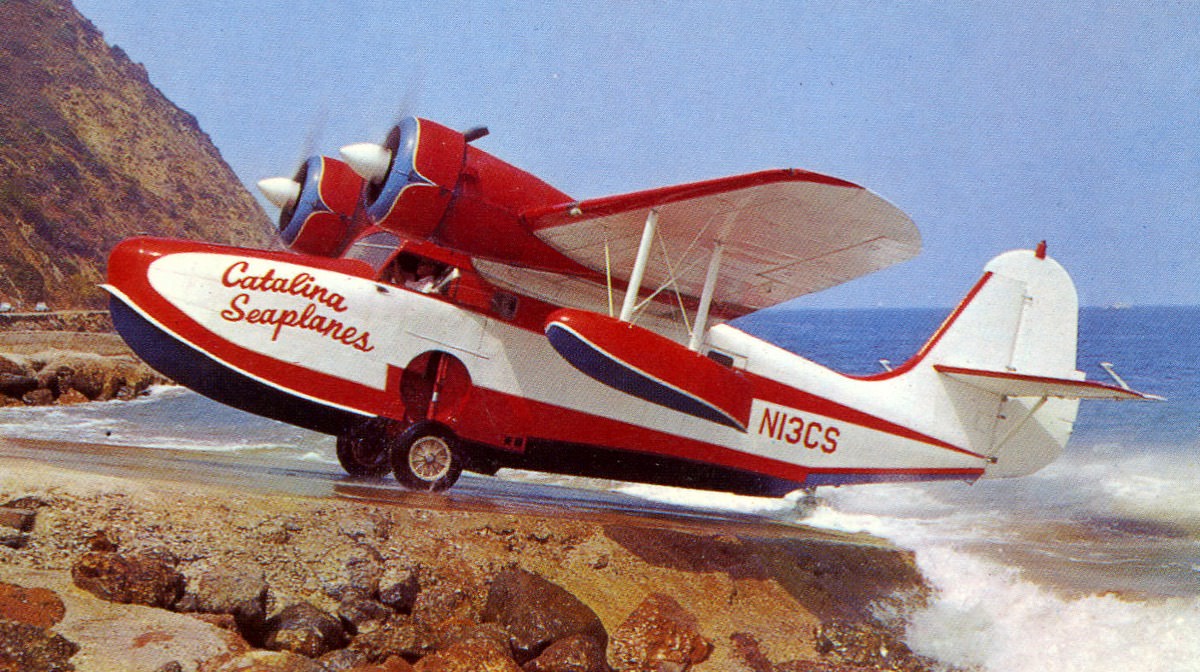
- G-21
- The original production version, these were powered by two 450 hp (340 kW) Pratt & Whitney Wasp Junior SB engines, at 7,500 lb (3,400 kg) gross weight, with six passengers, and 12 were built, all converted to G-21A standards.
- G-21A
- Increased gross weight (8,000 lb (3,600 kg)), 30 built.
- G-21B
- Export coastal patrol flying boat armed with .30 in (7.62 mm) machine gun in bow and dorsal hatches and two 100 lb (45 kg) bombs underwing, 12 built for Portuguese Naval Aviation.
- G-21C
- Conversion by McKinnon Enterprises, these were re-engined with four 340 hp (250 kW) Lycoming GSO-480-B2D6 air-cooled, geared, and supercharged flat-six engines and fitted with retractable wingtip floats, a fiberglass radar nose, a one-piece wraparound windshield, and enlarged cabin windows; gross weight increased to 12,499 lb (5,669 kg) as result of internal structural reinforcements. Two were converted as piston-powered models G-21C in 1958–1959, and two other airframes subsequently were converted in 1968, but with two 550 shp (410 kW) Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-20 turboprops per STC SA1320WE as G-21C Hybrids. Two G-21C Hybrids were identical to the later 10,500 lb (4,800 kg) model G-21E, but they were never certified as such.
- G-21D
- One G-21C was further converted by McKinnon with an extended nose marked by two extra windows on each side and accommodating another four passengers. Recertified as G-21D in 1960. In 1966, it was re-engined with two 550 shp (410 kW) PT6A-20 turboprops and fitted with revised Alvarez-Calderon electric flaps in accordance with STC SA1320WE, retaining the G-21D designation, but subsequently identified as the McKinnon “Turboprop Goose”.
- G-21E
- A fully certified new model, it was based on a simplified turbine conversion of the McKinnon G-21C, with 550 shp (410 kW) PT6A-20 engines (680 shp (510 kW) Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-27 engines optional) and more fuel, but without all of the structural reinforcements of the G-21C. 10,500 lb (4,800 kg) gross weight. One converted.
- G-21G
- The final McKinnon conversion also was fully certified as a new model with 680 shp (510 kW) PT6A-27 engines, 586 US gal (2,220 L; 488 imp gal) of fuel, and 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) gross weight. Two converted.
- Kaman K-16B
- Experimental tilt wing aircraft, with JRF-5 fuselage powered by two General Electric YT58-GE-2A engines; one built but not flown.
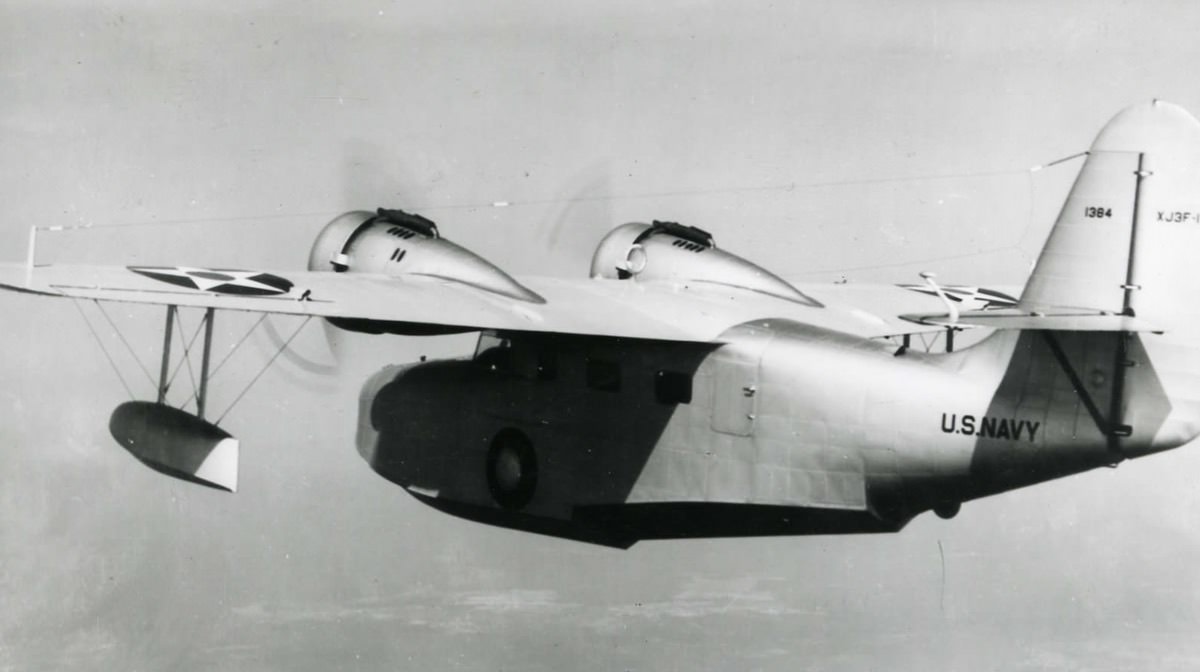
- XJ3F-1
- Prototype eight-seat utility amphibian, built for the US Navy; one built in 1938.
- JRF-1
- Production XJ3F-1, five built for US Navy.
- JRF-1A
- Similar to JRF-1, but with target towing gear and camera hatch added, five built for US Navy.
- JRF-2
- U.S. Coast Guard version with provisions for carrying stretchers; seven built.
- JRF-3
- Similar to the JRF-2, fitted with autopilot and deicing boots on the wing leading edges for Arctic operations. Three built for US Coast Guard.
- JRF-4
- Similar to JRF-1A, these could carry two underwing depth bombs. Ten built for US Navy.
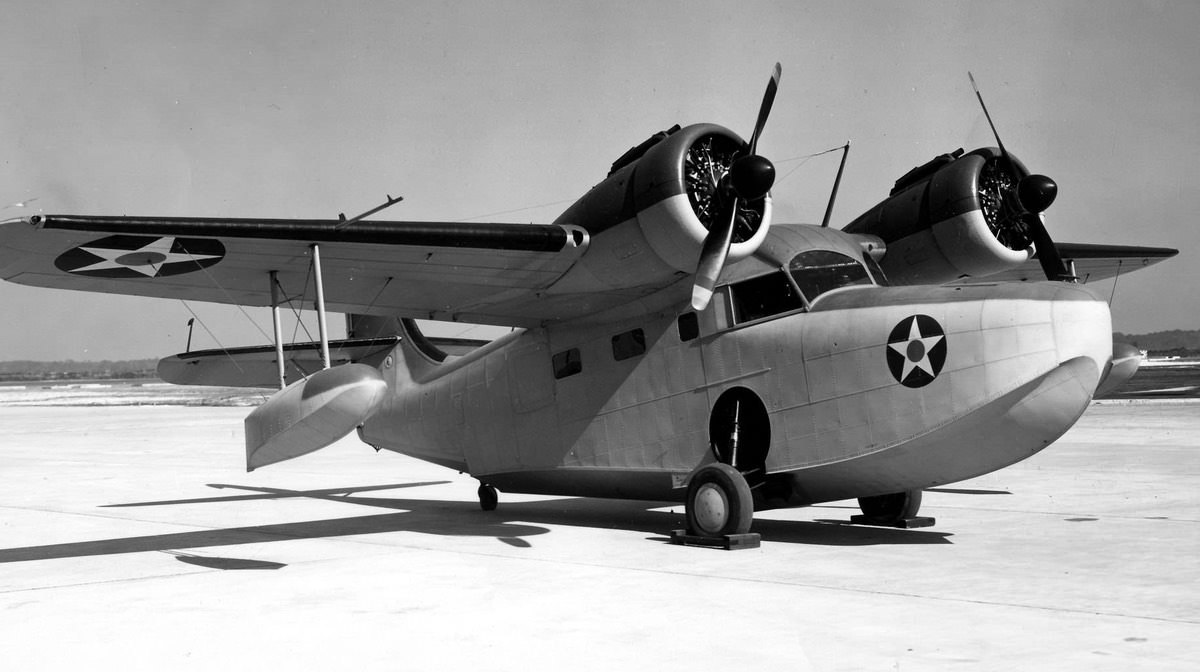
- JRF-5
- Major production version with bomb racks, target towing and camera gear, and deicing gear; 184 built. In 1953, a modified JRF-5 tested hydroskis for the US Navy.
- JRF-5G
- 24 JRF-5s transferred to the US Coast Guard.
- JRF-6B
- Navigation trainer purchased for supply under Lend-Lease; 50 built.
- OA-9
- Transport and air-sea rescue for United States Army Air Forces, 26 ordered in 1938, supplemented by five JRF-6Bs under the same designation.
- OA-13A
- Three G-21As impressed by the USAAF.
- OA-13B
- Two JRF-5s transferred to the USAAF.
- Goose Mk.I
- British designation for three JRF-5s supplied to the Fleet Air Arm.
- Goose Mk.IA
- British designation for 44 JRF-6Bs, supplied under Lend Lease for observer training by the 749 Naval Air Squadron in Trinidad.
- Goose Mk.II
- British designation for two JRF-5s staff transports for British Air Commission in the United States and Canada.
-
Canada
- B-77 – G-21A in storage at the Canada Aviation and Space Museum in Ottawa, Ontario.
-
Indonesia
- PB-521 – G-21A on static display at Suryadarma Air Force Base in Subang Regency, West Java.
-
Sweden
- 37810 – JRF-5 under restoration for static display at the Swedish Air Force Museum in Linköping, Östergötland.
-
United States
- 1048 – G-21A on static display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center of the National Air and Space Museum in Chantilly, Virginia.
- 1085 – G-21A on static display at the National Naval Aviation Museum in Pensacola, Florida.
- 1157 – G-21A under restoration for static display at the Tongass Historical Society in Ketchikan, Alaska.
- B-102 – G-21A N789 on display in airworthy condition at the Alaska Aviation Museum in Anchorage, Alaska.
- B-122 – G-21A on static display at the Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum in McMinnville, Oregon.
- B-130 – G-21A on static display at the Historic Aircraft Restoration Project in Brooklyn, New York.
- Reproduction – G-21A on static display at the Cradle of Aviation Museum in Garden City, New York.