Price: $19.95
- 4 magazines, 2 manuals, 20 technical documents & photos
- PDF contains 2,459 pages
- Content is keyword searchable
- Print a personal copy
- Pay via PayPal or Credit Card
- International orders welcome!
- Download files upon payment
February 1986
- XB-70 Valkyrie, The Triplesonic Twosome
- Northrop’s XB-49 Flying Wing
November 1992
- Test Flying the Triple-sonic XB-70 Starship
- Night Carrier Landings, Toughest Challenge of them All!
June 2003
- Bailout! Survival in the Sky, Bell X-2 and XB-70 Crashes
- Lindbergh at War, 1944
- High-G action in high-speed sled tracks
August 2005
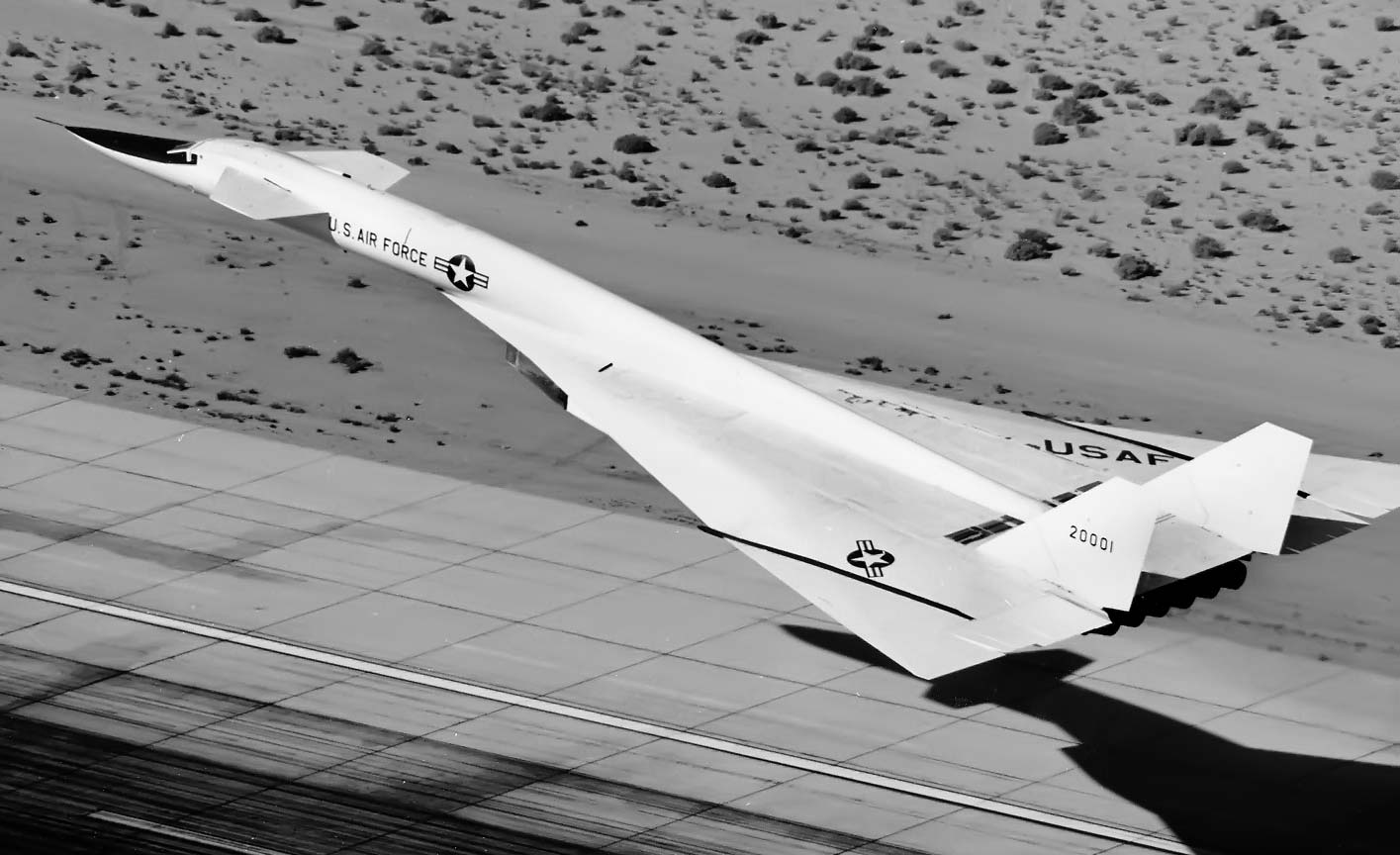
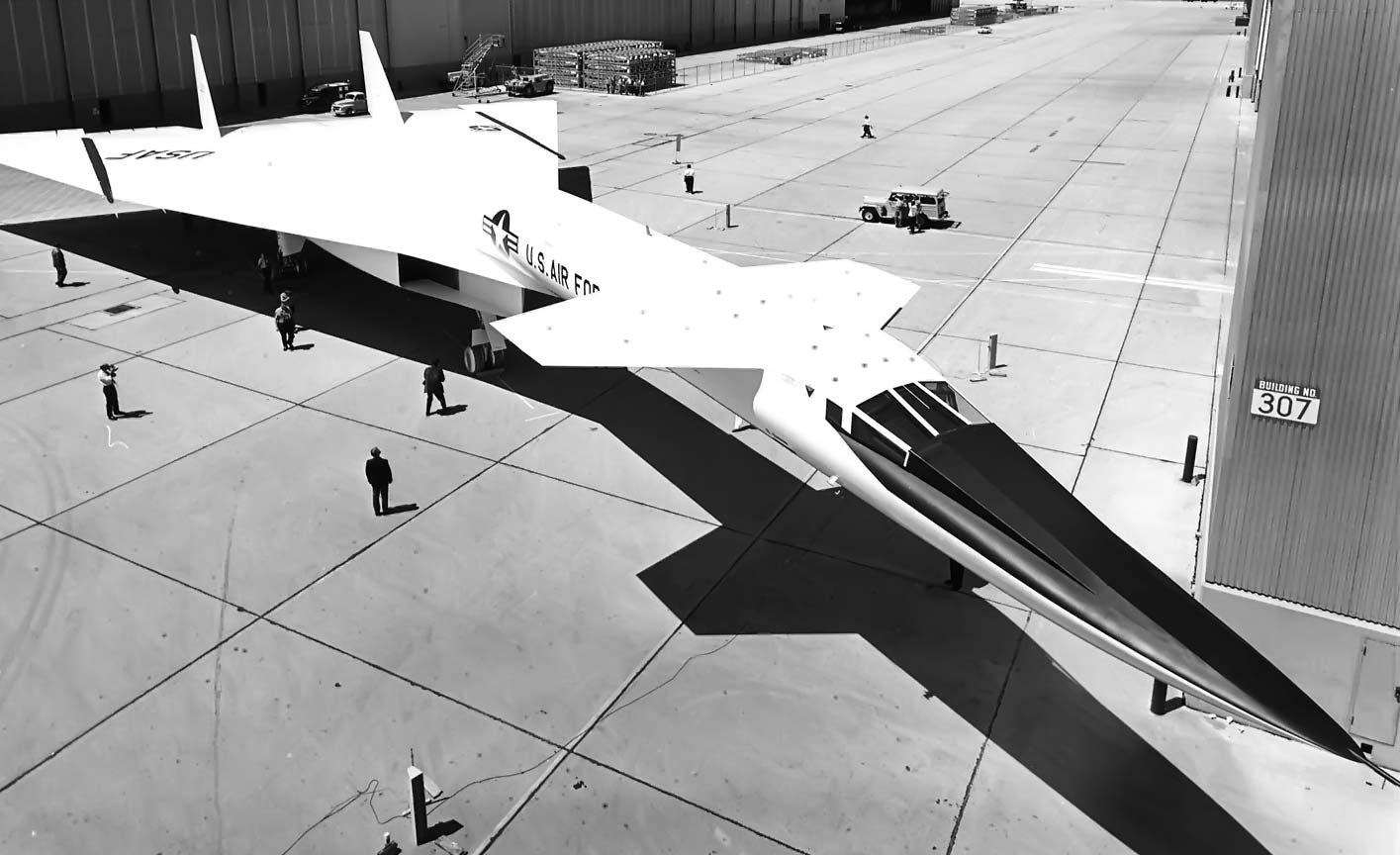
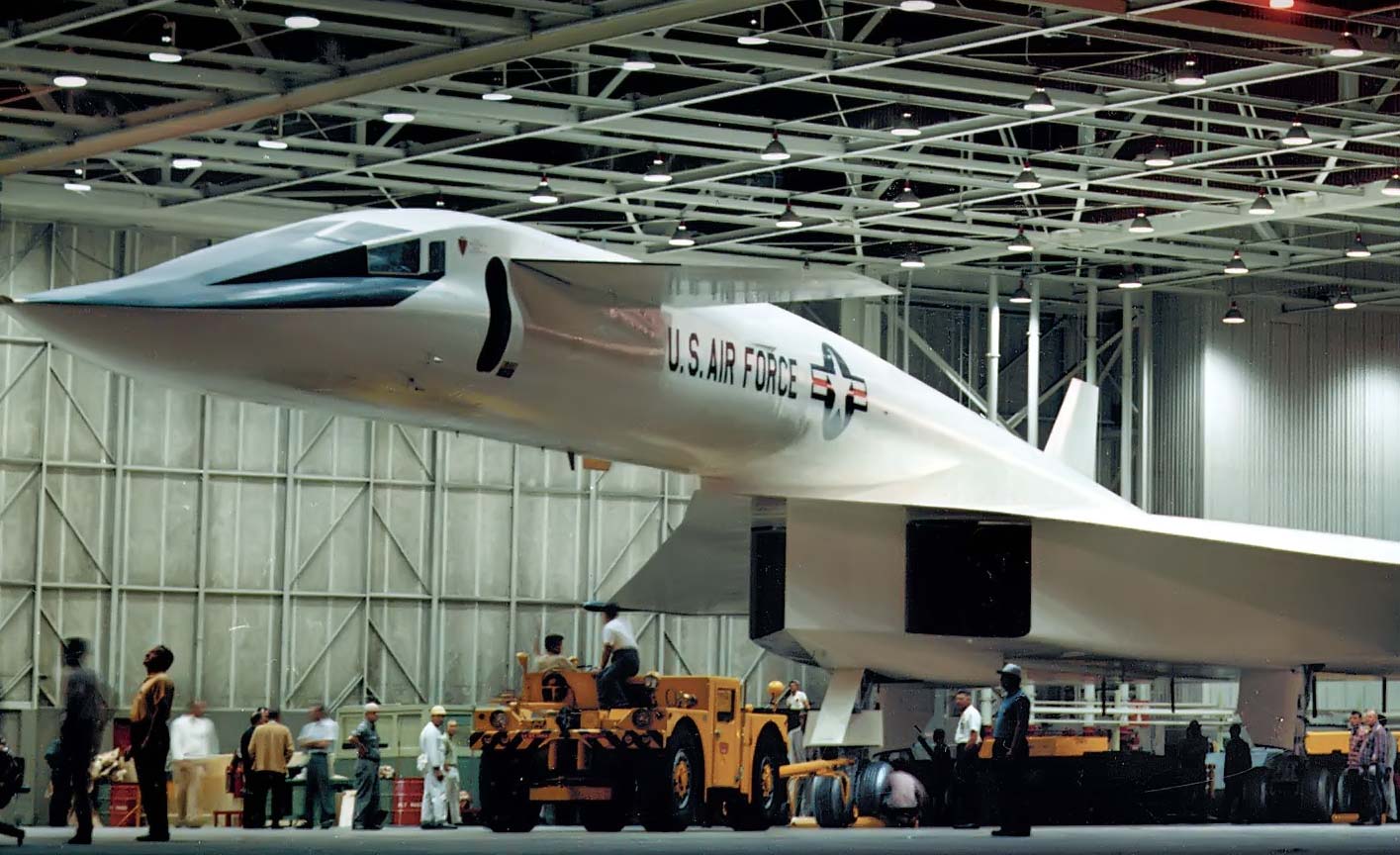
- XB-70 Rollout and First Flight
- Date with the U-2 Dragon Lady
- Golden Age of Aviation Ads
Manuals & Photos
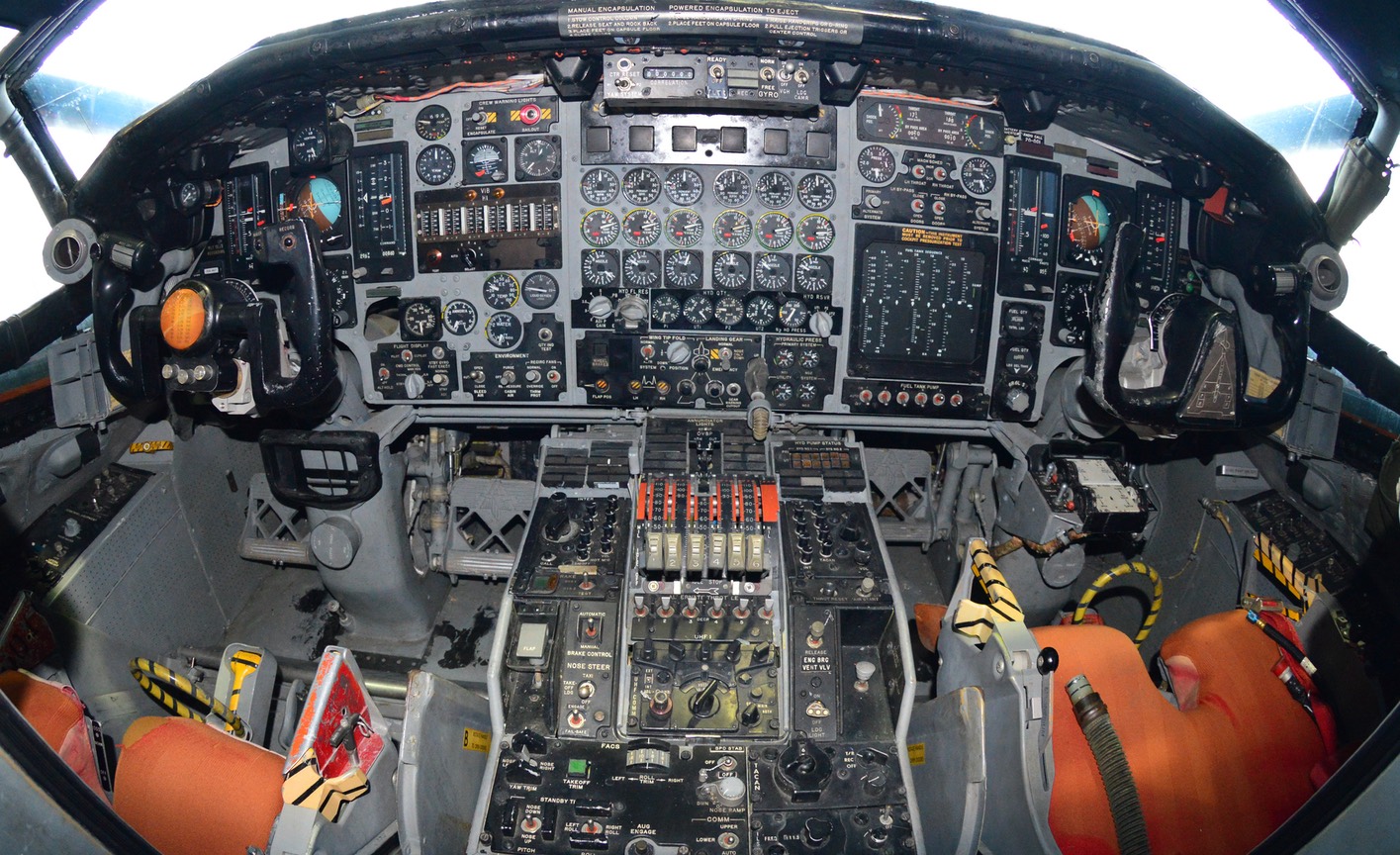
- XB-70 Flight Manual, 1965
- XB-70 Flight Manual Supplement (Declassified), 1967
- Over 240 photos of the XB-70 Valkyrie
XB-70 Technical Documents
- XB-70 Escape System, 1963
- XB-70 Aerodynamic Characteristics, 1980
- XB-70 Base Pressure 0.4 to 3.0 Mach, 1968
- XB-70 Cockpit Environmental Data, 1969
- XB-70 Exhaust Noise Ground Ops, 1971
- XB-70 Final Report Vol.II, 1972
- XB-70 Gas Generator Jet Thrust, 1970
- XB-70 Handling Qualities Landing, 1970
- XB-70 High Altitude Turbulence, 1971
- XB-70 Inlet Digital Simulation, 1970
- XB-70 Landing Approach Handling Qualities, 1970
- XB-70 Landing Loads, 1968
- XB-70 Lessons Applied to Supersonic Transport, 1968
- XB-70 Longitudinal Stability Six Flight Conditions, 1973
- XB-70 Mountain Wave Clear Air Turbulence, 1971
- XB-70 Sonic Boom Signature, 1992
- XB-70 Stability & Control, 1973
- XB-70 Summary Preliminary Data, 1965
- XB-70 Takeoff Performance Predictions, 1971
- XB-70 USAF Case Study, 1990
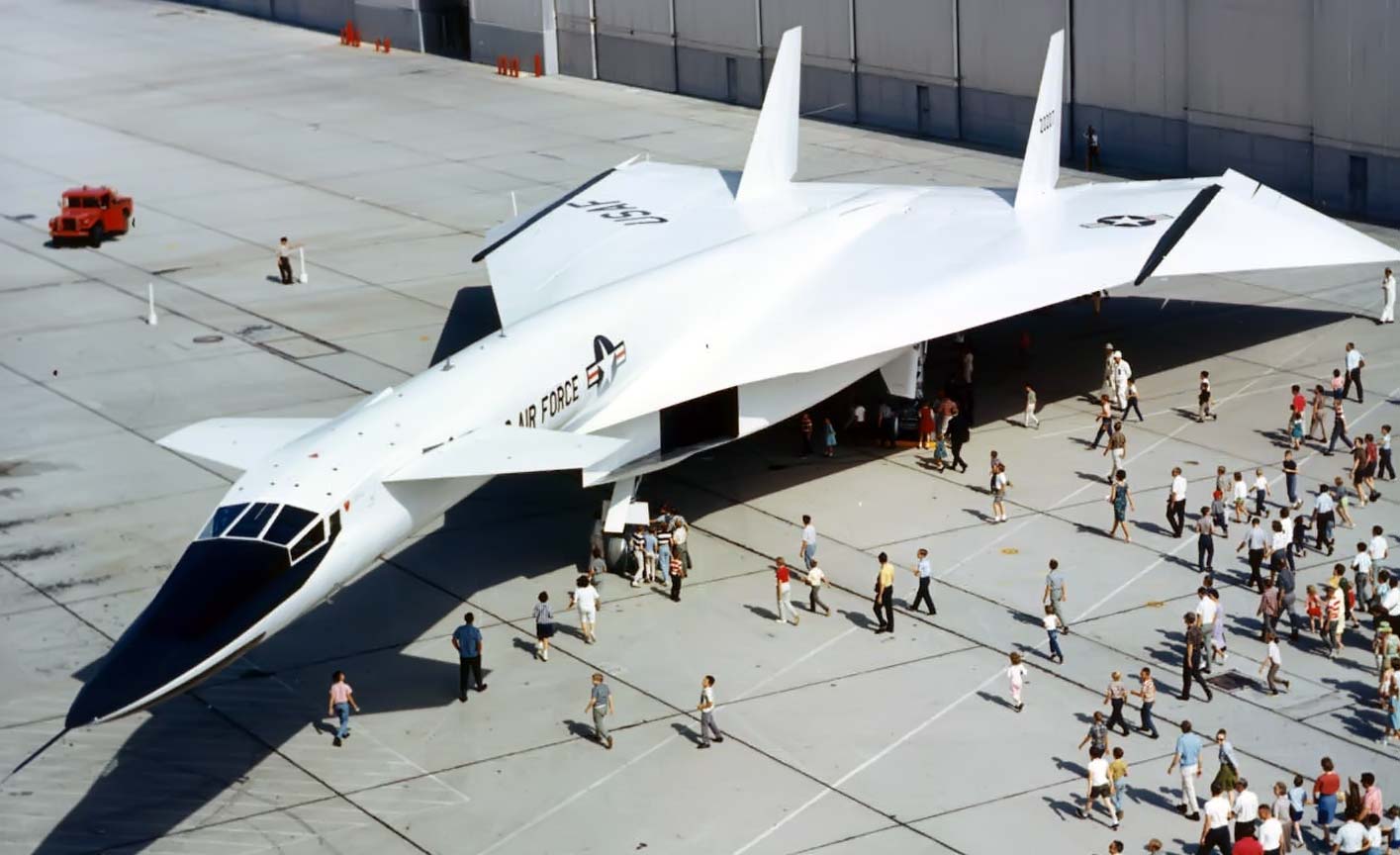
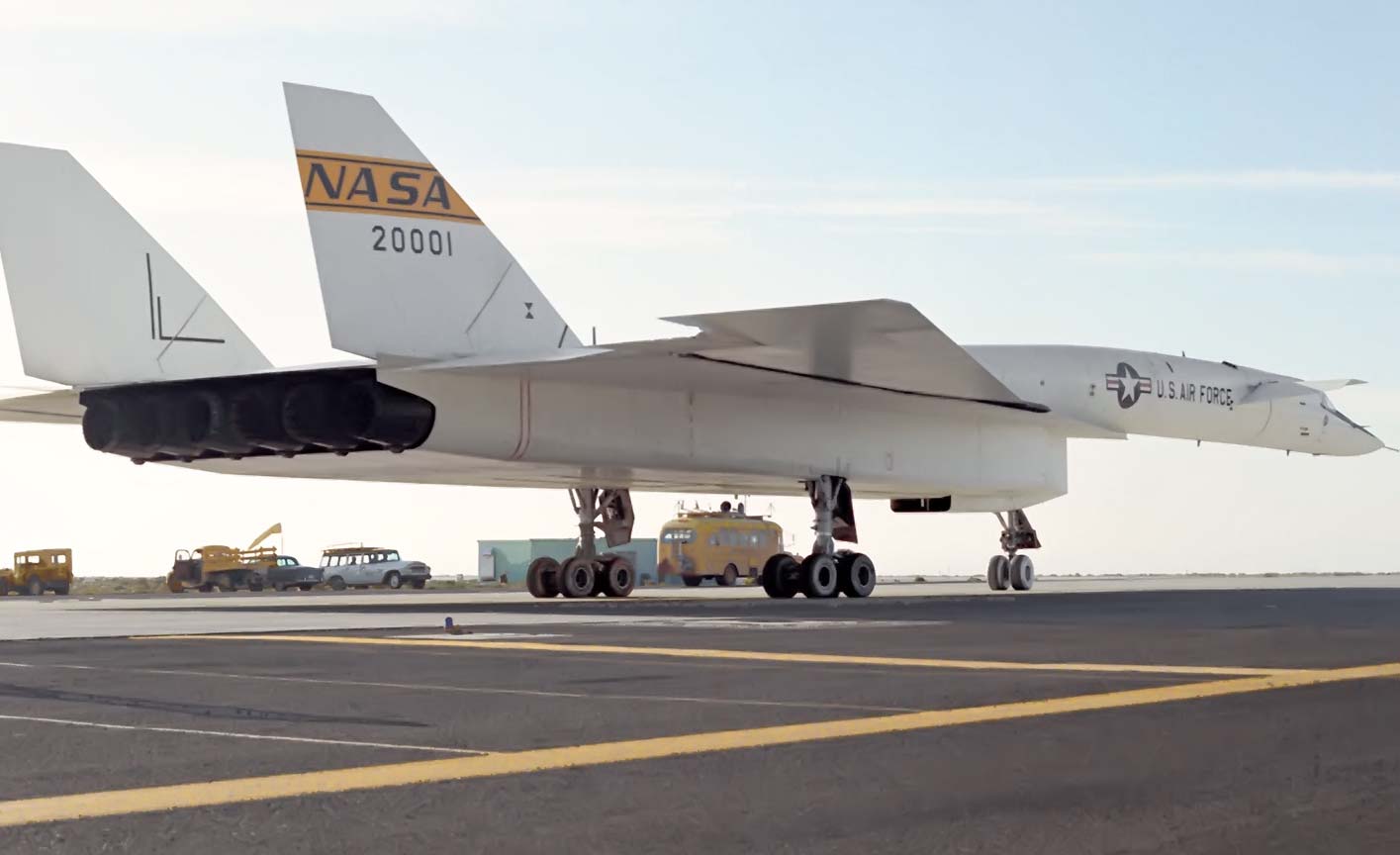
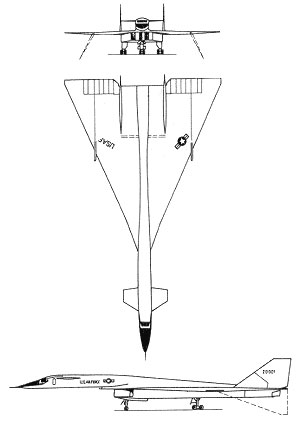
North American Aviation XB-70 Valkyrie
XB-70A Specs
Variants
On Display
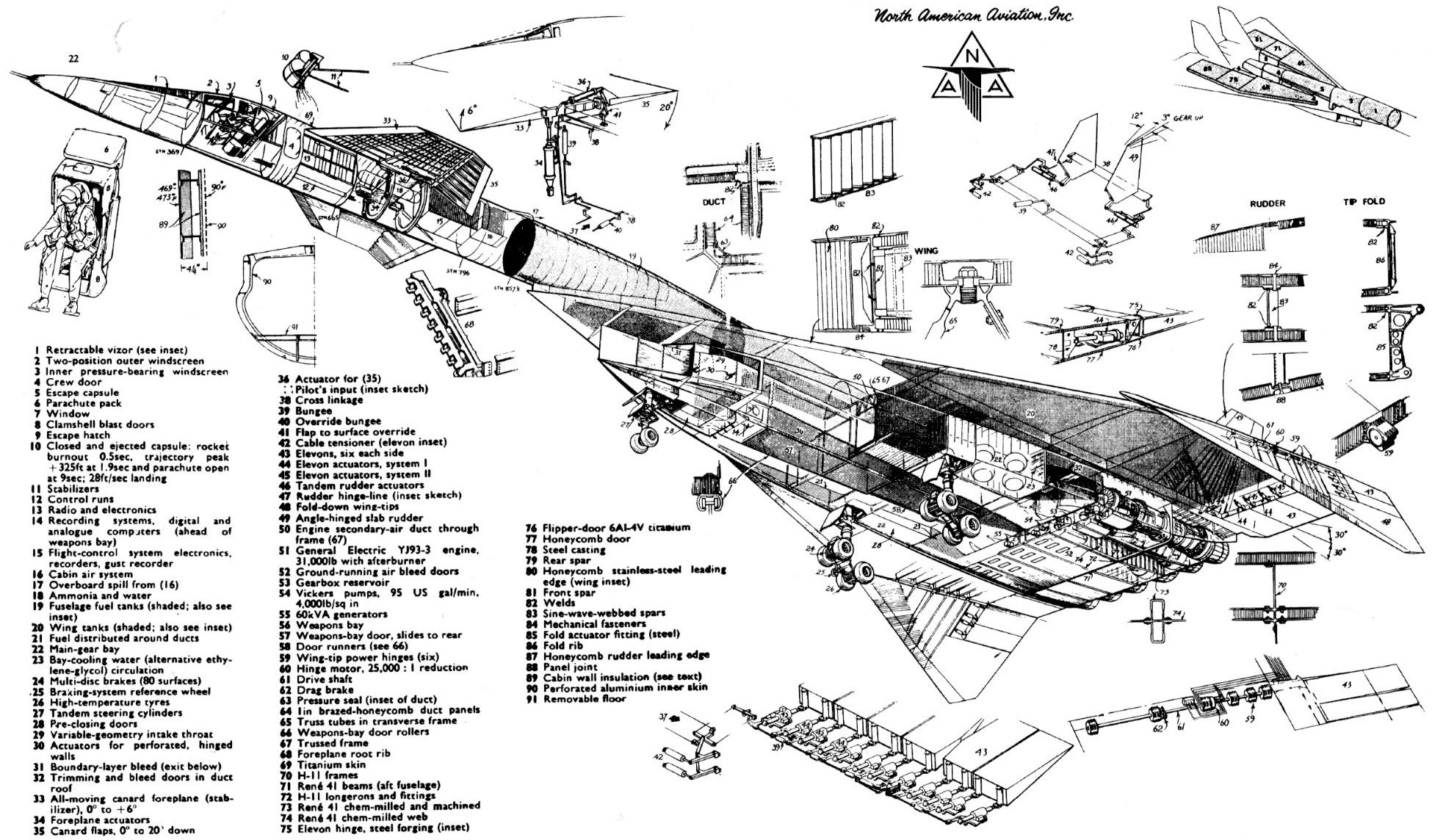
Cutaway
Videos
General Characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 189 ft 0 in (57.6 m)
- Wingspan: 105 ft 0 in (32 m)
- Height: 30 ft 0 in (9.1 m)
- Wing area: 6,297 ft² (585 m²)
- Airfoil: Hexagonal; 0.30 Hex modified root, 0.70 Hex modified tip
- Empty weight: 253,600 lb (115,030 kg; operating empty weight)
- Loaded weight: 534,700 lb (242,500 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 542,000 lb (246,000 kg)
- Powerplant: 6 × General Electric YJ93-GE-3 afterburning turbojet
- Dry thrust: 19,900 lbf[73] (84 kN) each
- Thrust with afterburner: 28,800 lbf[74] (128 kN) each
- Internal fuel capacity: 300,000 lb (136,100 kg) or 46,745 US gallons (177,000 L)
Performance
- Maximum speed: Mach 3.1 (2,056 mph, 3,309 km/h)
- Cruise speed: Mach 3.0 (2,000 mph, 3,200 km/h)
- Range: 3,725 nmi (4,288 mi, 6,900 km) on combat mission
- Service ceiling: 77,350 ft (23,600 m)
- Wing loading: 84.93 lb/ft² (414.7 kg/m²)
- lift-to-drag: about 6 at Mach 2
- Thrust/weight: 0.314
- XB-70A – Prototype of B-70. Two were built.
- AV-1, NAA Model Number NA-278, USAF S/N 62-0001, completed 83 flights spanning 160 hours and 16 minutes.
- AV-2, NAA Model Number NA-278, USAF S/N 62-0207, flew 46 times over 92 hours and 22 minutes, before it crashed in June 1966.
- XB-70B – AV-3, NAA Model Number NA-274, USAF S/N 62-0208, was originally to be the first YB-70A in March 1961. This advanced prototype was canceled during early manufacture.
- YB-70 – Planned preproduction version with improvements based on XB-70s.
- B-70A – Planned bomber production version of Valkyrie.[6] A fleet of up to 65 operational bombers was planned.
- RS-70 – Proposed reconnaissance-strike version with a crew of four and in-flight refueling capability.
| Serial Number | Aircraft Type | City | State | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62-0001 | XB-70A | Dayton | OH | US Air Force Museum | Displayed indoors. |
| 62-0207 | XB-70A | Crashed after mid-air collision June 8, 1966. | |||
| 62-0208 | XB-70B | Cancelled and scraped before being finished. |